System and method for detecting a fault in a multiple receiver system
a multiple receiver and fault technology, applied in the direction of receiver monitoring, transmission monitoring, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of faulty voice and/or data communication, poor calibration or hardware malfunction, and the receiver in the multiple receiver system occasionally suffers from faults, so as to save hardware costs and the associated costs of deployment and calibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
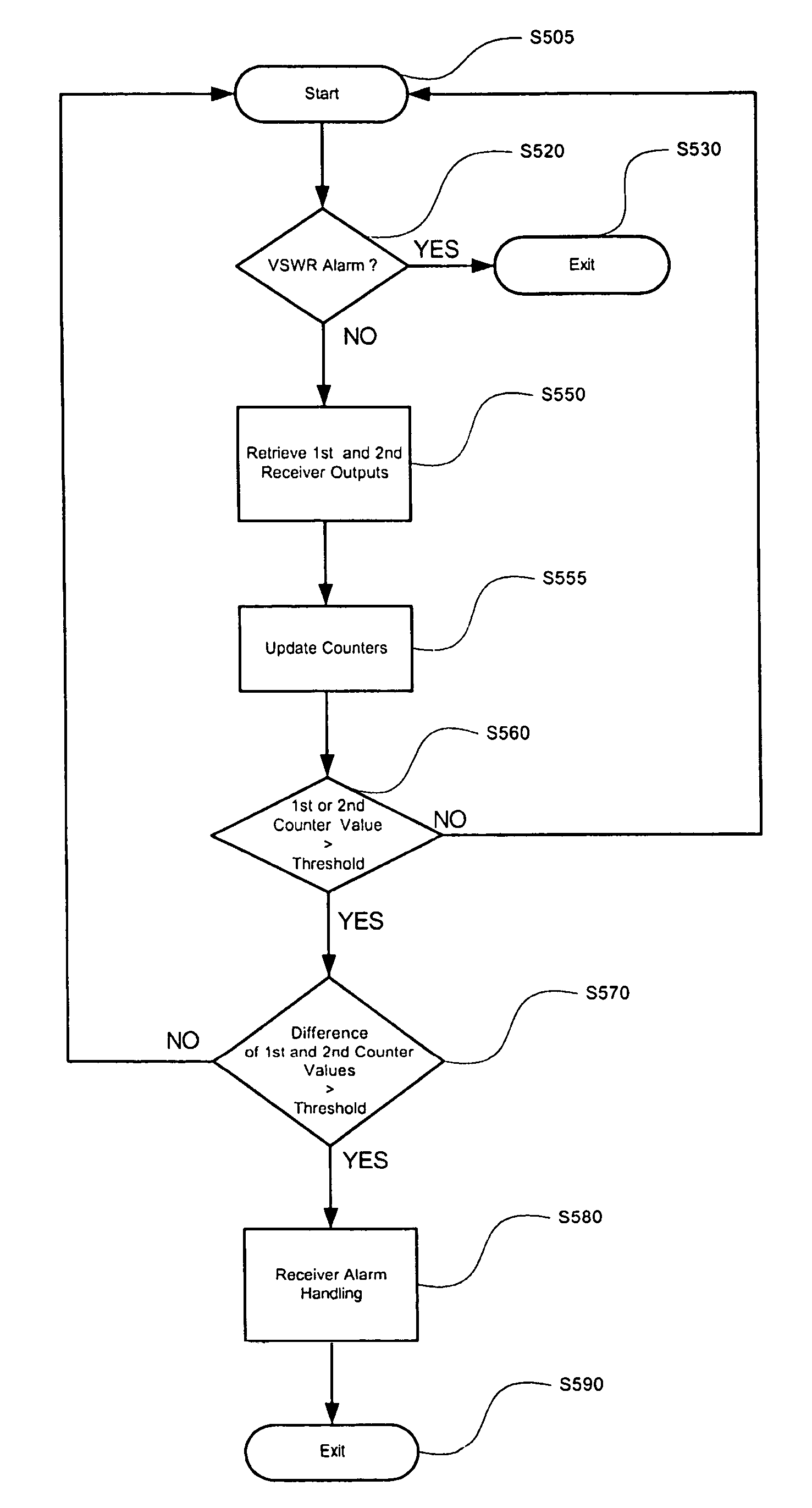
