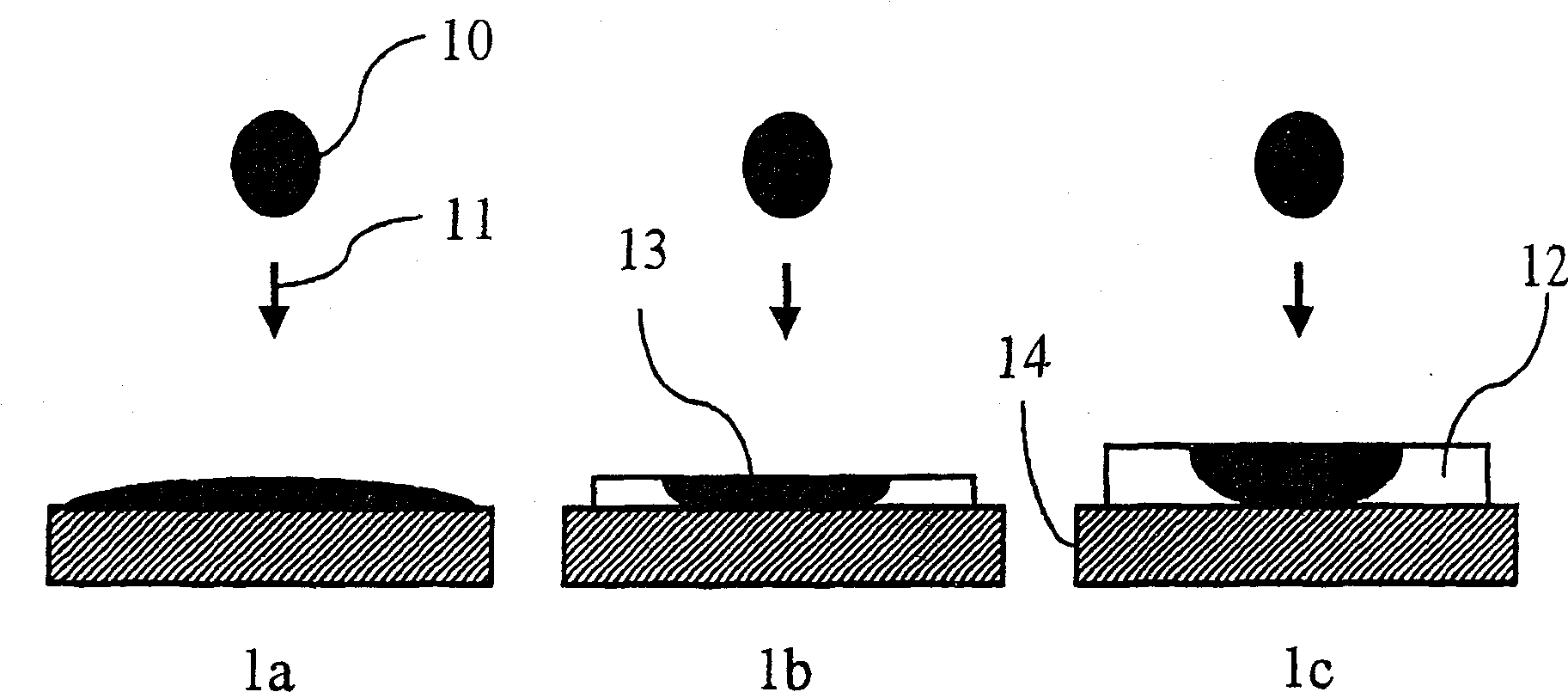
Printing of radiation curable inks into a radiation curable liquid layer
A technology of radiation curing and printing methods, applied in the post-processing of printing, printing, ink, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete acquisition of ink drops, unclear images, incomplete understanding of the exact nature of ink-medium, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0180] Preparation of radiation curable inkjet inks
[0181] Colorant dispersions for radiation curable inkjet inks can be prepared by mixing, milling and dispersing the colorant and resin. Mixing equipment may include pressure kneaders, open kneaders, planetary mixers, dissolvers, and Dalton universal mixers. Suitable milling and dispersing equipment are ball mills, pearl mills, colloid mills, high-speed dispersers, twin rolls, bead mills, paint conditioners, and triple rolls. Dispersions can also be prepared using ultrasonic energy.
