Loudness of normalizing sound recording
A loudness, digital audio technology, applied in the field of audio playback, can solve the problem of different playback loudness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
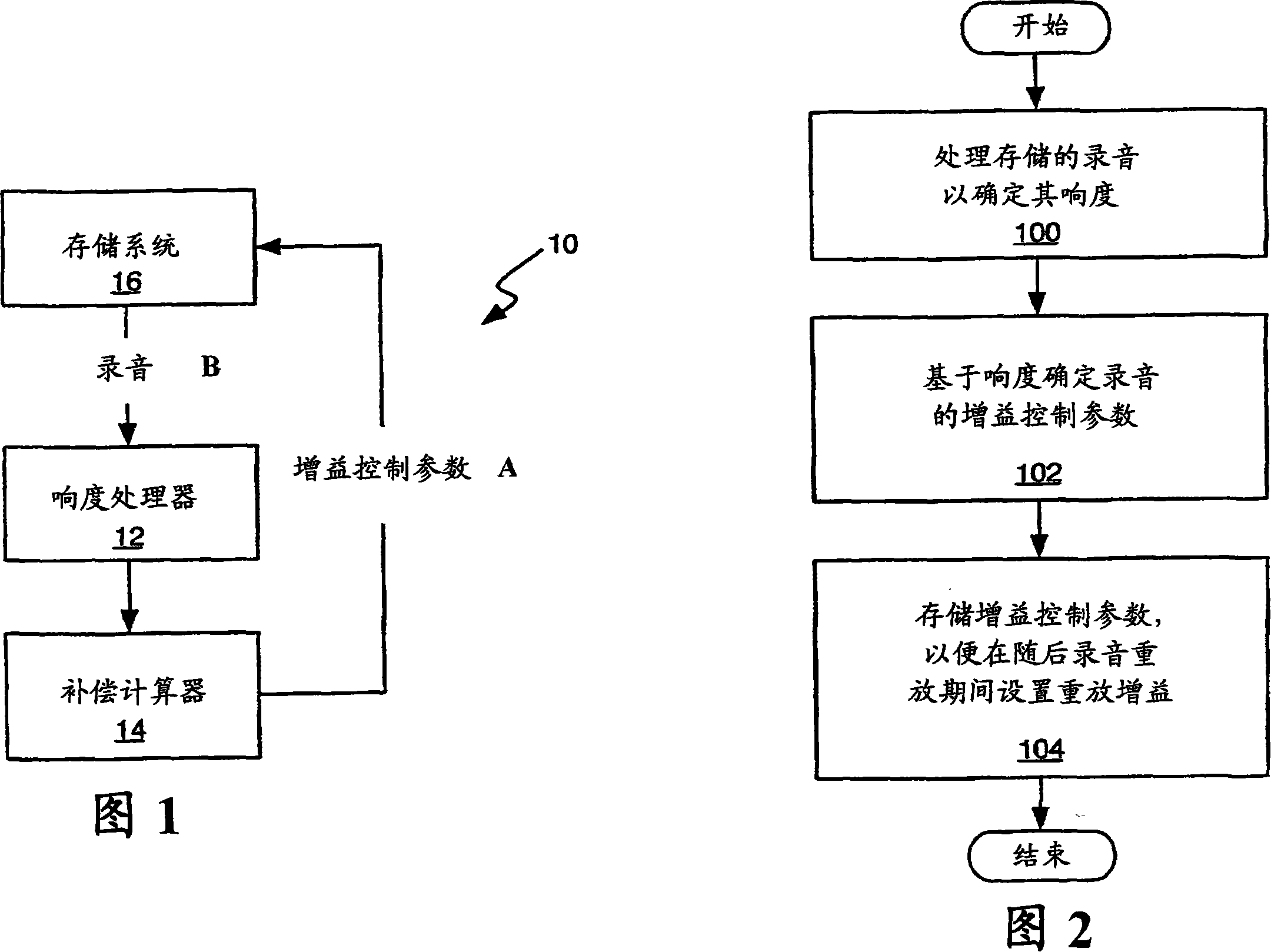
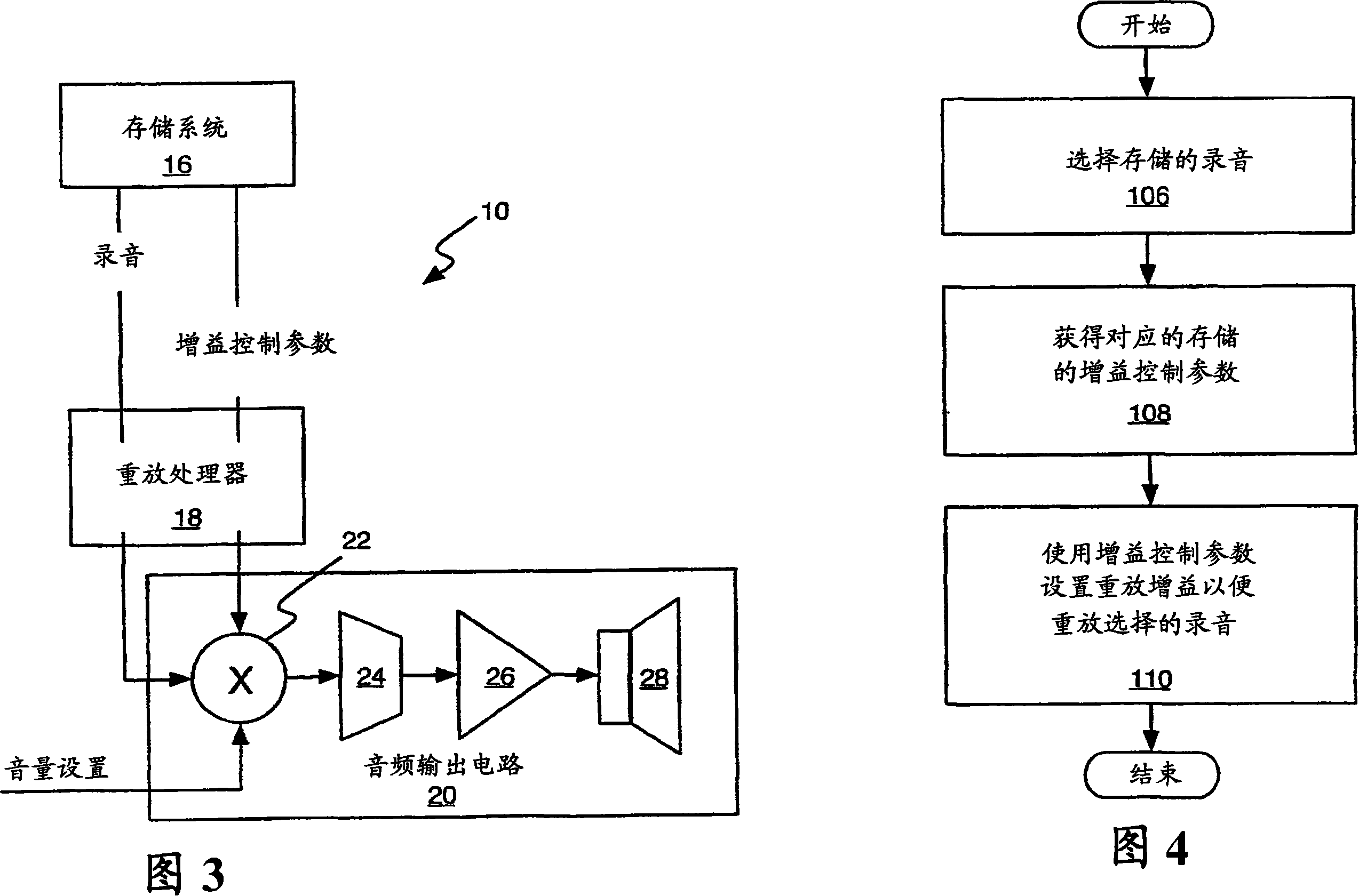
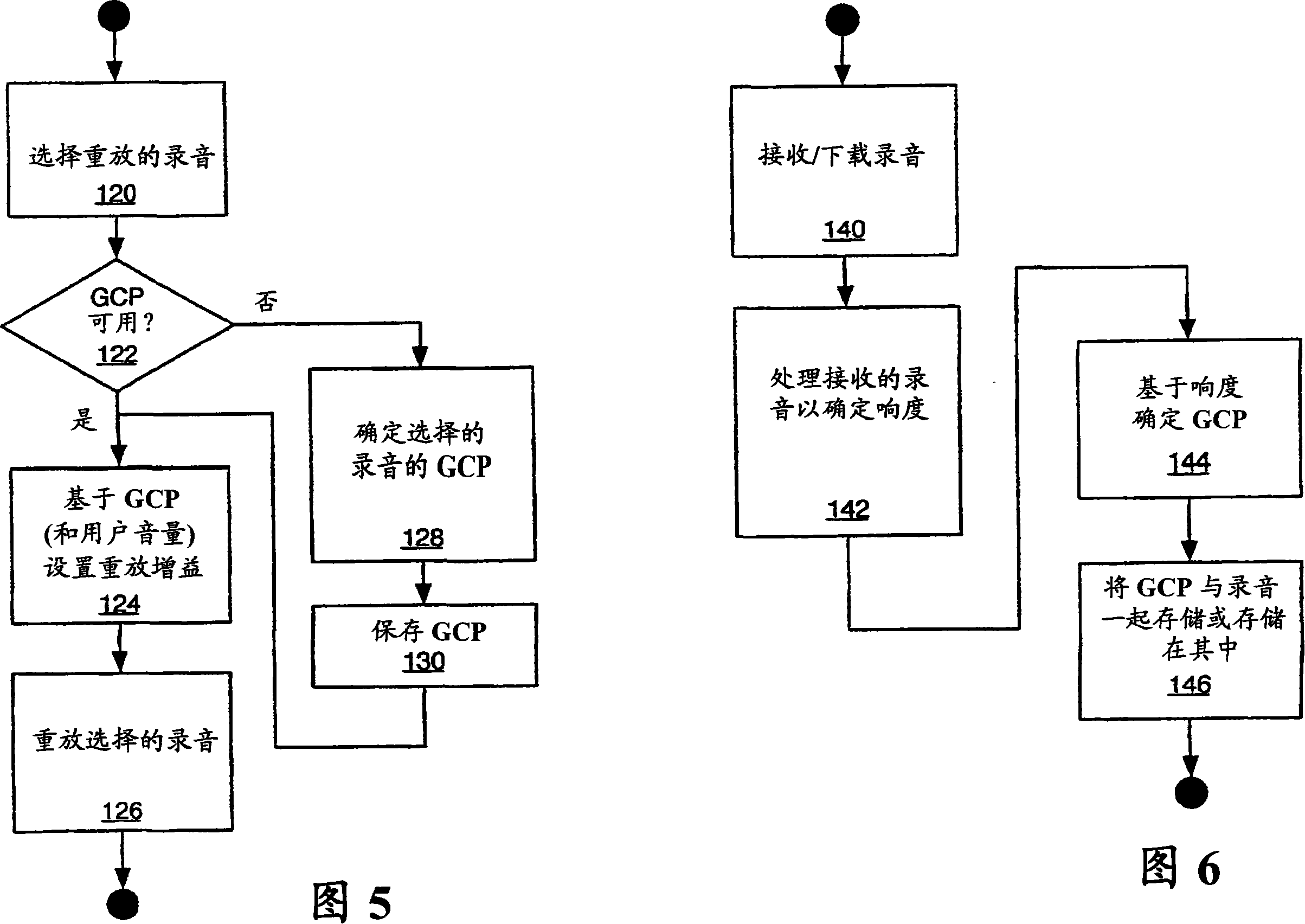
[0023] Before turning to the drawings, it may be helpful to organize the invention in terms of its underlying gain compensation process. The present invention provides a method and apparatus whereby one or more stored recordings are processed to determine their loudness. Based on the loudness of the recording, a gain compensation parameter is determined for each such processed recording and stored. When a given recording is selected for playback, the corresponding Gain Compensation parameter is used to fix the playback gain used to play the recording, which normalizes the playback loudness of the recording. That is, by compensating the playback gain for each recording according to the recording's corresponding gain compensation parameter, the playback loudness of two different recordings whose recordings are very different in loudness can become substantially the same.
[0024] With the above approach in mind, FIG. 1 functionally illustrates at least part of an audio processi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com