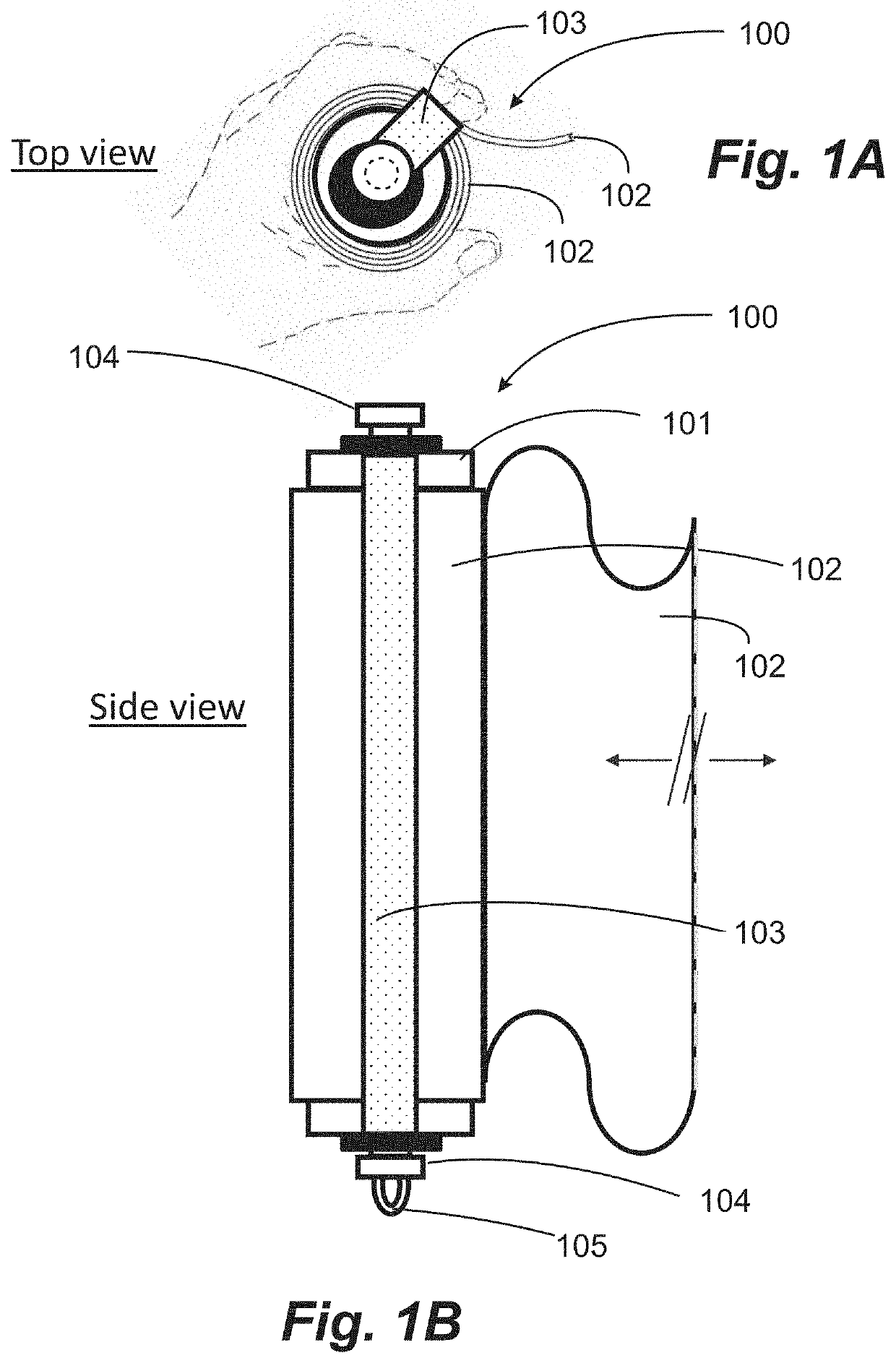
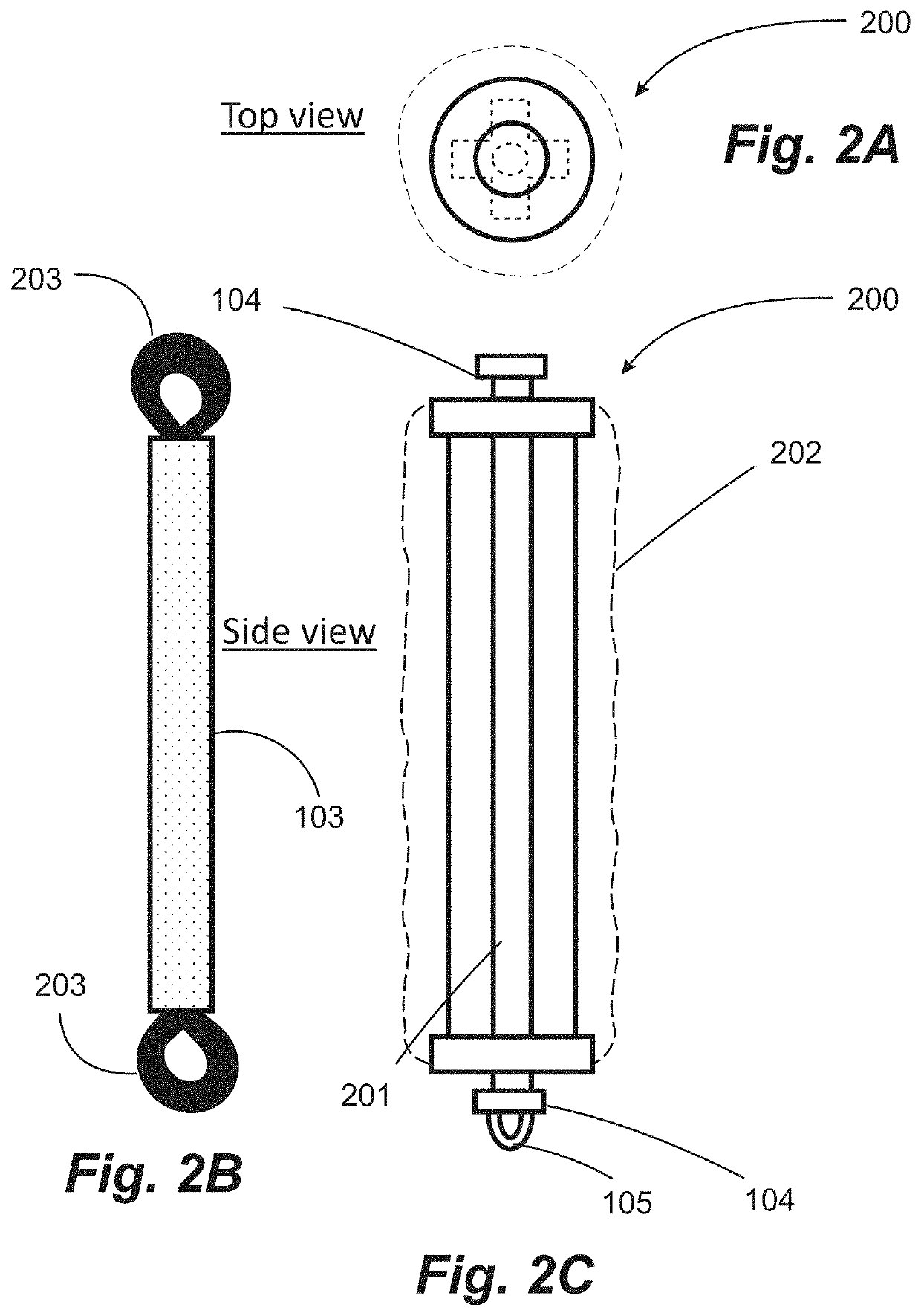
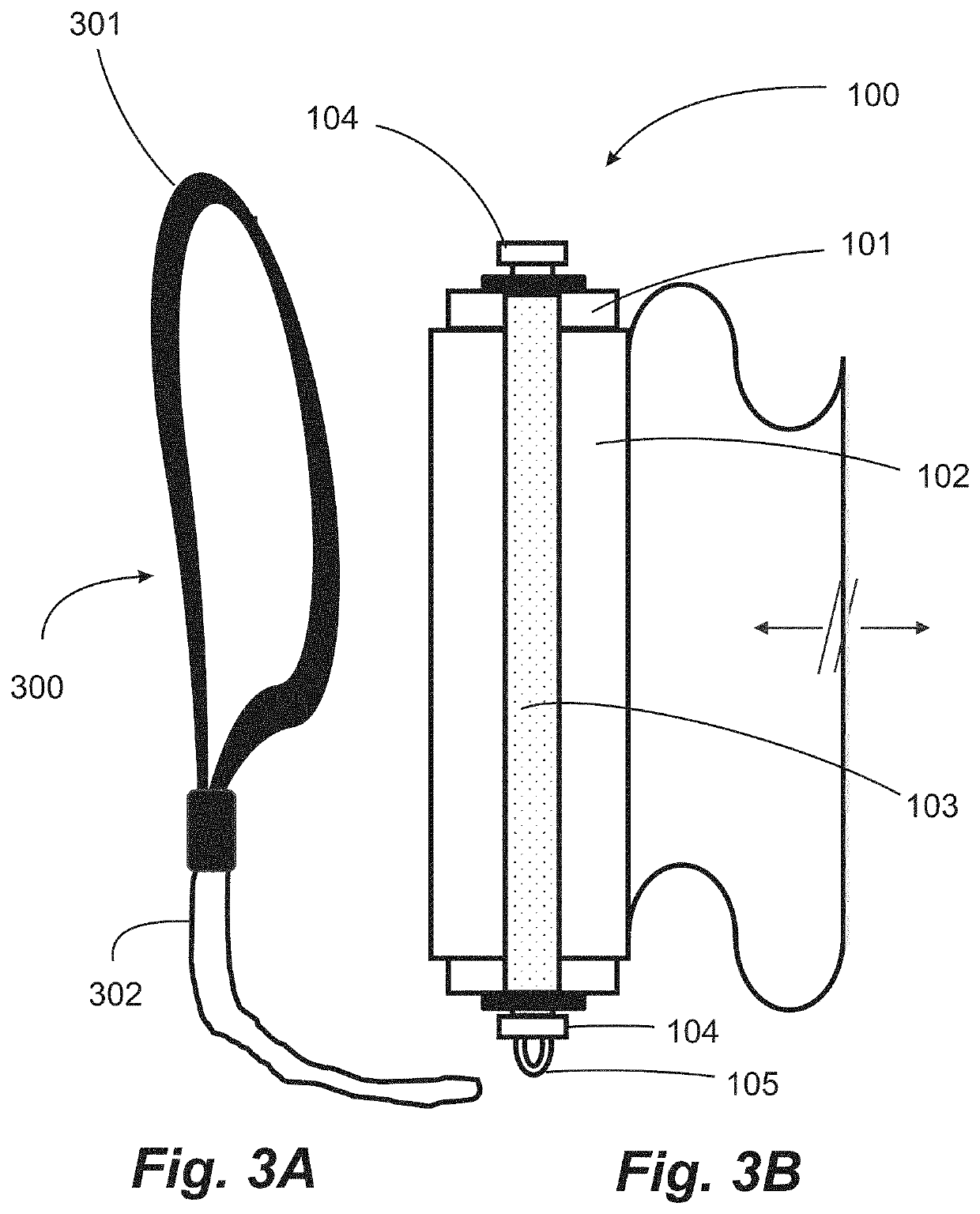
Generally, people tend to lose strength and
muscle mass due to injury, inactivity, and the aging process.
Loss of muscle and flexibility are two of the major contributors to joint and other injuries in adults, especially the elderly, and can significantly diminish the
quality of life of those effected and increase the cost to society of their
medical care.