[0182] Many different types of materials can be used as grinding media, such as glass, ceramics, metals and plastics. In a preferred embodiment, the grinding media may comprise particles, preferably substantially spherical particles such as beads consisting essentially of a polymeric resin or yttrium-stabilized zirconium beads.
[0183] In the processes of mixing, milling and dispersing, each process is carried out with cooling to prevent he...
Embodiment 1
[0228] This example illustrates how the dot size of an ink droplet is controlled by thickness.
[0229] Preparation of radiation-curable liquid layers
[0230] A colorless radiation curable liquid layer composition Ink-L was prepared according to Table 1 by mixing the ingredients and stirring for one hour to ensure good distribution of all components. Weight % (wt%) is based on the total weight of the radiation curable liquid layer composition.
[0231] Table 1
[0232] wt% of the following substances Ink-L DPGDA TM 66.5 Irgacure TM 907 2.5 Darocur TM ITX 5.0 Craynor TM CN 501 25.0 Byk TM -333 1.0
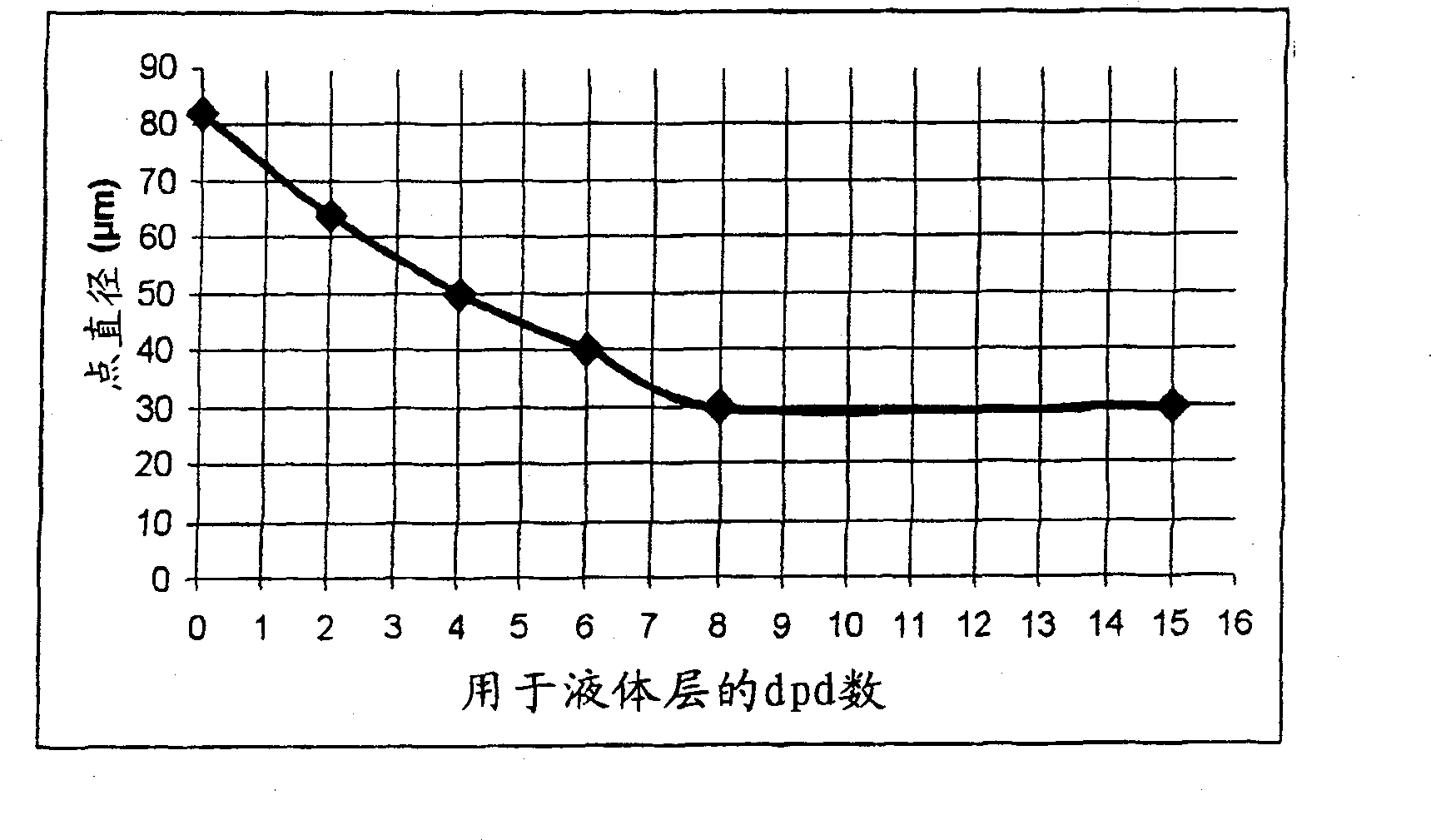
