Shock dampening post driver
a post driver and shock dampening technology, applied in the field of post drivers, can solve the problems of affecting the use of the post driver, so as to reduce the vibration and shock, and reduce the force transferred
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
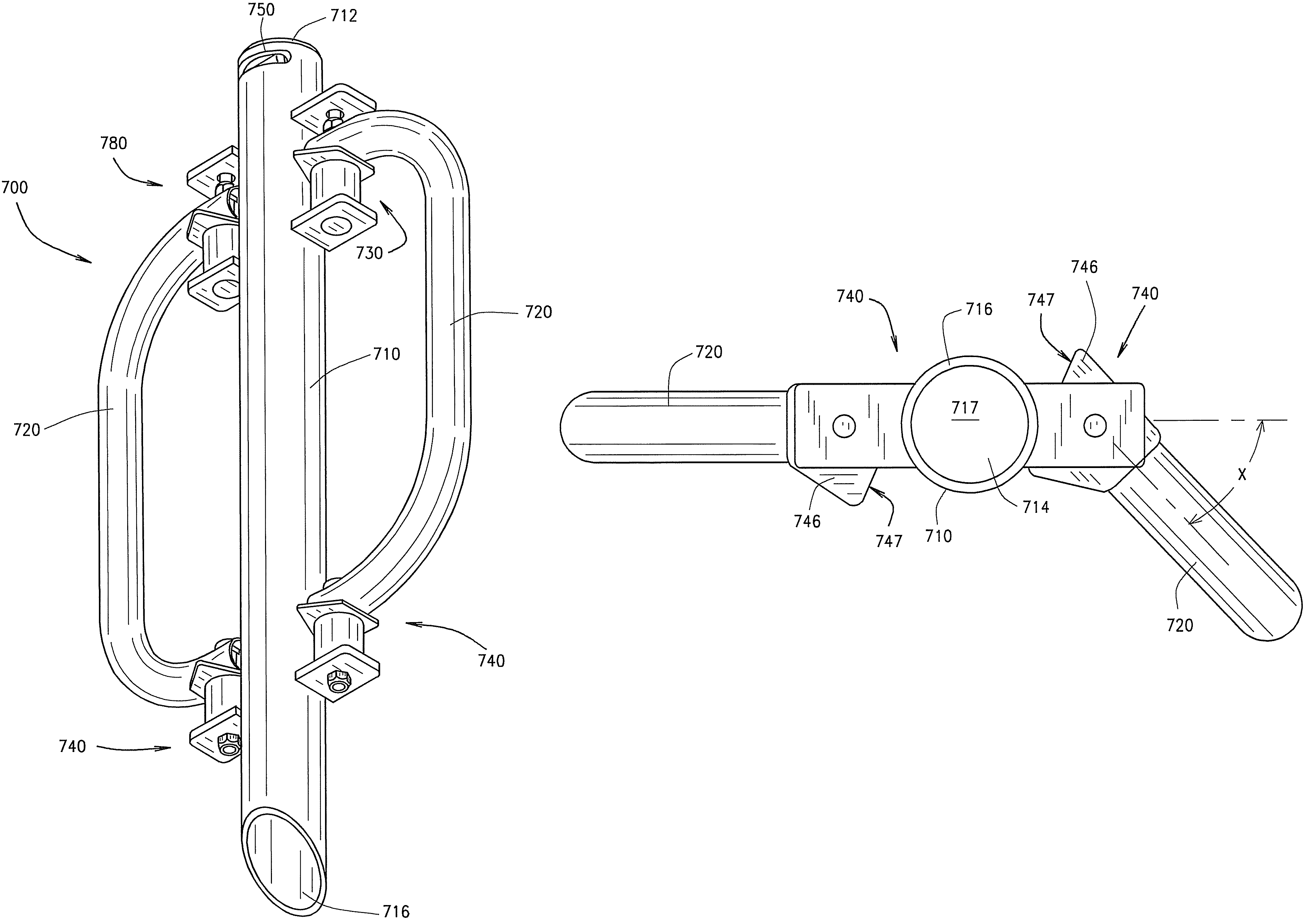
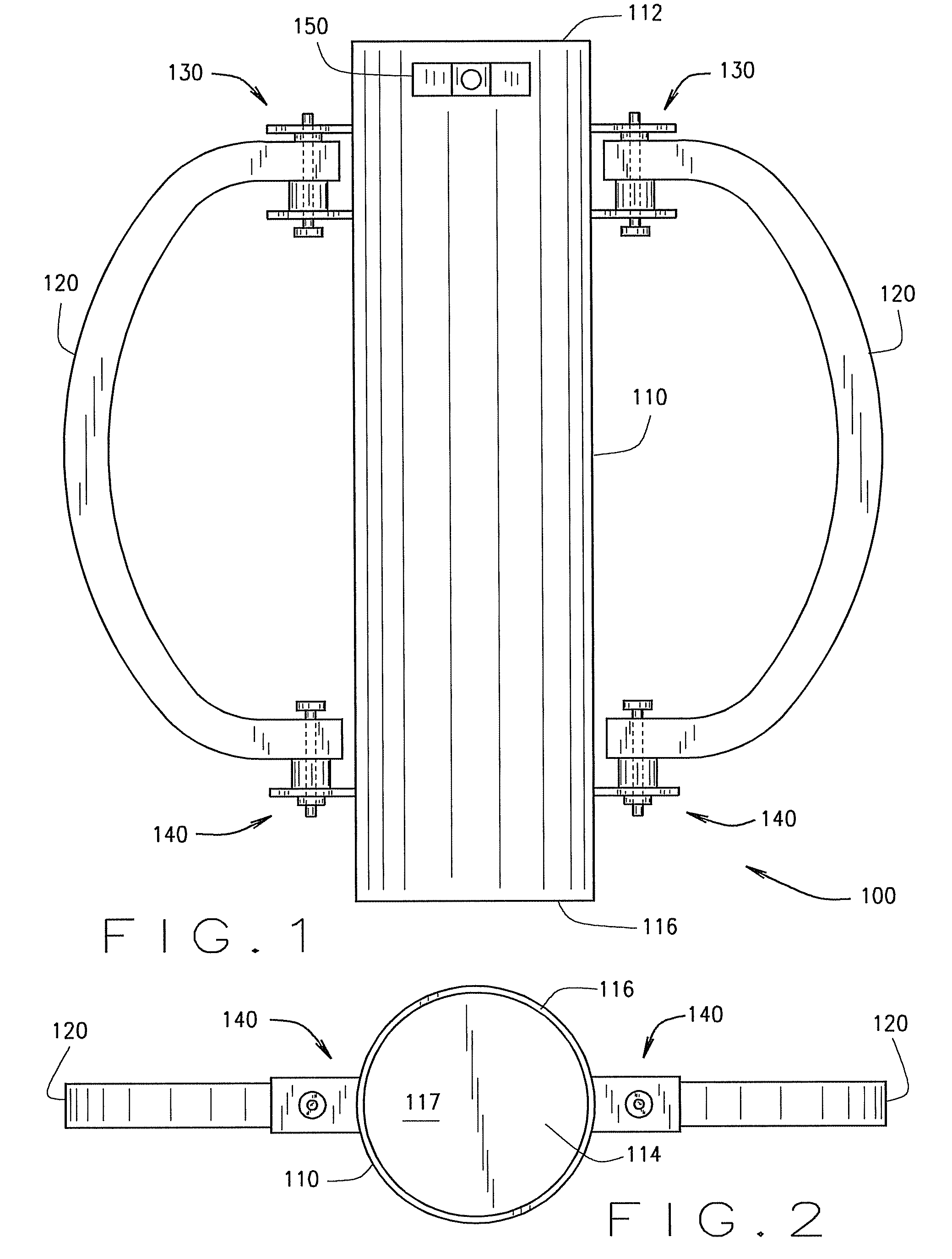
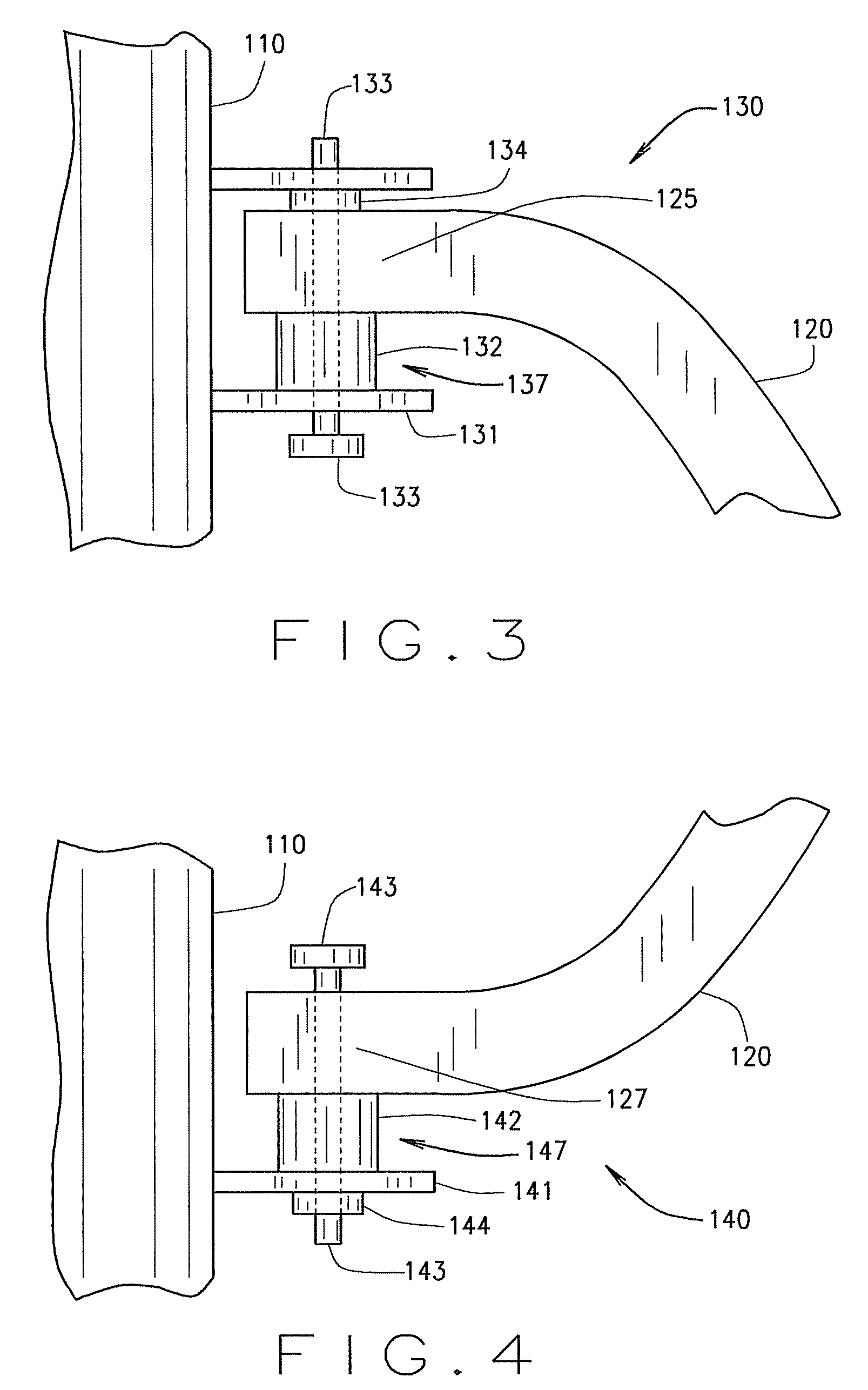
[0025]A shock-dampening post driving device, according to an embodiment of the present invention, includes a shaft having an axially extending interior cavity that extends to a closed top end of the shaft and to a distal open bottom end of the shaft. The closed top end of the shaft forms a striking surface that is used to strike posts. The shaft also has a first mounting bracket extending from an exterior wall of the shaft. Additionally, an upper mounting flange of a handle is mounted to the first mounting bracket of the shaft by a first floating mount with a first floating region. The first floating mount may be adapted to allow the handle to rotate about an axis parallel to the longitudinal axis of the shaft between a first and second position. Further, a first dampening spring is positioned between the upper mounting joint of the handle and the first mounting bracket. This first dampening spring extends into the first floating region, where it dampens vibration between the shaft ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com