Method for synchronizing program sections of a computer program
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
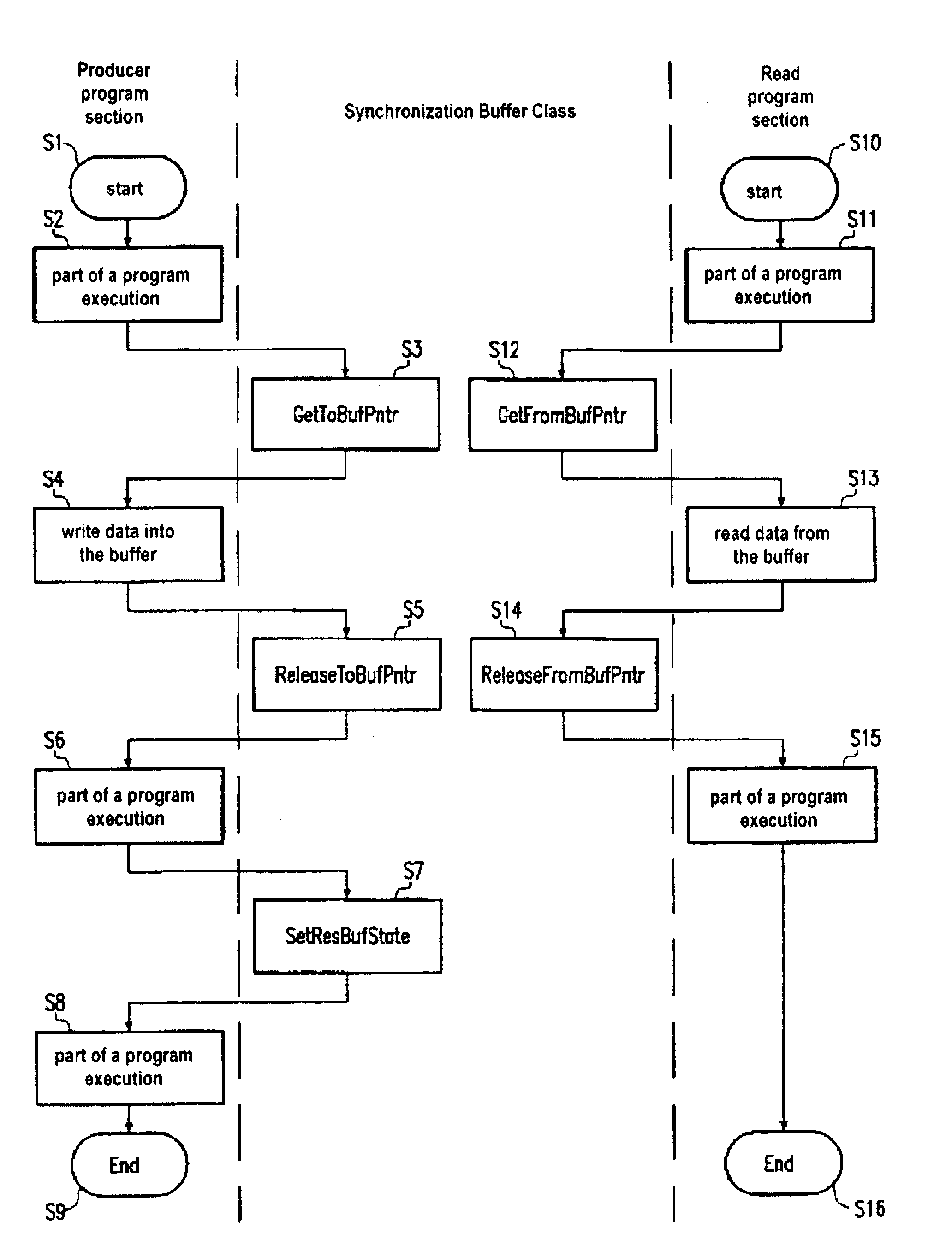
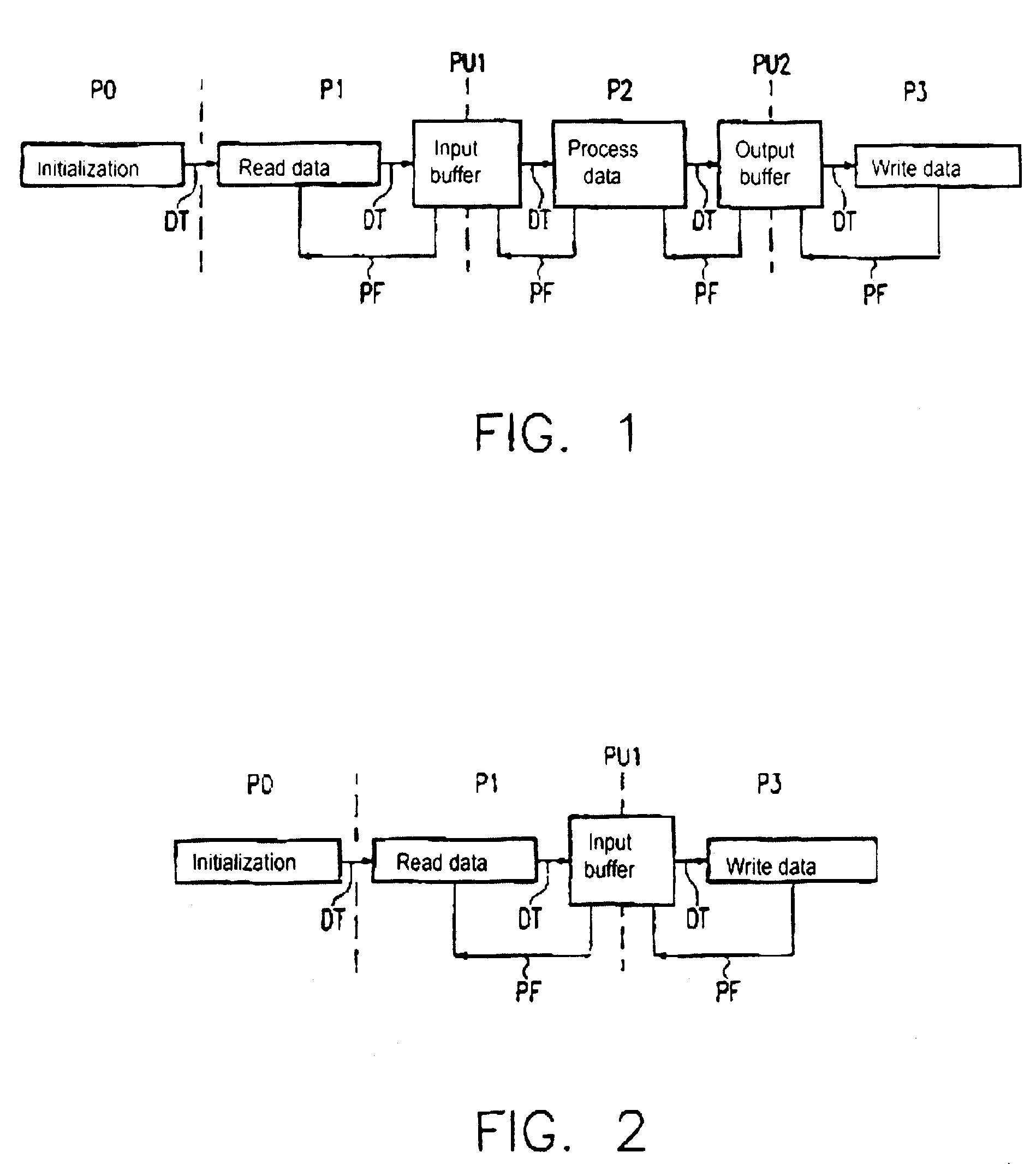
[0037]FIG. 1 schematically shows the operation of a computer program divided into a plurality of program sections P0 through P3. For illustration, only a simple computer program is schematically shown, its program sections implementing the initialization P0, the data reading P1, the data processing P2 and the data writing P3. The program section “read data” P1 must hand over data to the data section “process data” P2 and the latter must hand over data to the program section “write data” P3, for which reason a buffer PU1 is arranged between the program sections P1 and P2 and a buffer PU2 is arranged between the program sections P2 and P3.