[0233] The radiation curable liquid layer composition Ink-L was jetted on PET using a conventionally configured inkjet printer equipped with a UPH printhead from AGFA to produce ink receivers IR-2 to IR-7. A resolution of 360×360 dpi is used to print numerous dpd (drops per dot) as shown in Table 2, wherein 1 dpd is equal t...
Embodiment 2
[0248] In this example, the dot size of the inkjet ink jetted on the liquid layer after curing was evaluated.
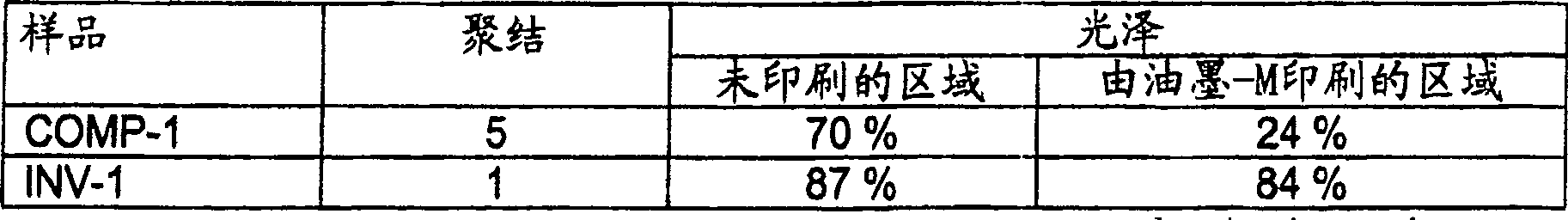
[0249] Ink receiver IR-8 was prepared in the same manner as ink receiver IR-7 of Example 1, except that the radiation curable inkjet ink Ink-M was used instead of Ink-L. Ink Receptor IR-5 and Ink Receptor IR-8 of Example 1 were first cured using a Fusion DRSE-120 conveyor equipped with a Fusion VPS / 1600 lamp (D-lamp) on a conveyor belt under UV light The ink receiver was transported at a speed of 20 m / min.
[0250] On cured ink receptacles IR-5 and IR-8, 1 dpd of radiation curable inkjet inks Ink-M and Ink-C were jetted from a conventionally constructed inkjet printer at a resolution of 360 x 360 dpi. The printed samples were cured by the same procedure used to cure ink receptors IR-5 and IR-8. Radiation curable ink Ink-M was not jetted on ink receptacle IR-8 due to visual differentiation difficulties.
[0251] table 5
[0252] ink receiver Dot Diamet...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com