Timing calibration using radioactive sources
A radiation source and radioactive technology, applied in the field of digital imaging, to achieve the effect of less hardware
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
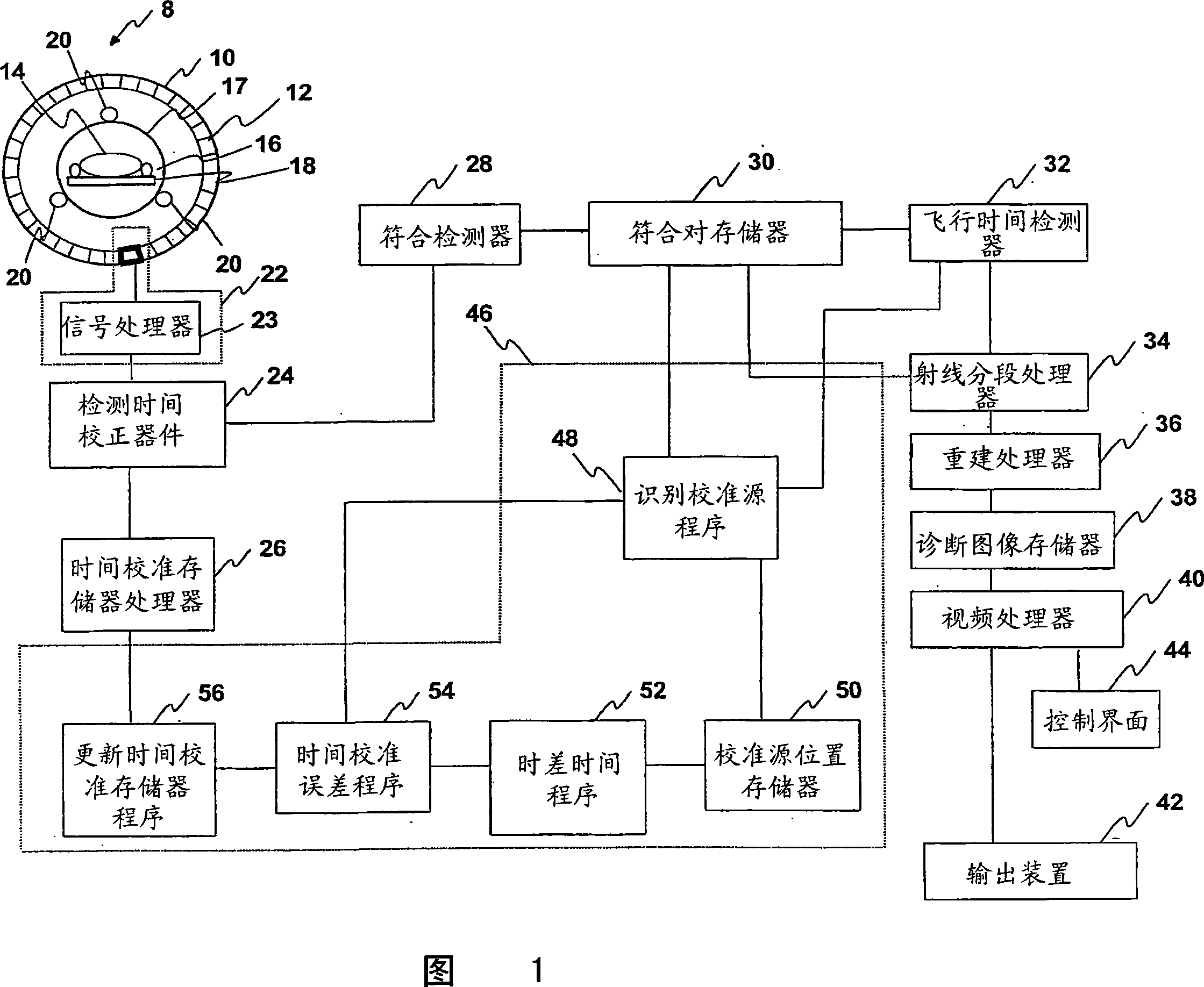
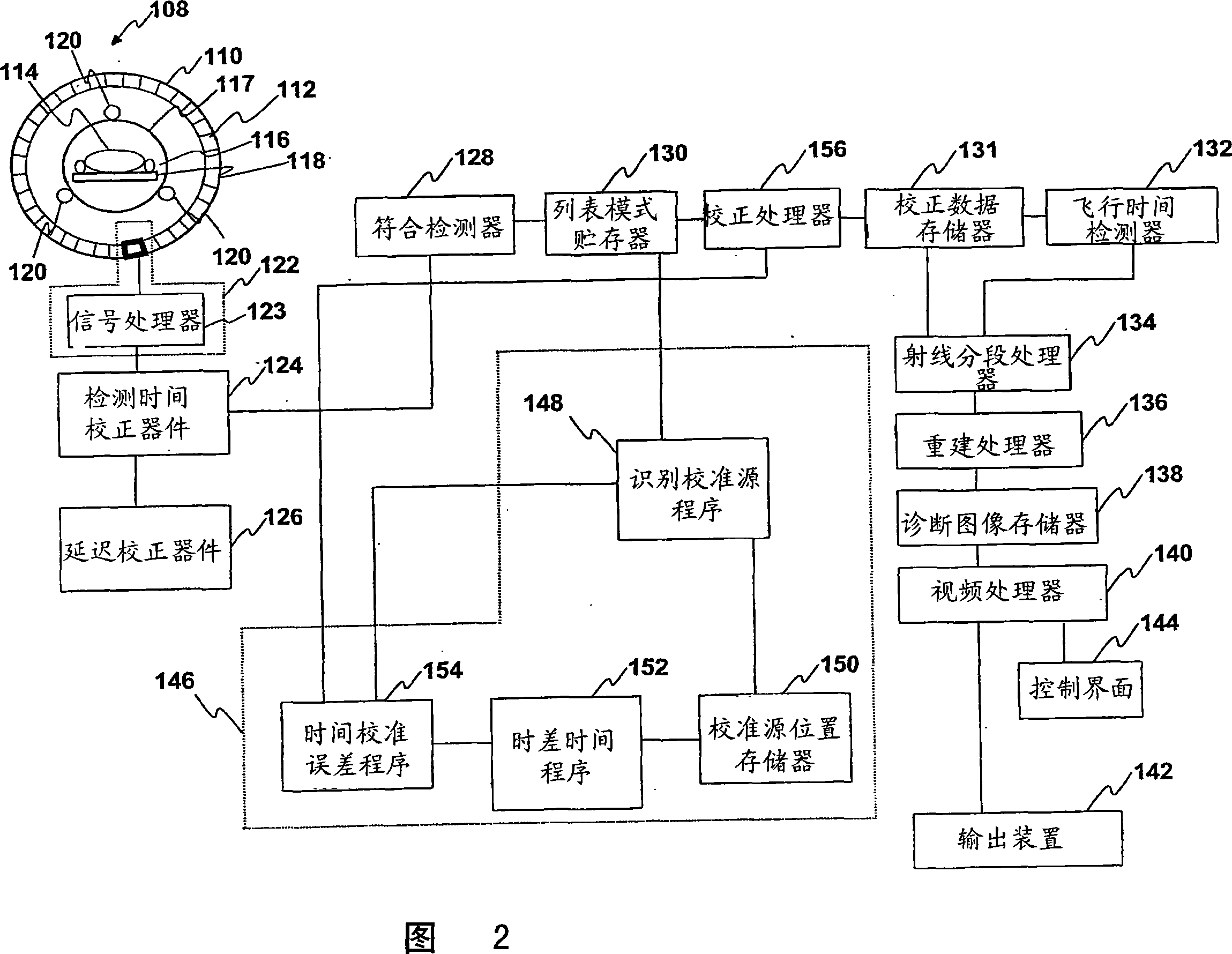
[0019] Referring to FIG. 1, the PET scanner 8 includes a cylinder 10 in which a radiation detector 12 is installed. Cylinder 10 typically has a diameter of 90 to 150 cm and a length of typically 30 to 90 cm. Preferably the radiation detector 12 is small enough to resolve the location of the received radiation within 1 to 5mm. A subject 14 to be examined is located in the central bore 16 . The aperture 16 is typically closed by a cosmetic radiotranslucent plastic cylinder 17 of about 60 to 90 cm. Subject 14 is generally received on a patient support 18 that is axially movable into and out of aperture 16 .
[0020] The subject 14 is injected with a radiopharmaceutical carrying a radioisotope which decays in a positron annihilation reaction. The radiopharmaceutical typically emits about 15 million gamma rays per second, which are detectable by detector 12 in cylinder 10 . A plurality of positron annihilation radiation sources 20 are located within the detector cylinder 10, bu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com