Processing Device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment
[0017]Hereinafter, an embodiment of an image processing device is described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 9.
Configuration
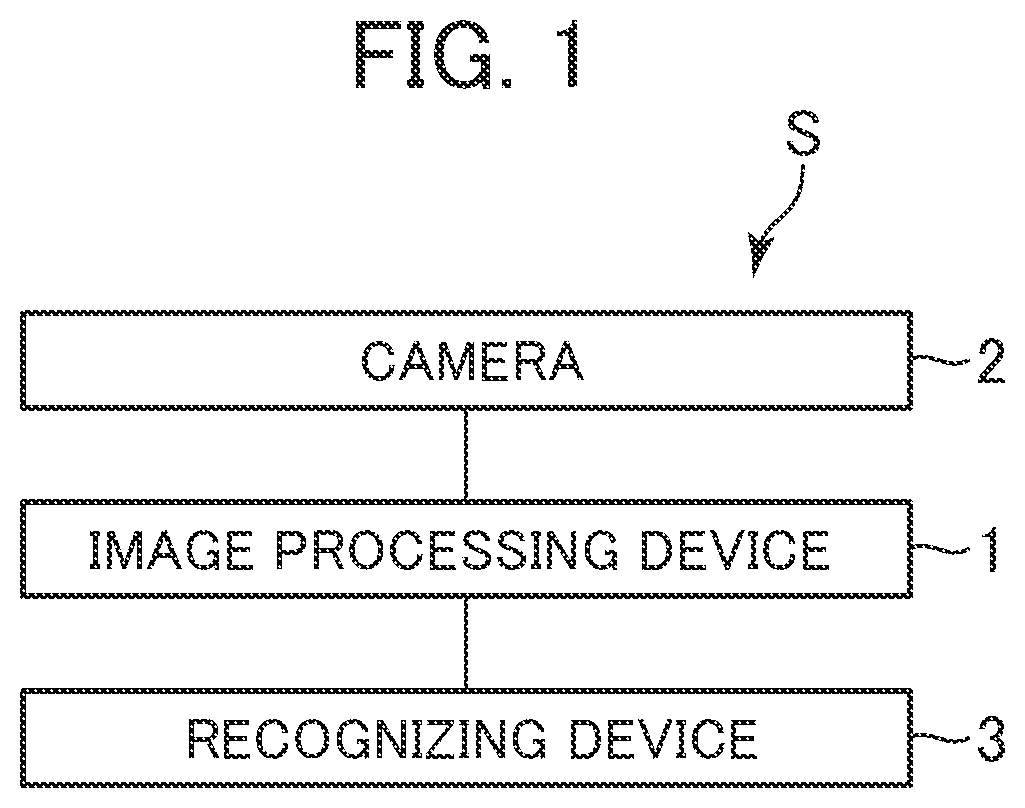
[0018]FIG. 1 is a diagram depicting a configuration of an image processing system S including an image processing device 1. The image processing system S includes the image processing device 1, a camera 2, and a recognizing device 3. The camera 2 outputs an image (hereinafter referred to as “captured image”) acquired by imaging to the image processing device 1. The image processing device 1 executes a distortion correction process on the captured image to generate an image (hereinafter referred to as “distortion-corrected image) obtained by correcting distortion and outputs the distortion-corrected image to the recognizing device 3. The recognizing device 3 executes various applications using the distortion-corrected image. The image processing device 1, the camera 2, and the recognizing device 3 may be connected to each other by wires and may transmit and receive ...
operation example
[0032]An operation example of the image processing device 1 is described with reference to FIG. 7. FIG. 7(a) depicts regions that are included in the high-speed storage unit 145 and on which writing is executed first to fourth. FIG. 7(b) depicts regions that are included in the high-speed storage unit 145 and on which writing is executed thirty fourth to thirty seventh. FIG. 7 (c) depicts values stored in the management table 144. A number indicated in each of grid cells depicted in FIGS. 7 (a) and 7 (b) indicates the number of times that writing is executed when image information is written to the grid cell. The regions enclosed by bold lines in FIG. 7 are regions corresponding to addresses generated by the simple address generating unit 142.
[0033]Since information of the captured image is not stored in the high-speed storage unit 145 before the start of the operation example depicted in FIG. 7, the maximum values among the Y coordinates are zero for all columns of c1 to c128, as i...
first modified example
[0048]It is not a requirement that the number of pixels that can be stored in the high-speed storage unit 145 is in units in which data is read from the low-speed storage unit 13, and the number of pixels that can be stored in the high-speed storage unit 145 may be an integer multiple of the units in which data is read from the low-speed storage unit 13. Moreover, the number of pixels that can be stored in the high-speed storage unit 145 may be any other number of pixels. In addition, the foregoing X direction and Y direction, or column direction and row direction, can be interchanged.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com