Server and software protection method and system
A server-side, software protection technology, applied in the direction of program/content distribution protection, equipment, user identity/rights verification, etc., can solve the problem of client-side program security threatening server-side applications and data, etc., to ensure security and protect On the server side, the effect of ensuring security
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
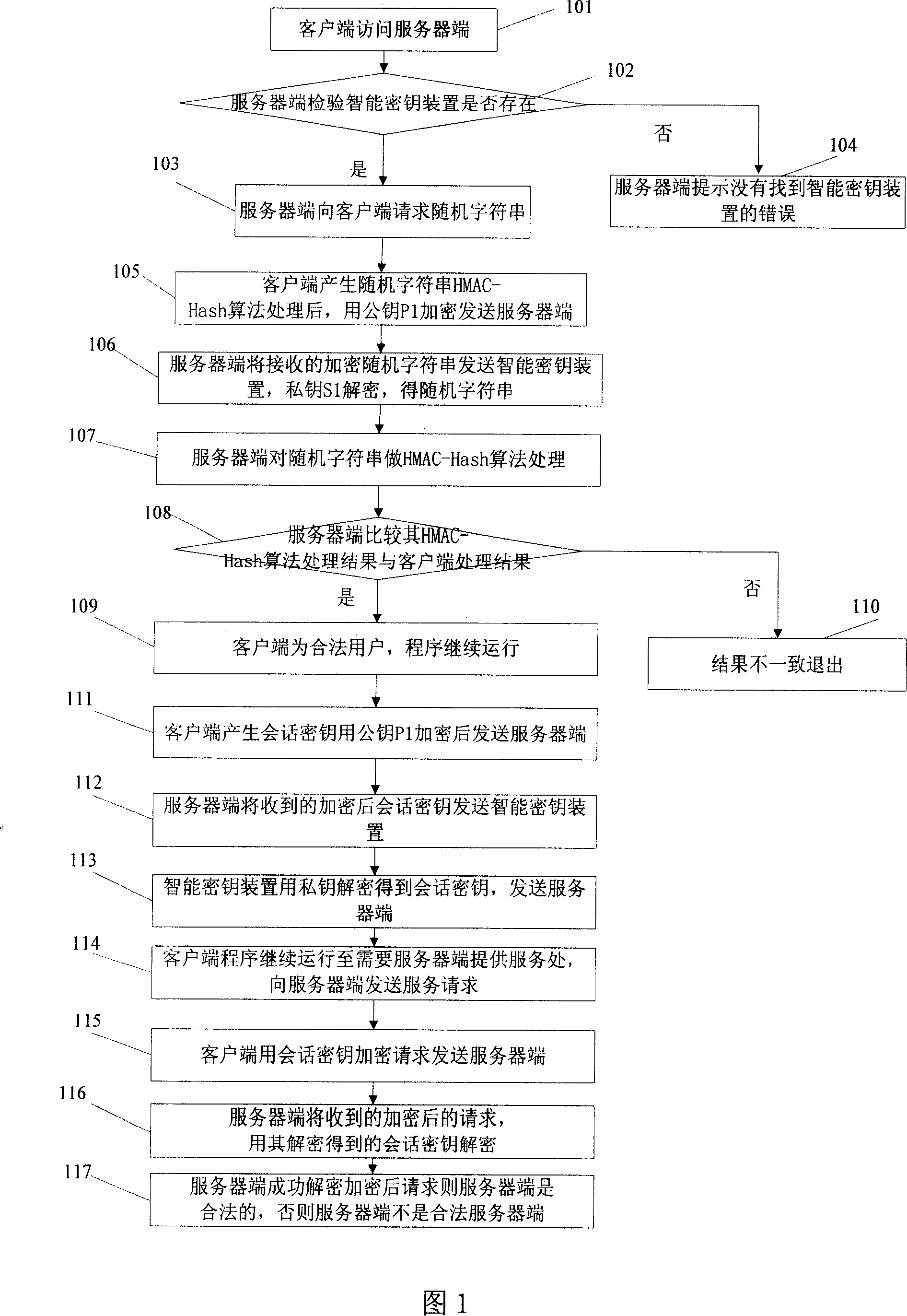
[0045] As shown in Figure 1, in this embodiment, the client program contains a public key P1, and the server-side smart key device contains a corresponding private key S1, and the server uses an impulse response mechanism to verify the client.
[0046] The specific verification steps are as follows:
[0047] Step 101: the client accesses the server;
[0048] Step 102: The server side checks whether the smart key device exists, if there is, execute step 103, otherwise execute step 104;
[0049] Step 103: the server side requests a random character string from the client side;
[0050] Step 104: The server prompts an error that the smart key device is not found;
[0051] Step 105: After the client generates a random string and processes it with the HMAC-Hash algorithm, it encrypts it with the public key P1 and sends it to the server;
[0052] Step 106: The server sends the encrypted result of the random character string in the received content to the smart key device, and dec...