A common drawback of all of these methods, however, is that the apparatuses are expensive, require substantial space to house or require membership / commuting to a special facility, cannot be used at home or while traveling, require spotters or third-party assistance, are complicated to operate, and importantly do not offer refinements in terms of resistance levels of adjustments or movement required for many strengthening and rehab exercises, especially non-linear movements and work movements involving short spans of travel, such as those used for wrists, elbows, and shoulders.
First, there are undefined rolls of band material, sometimes referred to as “therapy bands” due to their initial proliferation in
physical therapy use.
Despite the benefits of exercise with resistance bands, they suffer from numerous functional and property drawbacks which limit their usefulness and adoption, especially among the elderly, recuperating, and others who could derive a unique benefit from their properties.
Perhaps the largest of these limitations is a lack of grip and difficulty clasping the band during exercise.
Given that the beneficial work resistance provided by resistance bands is generated through a pulling motion (elongating the band and creating increasing tension across the band), the shape of resistance bands with their flat, uniform tape-like configuration and undefined terminations with no
handle make them very hard to clasp while exerting force in a pulling potion.
For the elderly and those in rehab, clenching resistance bands with the hand can be difficult and painful, and can exacerbate
arthritis and similar joint conditions, as well as aggravating convalescing injuries.
This situation is severely compounded by the introduction of
perspiration in workout contexts, where loss of grip allows the band to snap back in an uncontrolled fashion which can
cause injury.
If the grip is lost during the motion of the exercise while the band is elongated, the energy of the band is released causing the band to violently snap back to its original shape.
This frustrates the benefit of the exercise, impairs the workout experience, and has the potential to cause serious injury.
Another problem with resistance bands is they tend to adhere or stick to themselves over time.
Separating the band, essentially peeling the band apart to return it to its
usable shape, requires significant dexterity, takes time, and weakens the integrity of the band.
Moisture from work-out
perspiration tends to migrate to folded areas where it is retained, amplifies adhesion, and accelerates breakdown and rot.
With no solution available in prior art, the constant sticking-and-unsticking process associated with resistance bands takes time and reduces convenience, adds to the cost of more frequent replacement, and creates significant
safety risk of pre-mature band failure.
The bunching of the resistance band into gathers also shortens the life of the resistance band and renders the action of the band more similar to a resistance tube than the band as intended.
This, in addition to
arthritis and other risks mentioned above, also creates the risk of
lost circulation and potential nerve damage over time, especially in elderly users.
Major continuing challenges not addressed are the complexity of attaching the resistance band to the
handle and the risk of mechanical attachment failure.
A major challenge inherent with any
handle-type solution is inadvertent separation of the resistance prior are handles (most of which apply only to resistance tubes and not resistance bands) embody band from the handle mechanism, which can cause the band to snap back toward the user, possibly causing injury.
To mitigate the risk of attachment failure, prior are handles (most of which apply only to resistance tubes and not resistance bands) embody mechanisms to secure the band to the handle frame with a variety of In order to adjust the length of the band, these mechanisms must be loosened and re-tightened which can be time-consuming and difficult for elderly or convalescing users.
Moreover, these items can fail without warning, allowing the band to snap back, and moreover involve numerous small parts capable of being projected by the band if it dislodges and forcibly contracts.
Safety issues aside, most proposed solutions involve
moving parts used to clamp a gathered (or in a few cases spread) resistance band that must be manipulated by the user, loosing and tightening screws or impingers for adjustment, and which require additional manufacturing and
assembly steps.
As a result, the current state solutions in the art is
time consuming, requires manual dexterity, creates a failure
hazard, and limits the overall experience of the workout.
Another significant drawback inherent in handles is that they do not accommodate exercises involving “short-pull” travel ranges, especially those where the starting points of the exercise movement are relatively close together.
Another unmet need is the fact that handles are of a fixed
diameter and are not interchangeable.
Lastly handles in the art typically do not allow micro adjustments in the length of the resistance band.
Because prior art proposals rely on mechanical clamps, buckles, and impingers and the like to secure the band to the arms of the handle, it is not possible to make minor adjustments quickly to the length of pull—and thus the amount of work accomplished—during work out.
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More