Non-volatile memory circuit
a memory circuit and non-volatile technology, applied in static storage, digital storage, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the area and the number of processes, the memory capacity of the bleeder resistor trimming is small, and the structure of the element becomes complicated, so as to improve the write characteristics and improve the write characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025]An embodiment of the present invention is described in detail below.
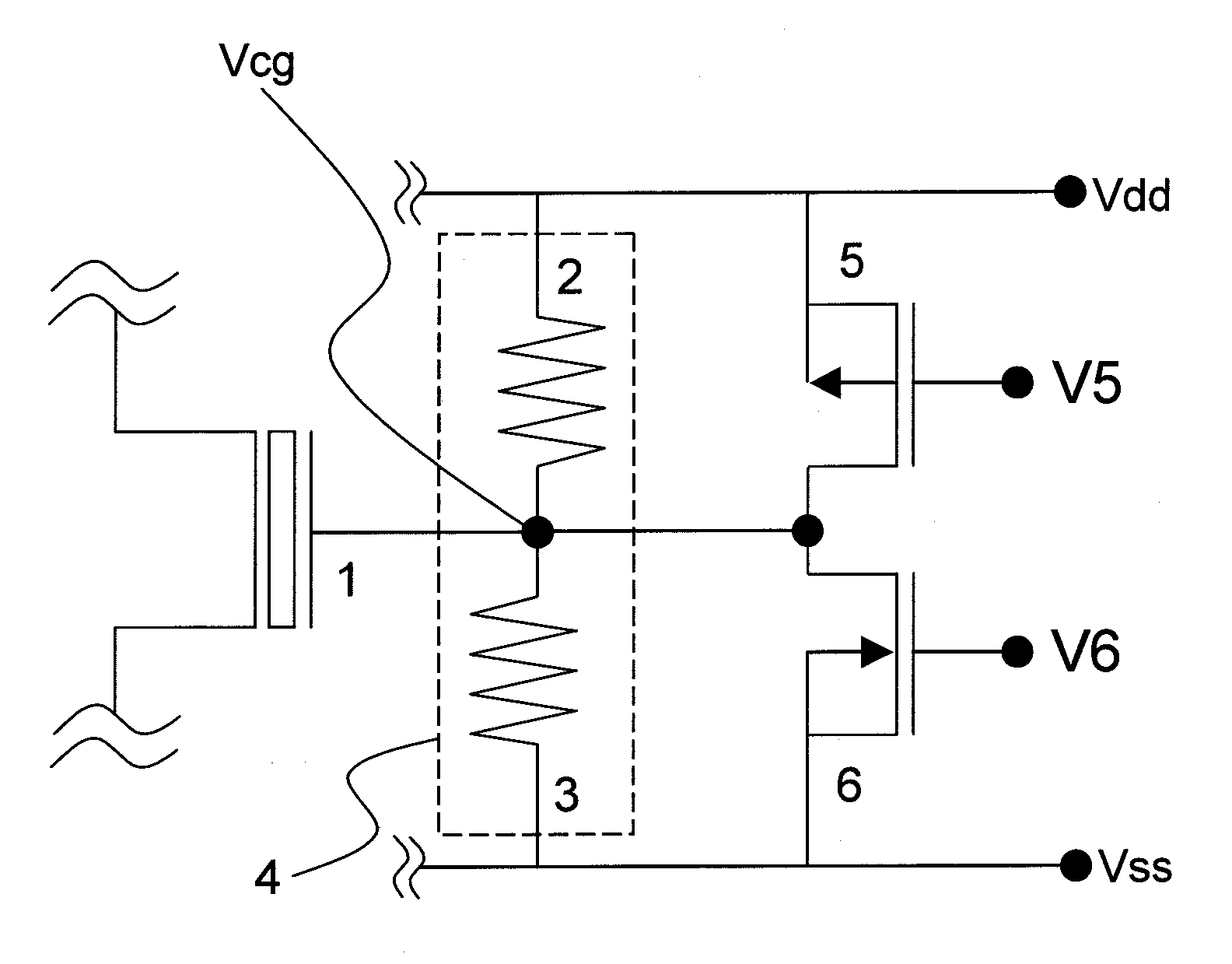
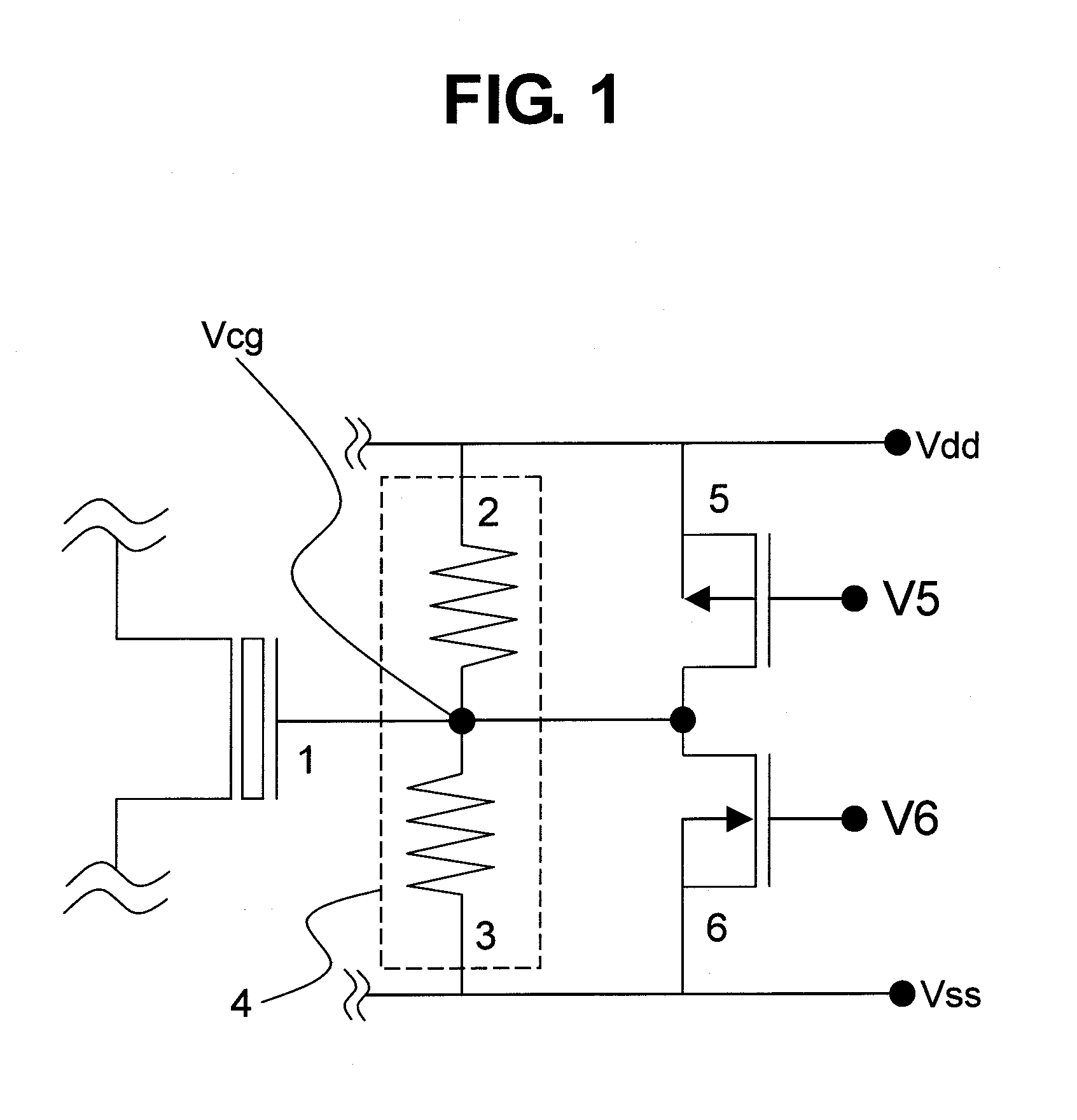
[0026]FIG. 1 is a non-volatile memory circuit illustrating an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1, the non-volatile memory circuit according to the present invention is described below.