Embodiment 2
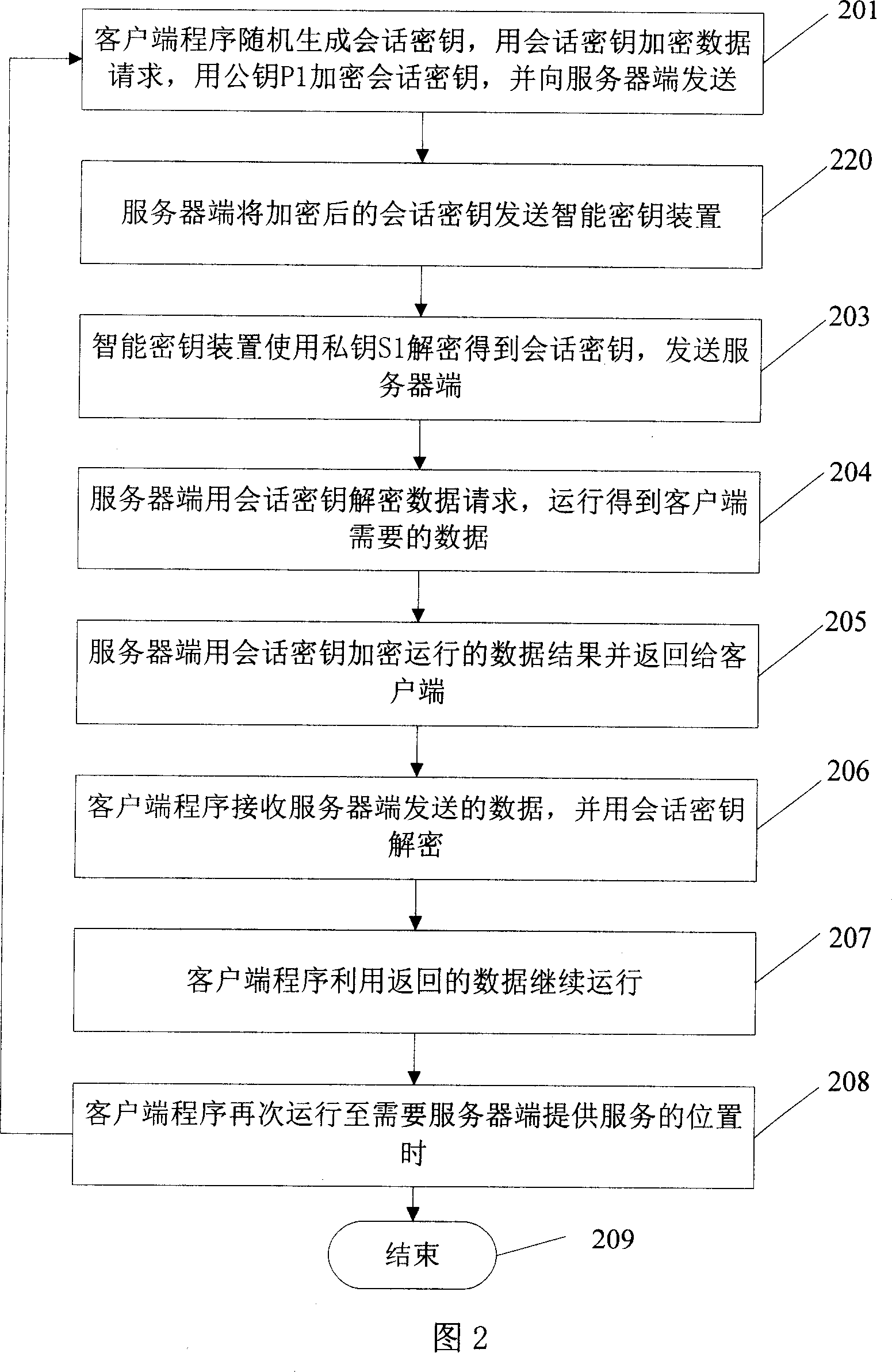
[0065] As shown in Figure 2, in this embodiment, the client program contains a public key P1, and the server-side smart key device contains a corresponding private key S1, and the server-side and client-side databases preset HMAC-Hash algorithm. Because the client lacks functions, data, and codes, in this embodiment, the client needs the server to provide data, and does not need to use the relevant algorithms in the server-side smart key device.
[0066] The specific steps of client-server communication are as follows:
[0067] Step 201: the client program randomly generates a session key, encrypts the data request with the session key, encrypts the session key with the public key P1, and sends it to the server;
[0068] Step 202: the server sends the encrypted session key to the smart key device;
[0069] Step 203: The smart key device uses the private key S1 to decrypt to obtain the session key, and sends it to the server;
[0070] Step 204: the server uses the session ke...