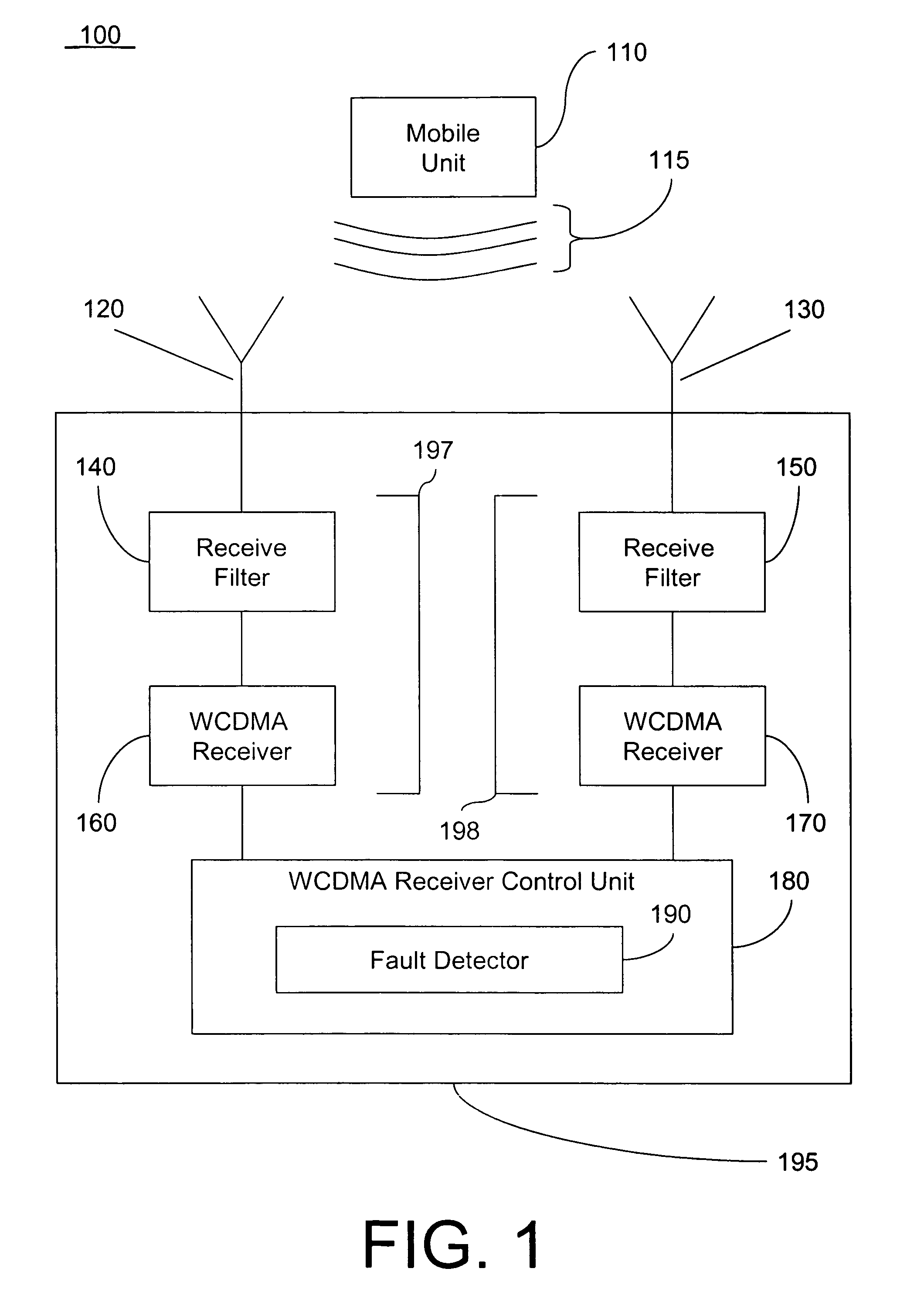
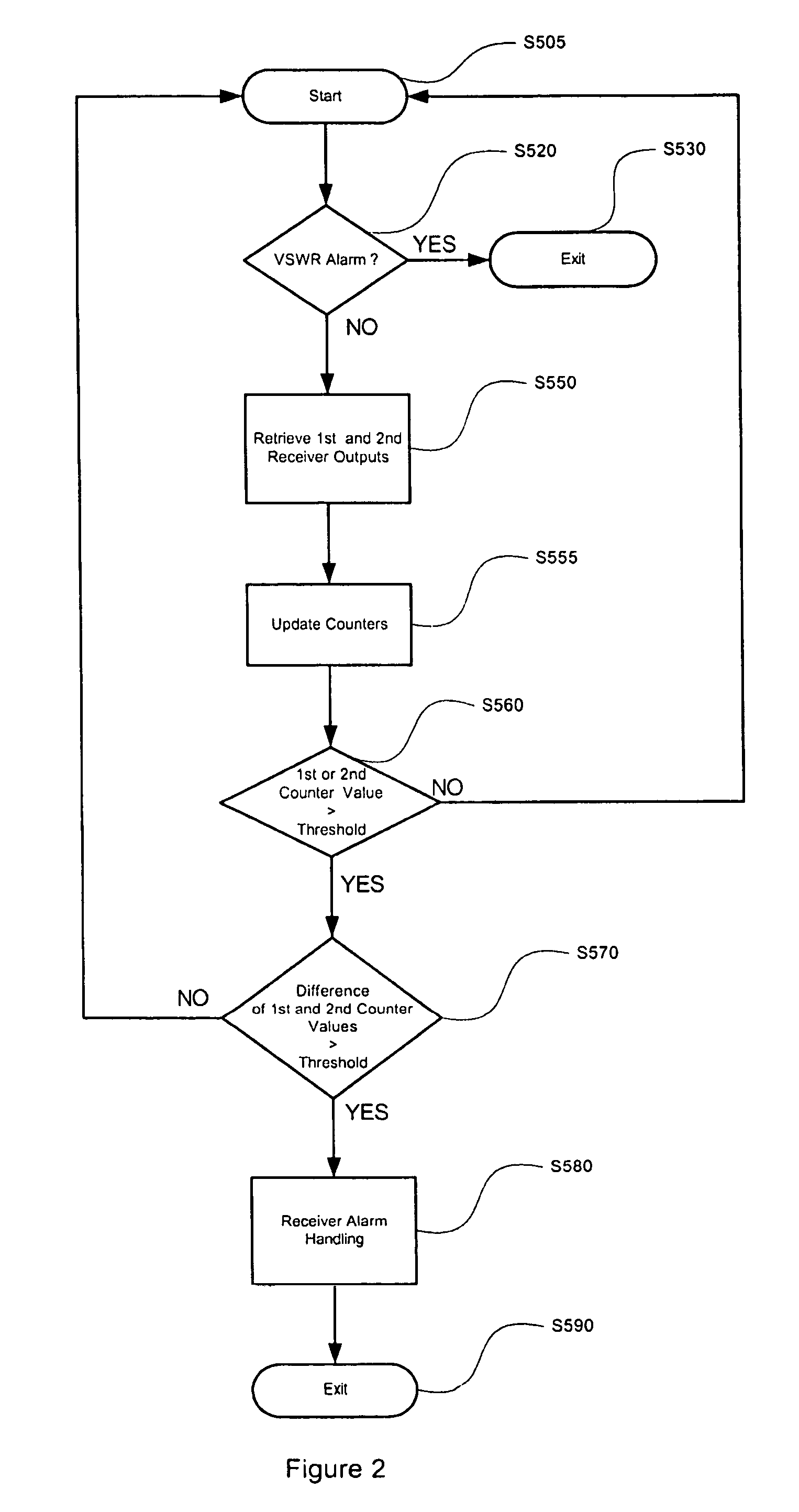
[0011]In an example embodiment of the invention, a fault detector may be used to determine whether a wideband code division multiple access (WCDMA) receiver is faulty. Information regarding an uplink signal of a mobile unit or other radio transmit device may be used by a fault detector to determine whether a fault in a receiver is present. The fault may be detected by taking advantage of existing WCDMA resources.
[0012]In an example embodiment of the invention, a fault detector receives classification values from at least two receivers located in a base station. The classification values may be based on the outputs of the at least two receivers. The at least two receivers process signal information of signals received from at least two antennas. Each of the antennas receive the same uplink signal from a mobile unit or other radio transmit device. First described is an example embodiment of a network that may be used in detecting a fault in a receiver. Next described is an example fau...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com