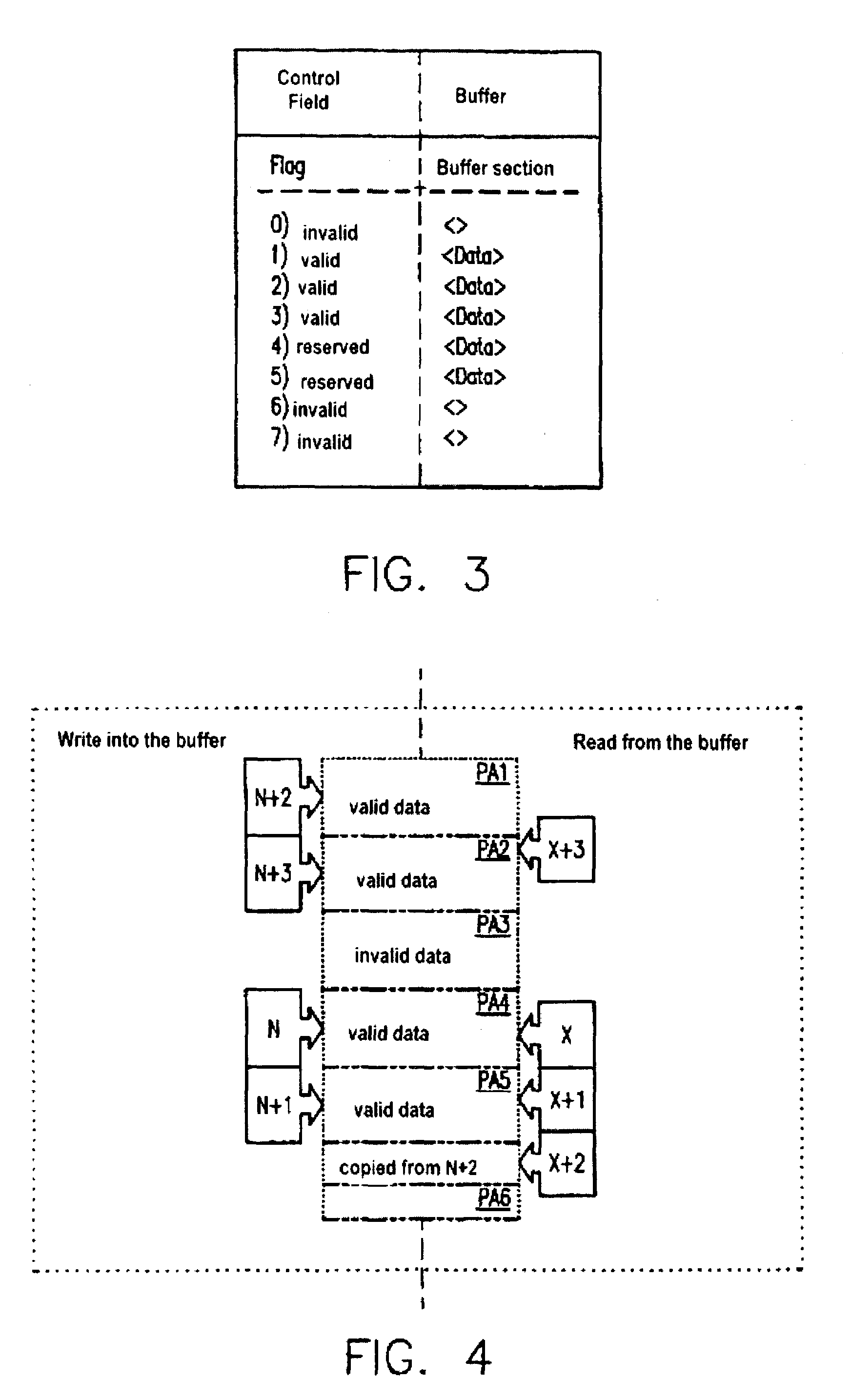
[0038]From the point of view of the program section “process data” P2, the buffer PU1 is an input buffer that inputs data into the program section P2, and the buffer PU2 is an output buffer that accepts data of the program section P2. With the inventive method, the data transfer DT from a program section to a buffer—for example from P1 to PU1 or from...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com