Method for adjusting the level of optical signals
A technology of signal power level and power level, which is applied in lasers, laser components, and lasers using scattering effects, etc., can solve problems such as faulty pulses and cannot be quickly balanced, and achieve good noise performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
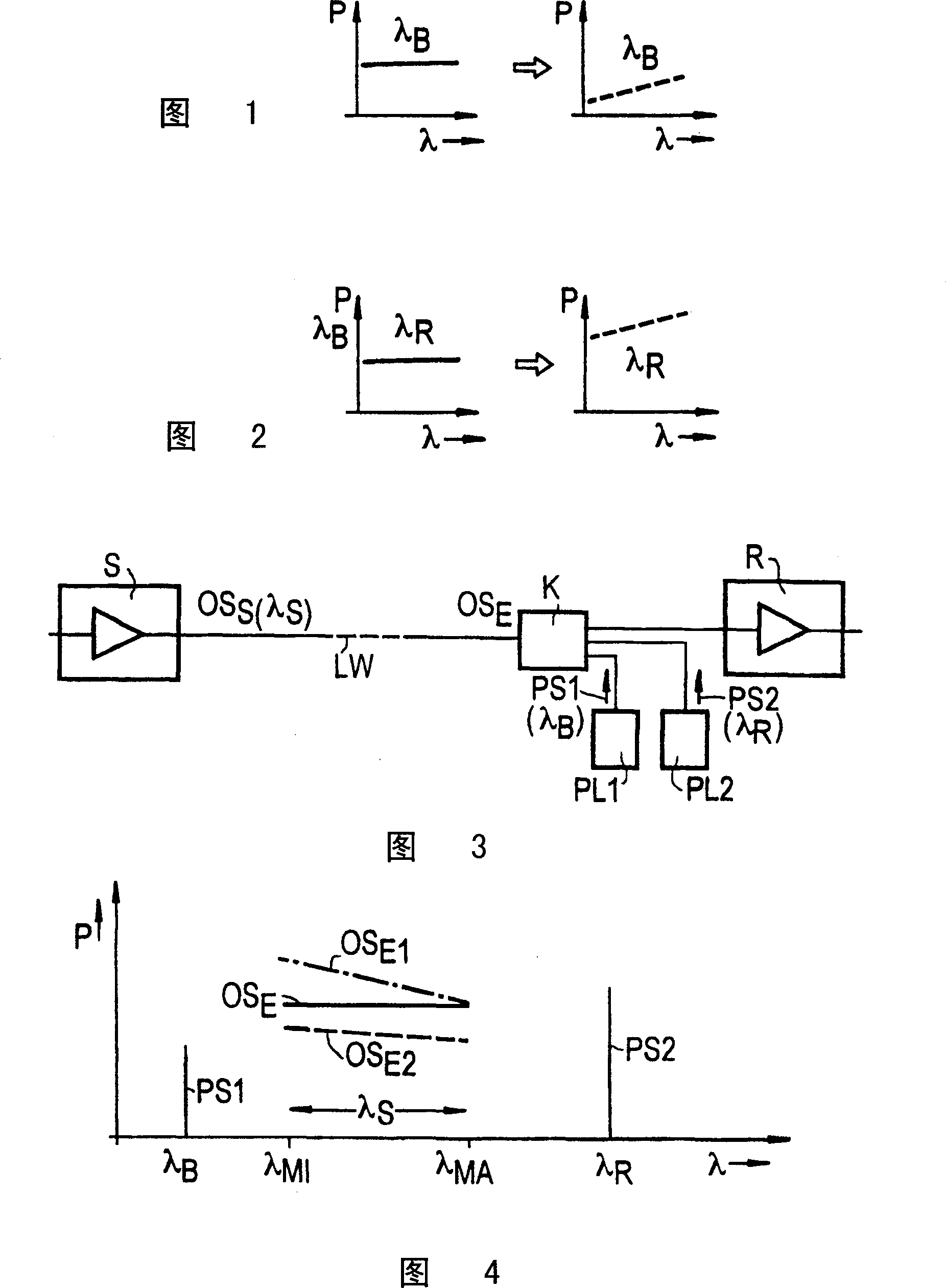
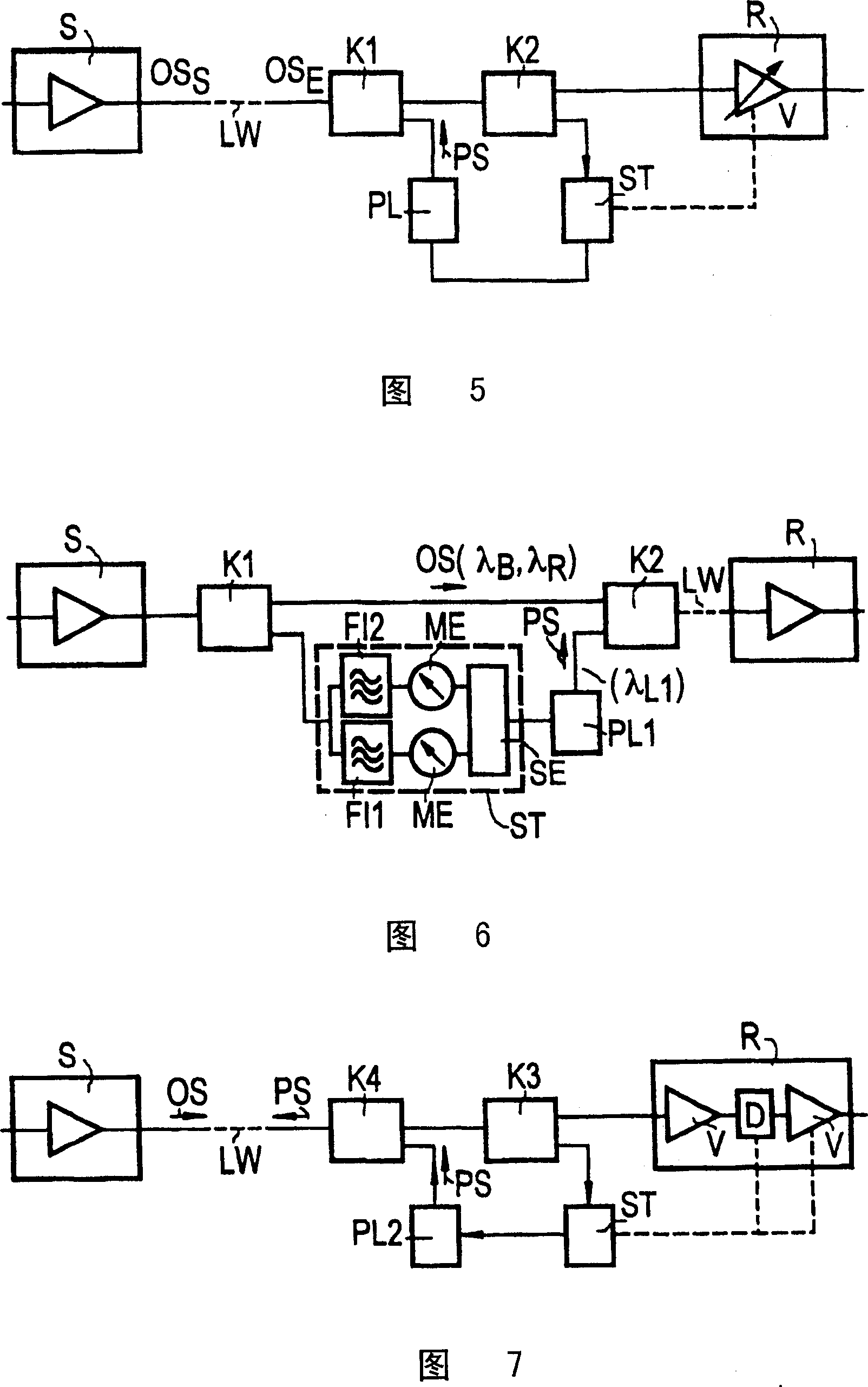
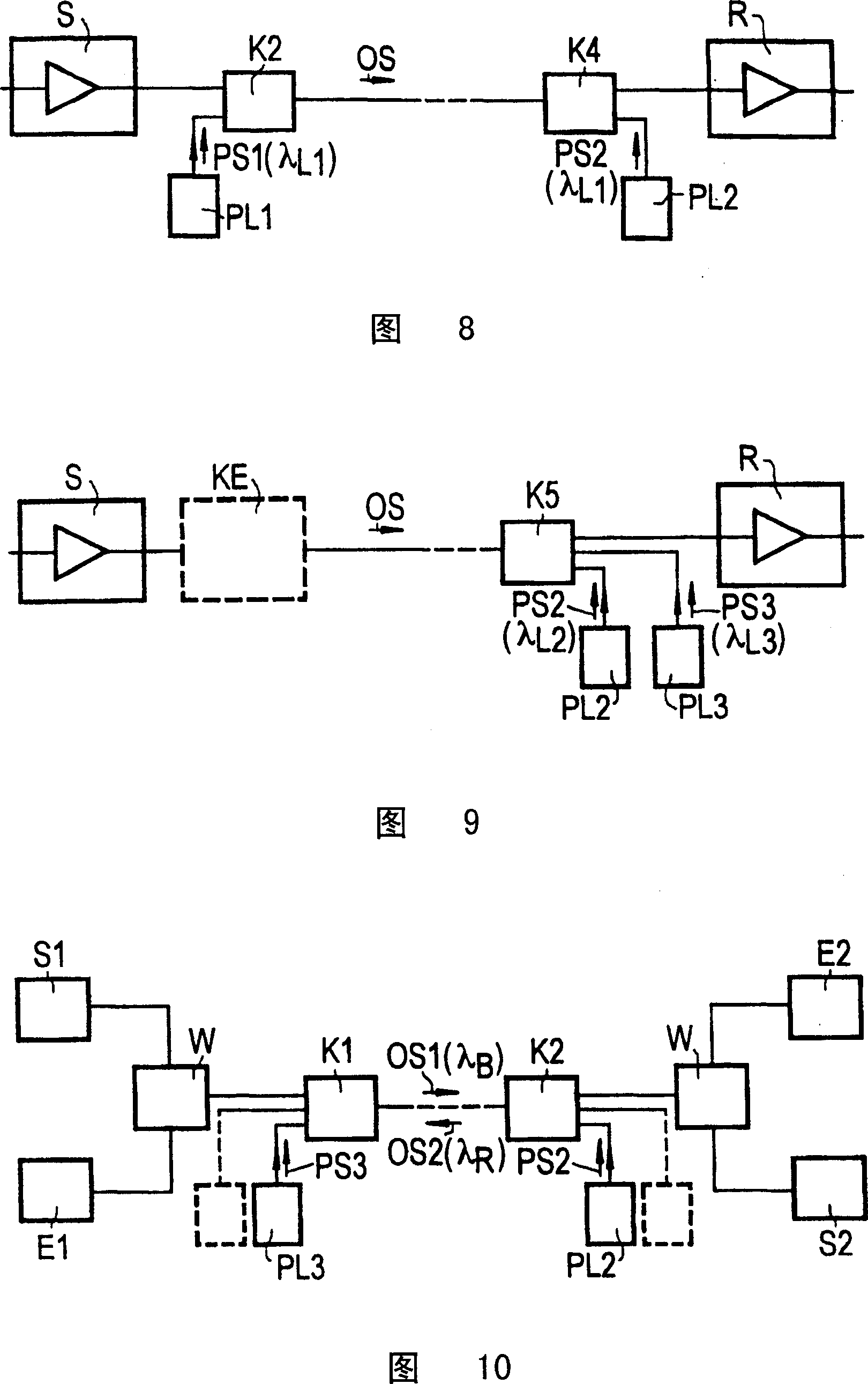
[0040] Accompanying drawing 3 shows that the transmission section has a transmitting device S, such as a laser or an amplifier, which will have a relatively large wavelength range λ s optical signal OS s Feeds into the optical waveguide LW and has a receiver R which also has an amplifier. For example, an optical signal may involve a digital multiplexed signal with relatively large bandwidth or a wavelength multiplexed signal. The optical signal (received signal) OS that will be damped due to the transmission section E Input to the receiving device R.
[0041] Two pump lasers PL1 and PL2 are installed at the receiver, and the pump laser will be located at the minimum wavelength λ of the optical signal MI The following wavelength is λ B The pump signal PS1, and will be located at the optical signal maximum wavelength λ MA The above wavelength is λ R The pumping signal PS2 (Fig. 2) is fed into the optical waveguide through the coupler K. The pump signal PS2 makes the optic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com