Embodiment 3
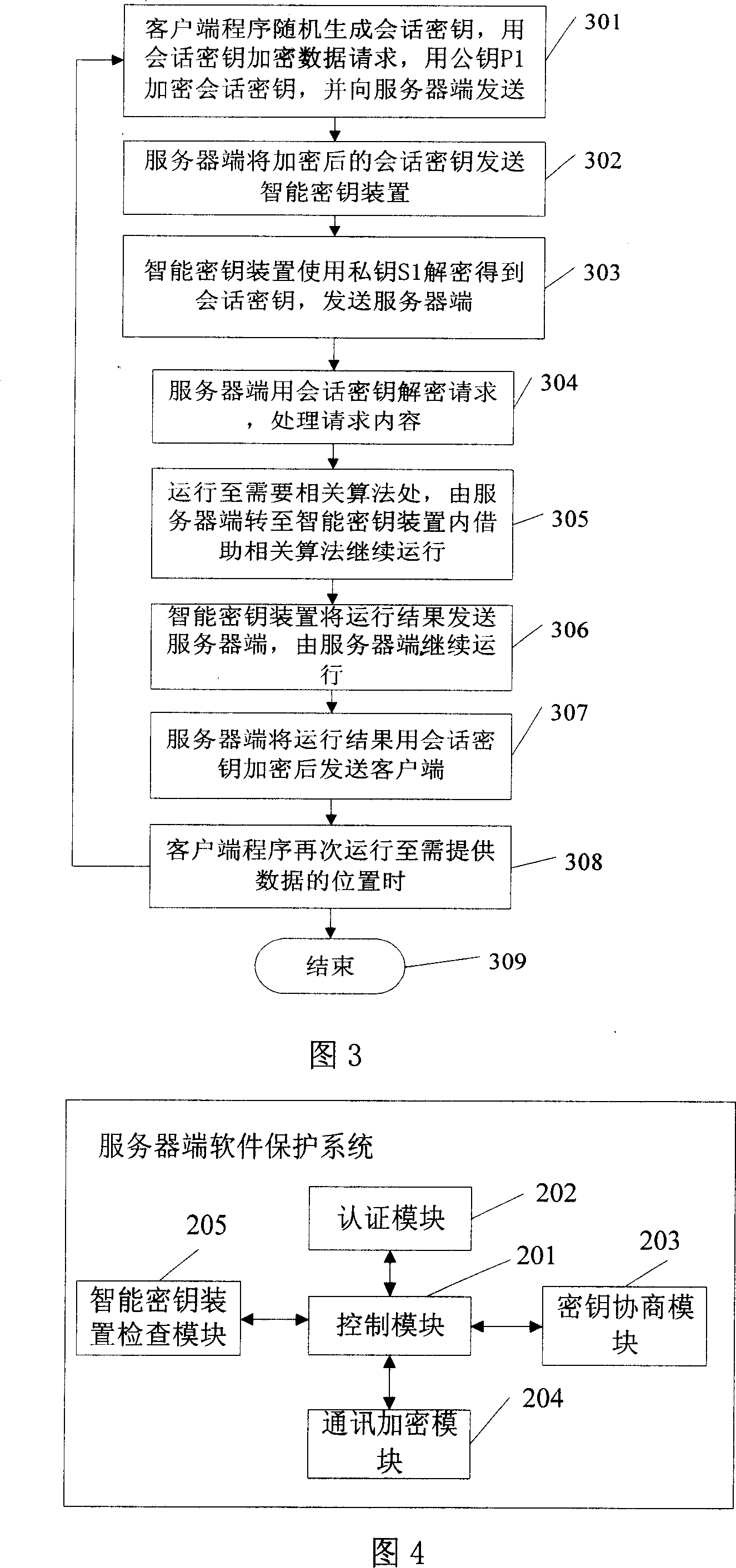
[0077] As shown in FIG. 3 , in this embodiment, the client needs the server to provide data, and the server is a legitimate server and requires the participation of relevant algorithms in the server-side smart key device.
[0078] Step 301, the client program randomly generates a session key, encrypts the data request with the session key, encrypts the session key with the public key P1, and sends it to the server;
[0079] Step 302: the server sends the encrypted session key to the smart key device;
[0080] Step 303: The smart key device uses the private key S1 to decrypt to obtain the session key, and sends it to the server;
[0081] Step 304: the server decrypts the request with the session key, and processes the request content;
[0082] Step 305: Run to the place where the relevant algorithm is needed, and transfer from the server to the smart key device to continue running with the help of the relevant algorithm;
[0083] Step 306: the smart key device sends the runni...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com