T-sensor devices and methods of using same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
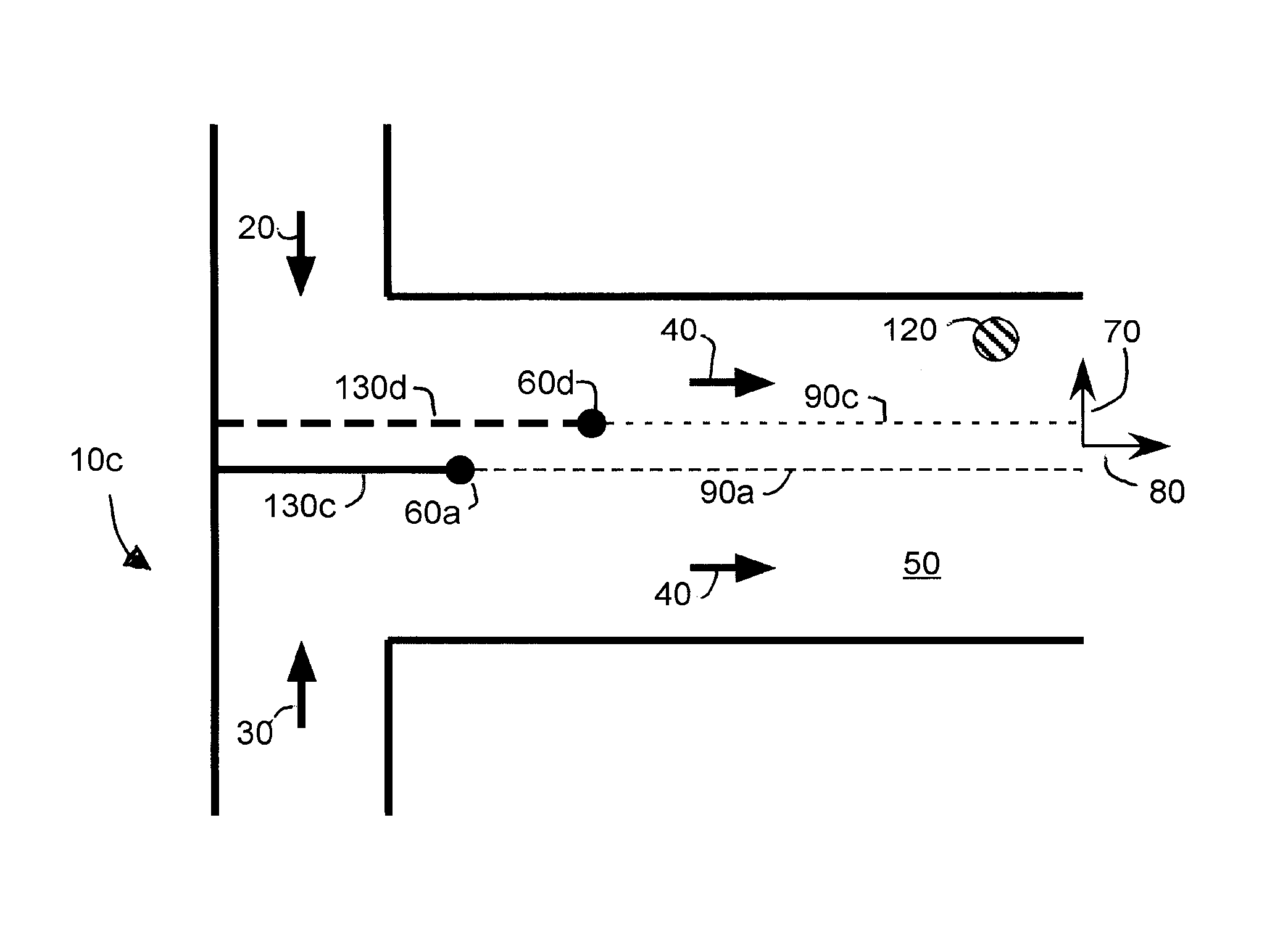
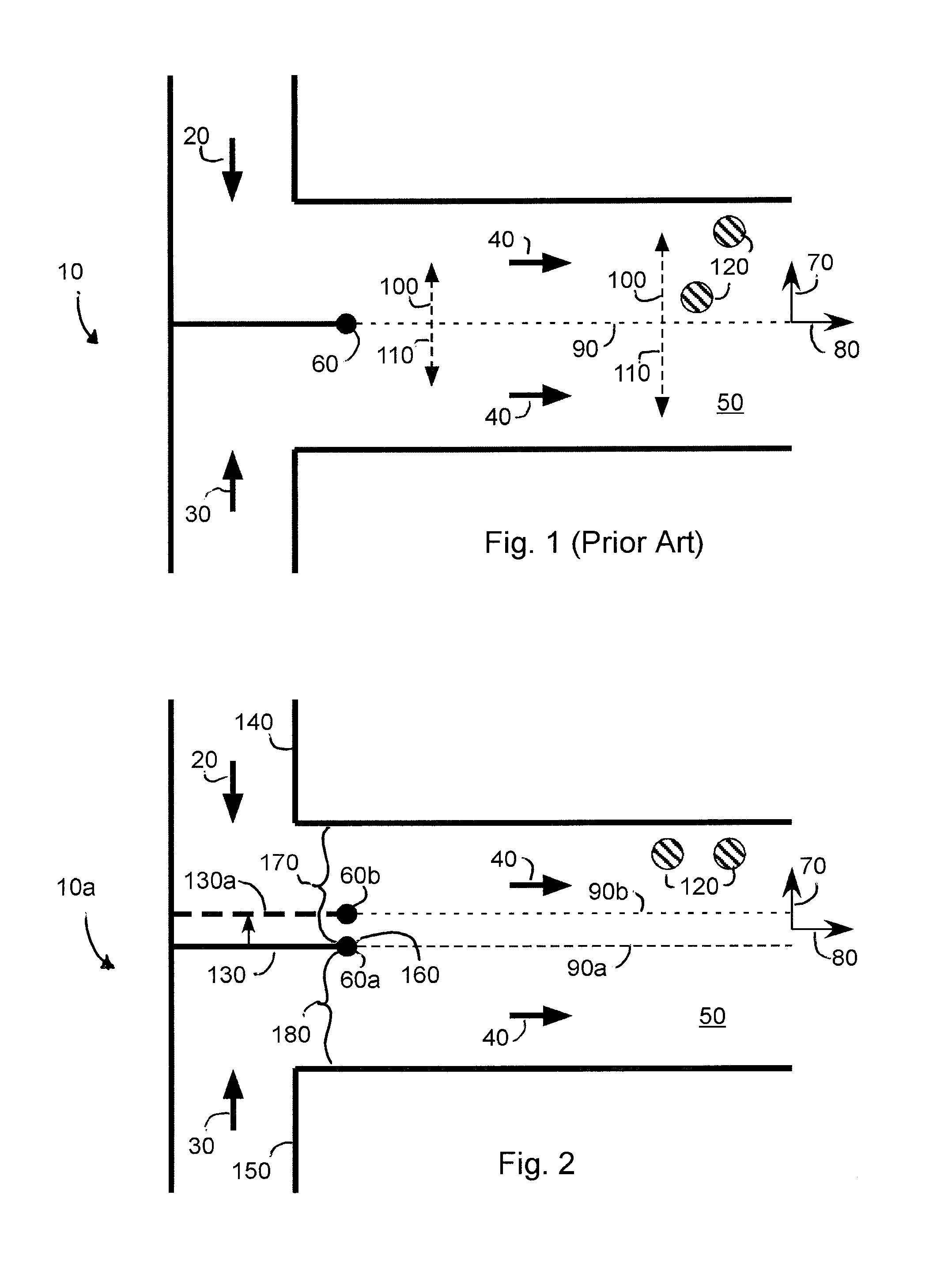
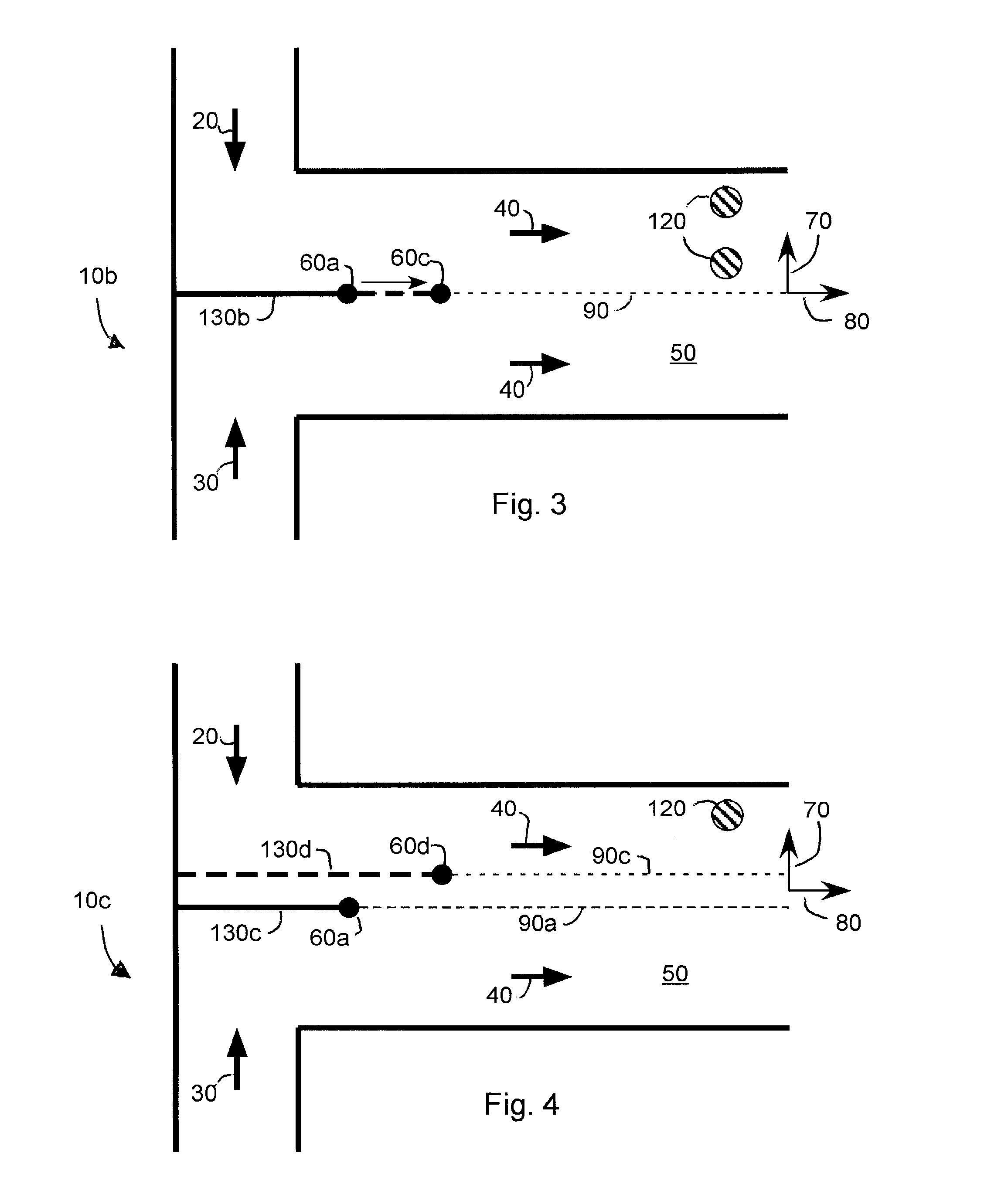
[0025]FIG. 2 is a schematic representation of a T-sensor 10a according to an embodiment of the invention having a limited number of sensing locations 120 and two joined flows 20, 30 with a laterally movable but longitudinally fixed divider 130 between the two input flows (reference numbers for similar elements in the T-sensor shown in FIG. 1 also appear in FIG. 2). An input fluid (e.g., Fluid A—see arrow 20) flows into the T-sensor through a first supply conduit 140. A second input fluid (e.g. Fluid B—see arrow 30) flows into the T-sensor through a second supply conduit 150. The first fluid and the second fluid are separated from each other by the divider 130. The end of the divider 160 where the two fluids first contact each other is defined as an initial diffusion start point 60a. It will be appreciated that FIG. 2 depicts the T-sensor in only two-dimensions (i.e., the plane defined by the paper on which FIG. 2 is drawn) and thus the end of the divider 160 appears in FIG. 2 as a p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com