[0027]In this embodiment, as illustrated in FIG. 1, a P-channel non-volatile memory element 1 includes a floating gate and a control gate capacitively coupled to the floating gate. The control gate is connected to a divided voltage output of a resistor divider 4 including a first resistor 2 and a second resistor 3 for dividing a voltage difference between a power supply voltage and a ground voltage, and is also connected to a P-channel switch transistor 5 connected in parallel to the first resistor 2 and an N-channel switch transistor 6 connected in parallel to the second resistor 3.
[0028]Next, a description is given of the operation of the non-volatile memory circuit according to this embodiment.
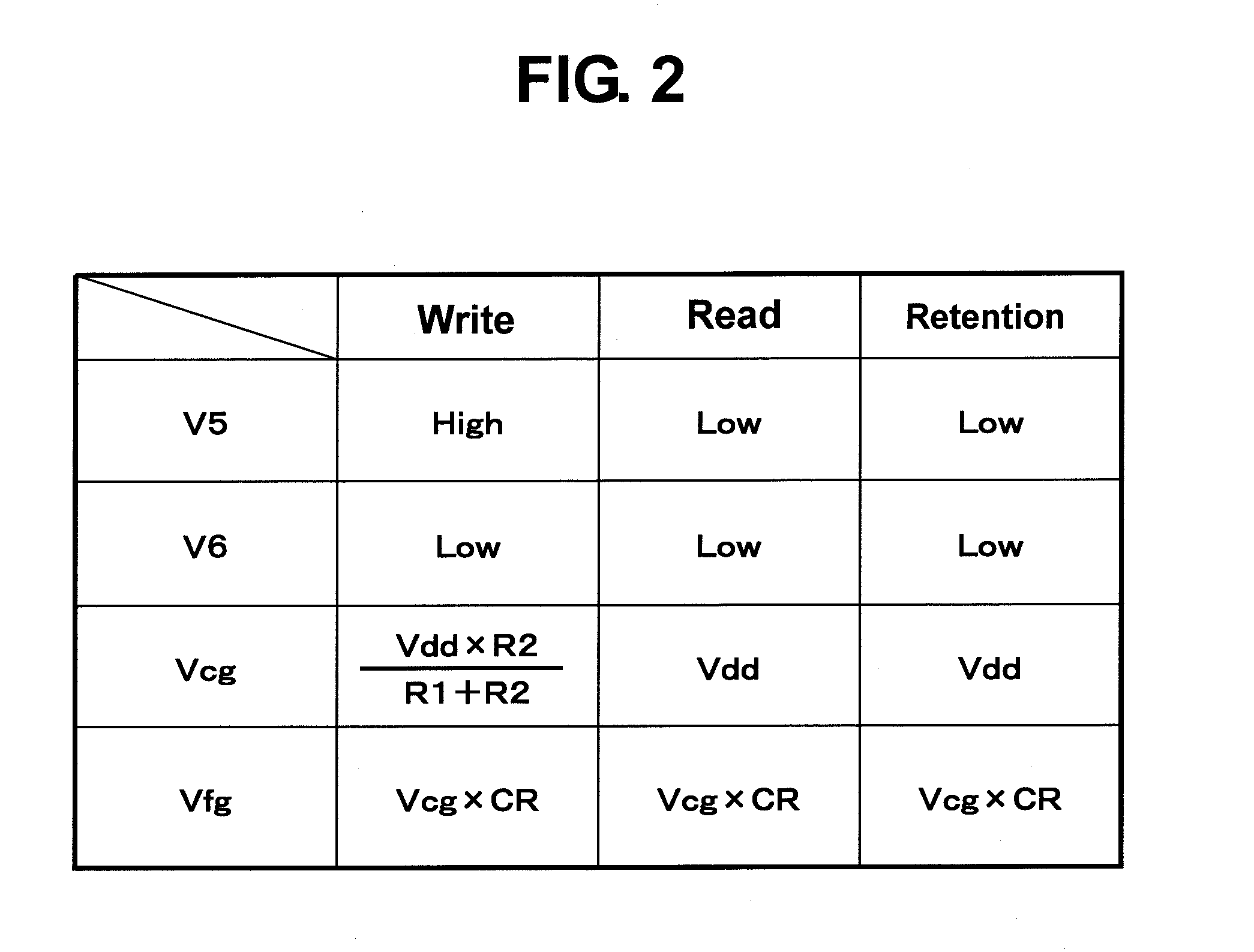
[0029]The r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com