Intramedullary nail
a technology of intramedullary nail and nail, which is applied in the field of intramedullary nail, can solve the problems of degree of adjustment, difficult operation, and inability to completely deny, and achieve the effects of easy insertion, correct adjustment, and simple construction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
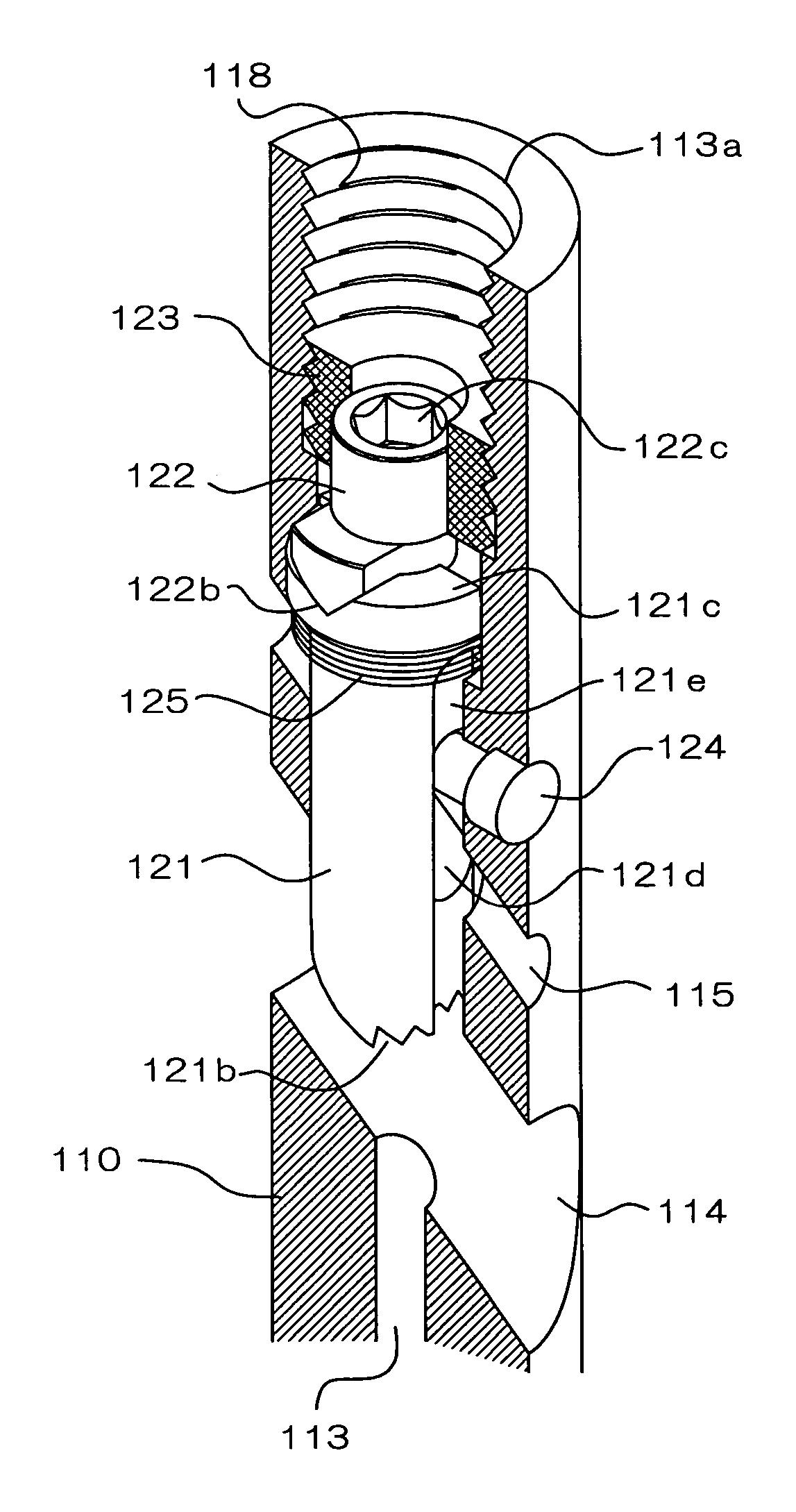
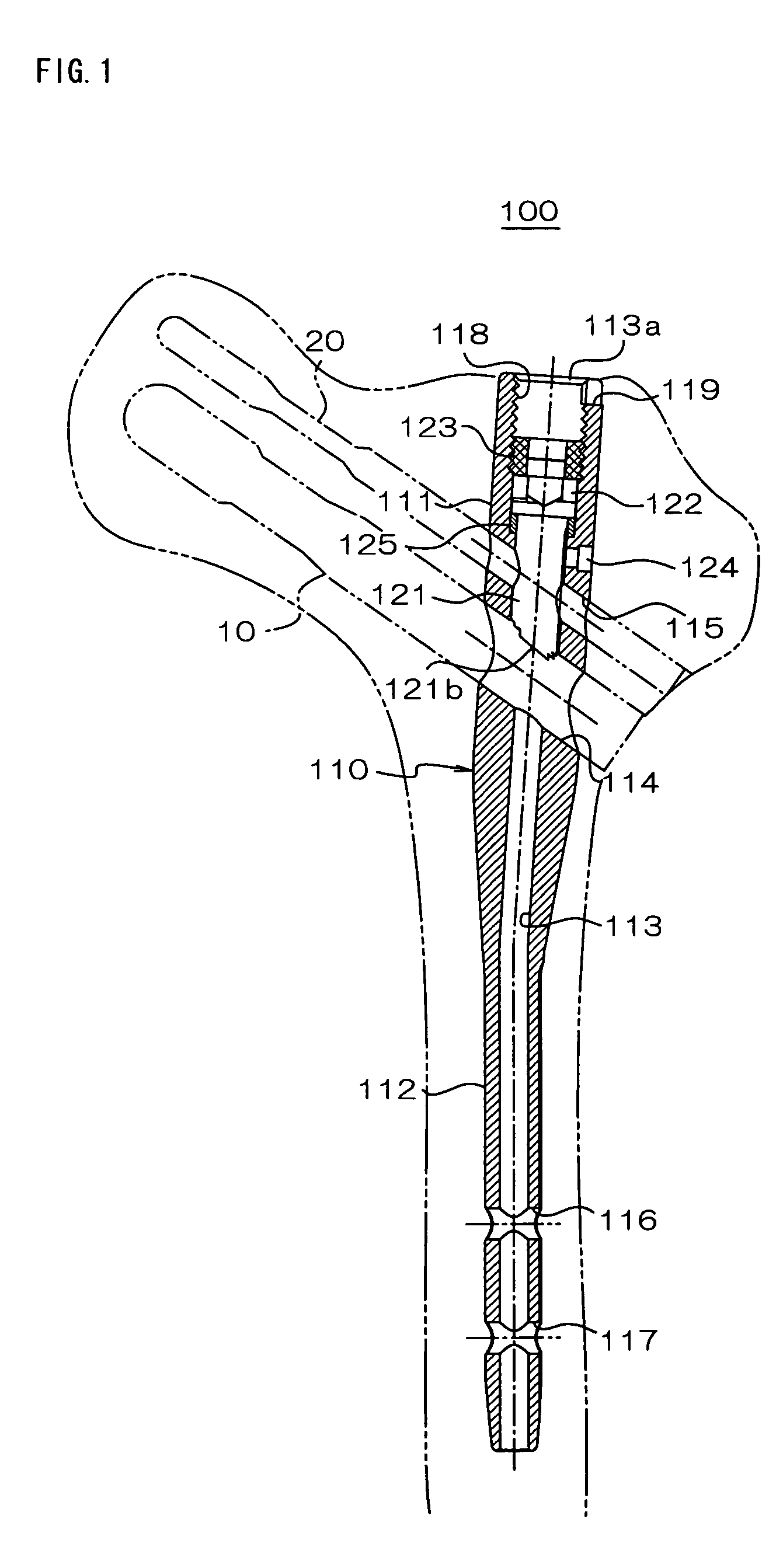
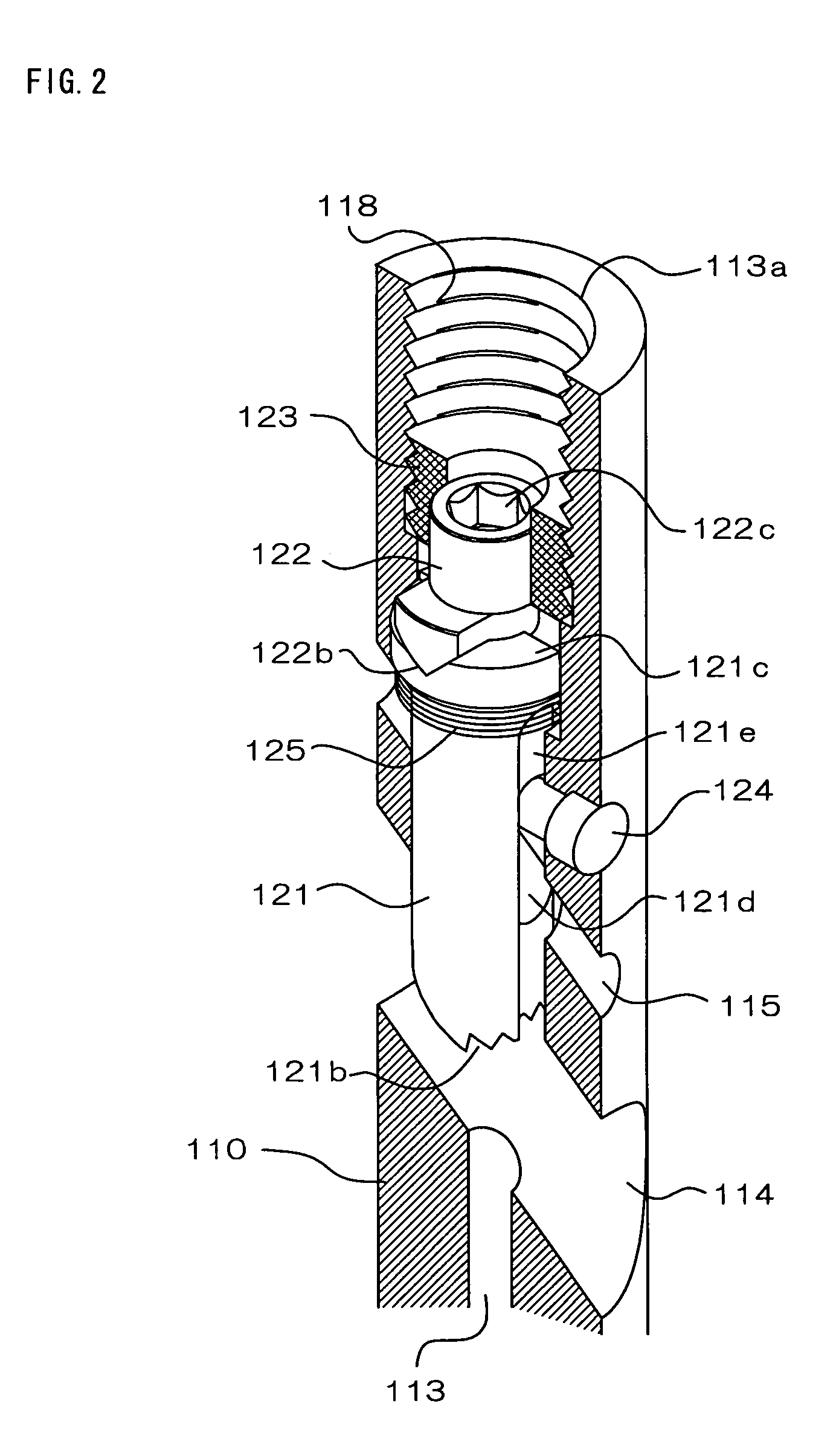
[0028]Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described along with an illustrated example. FIG. 1 is a longitudinal sectional view showing an overall construction of an intramedullary nail 100 of the present embodiment, and FIG. 2 is an enlarged partial longitudinal section perspective view showing a longitudinal section of a proximal region of the intramedullary nail 100 in an enlarged manner. This intramedullary nail 100 has a nail body 110 extending axially from a proximal end portion to a distal end portion. This nail body 110 is preferably composed of a biocompatible material such as, for example, titanium, titanium alloy, a biodegradable resin and the like. The nail body 110 has a proximal region 111 provided at its proximal end side and a distal region 112 connected to the proximal region. The proximal region 111 preferably has a diameter larger than that of the distal region 112, and the proximal region 111 and the distal region 112 preferably have axis l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com