A mobile self-organized network path selection method based on bandwidth restraint and minimum load
A mobile ad hoc network and path selection technology, applied in the field of mobile networks, can solve problems such as weakened connectivity, shortened network lifetime, and difficulty in determining bandwidth resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
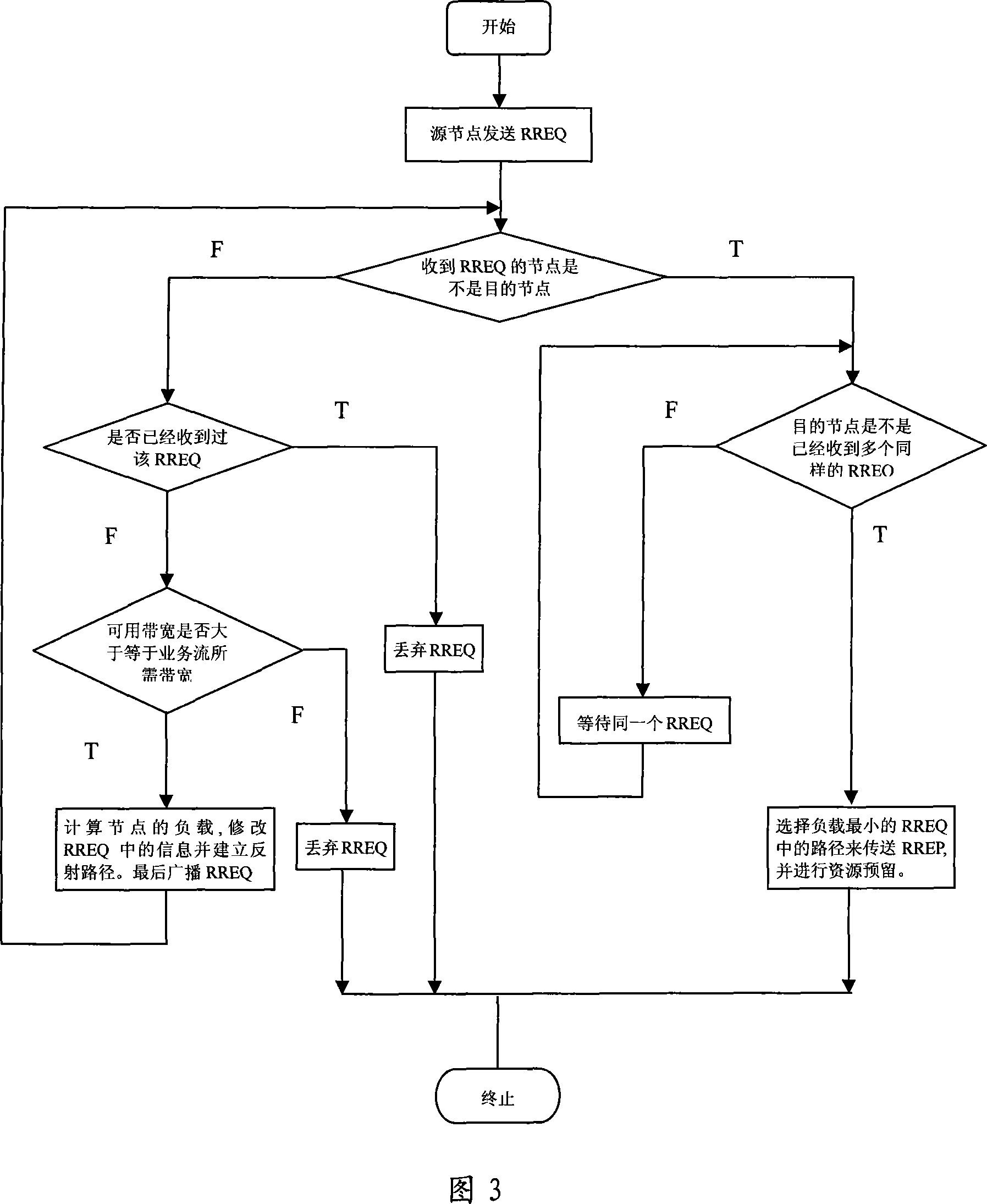
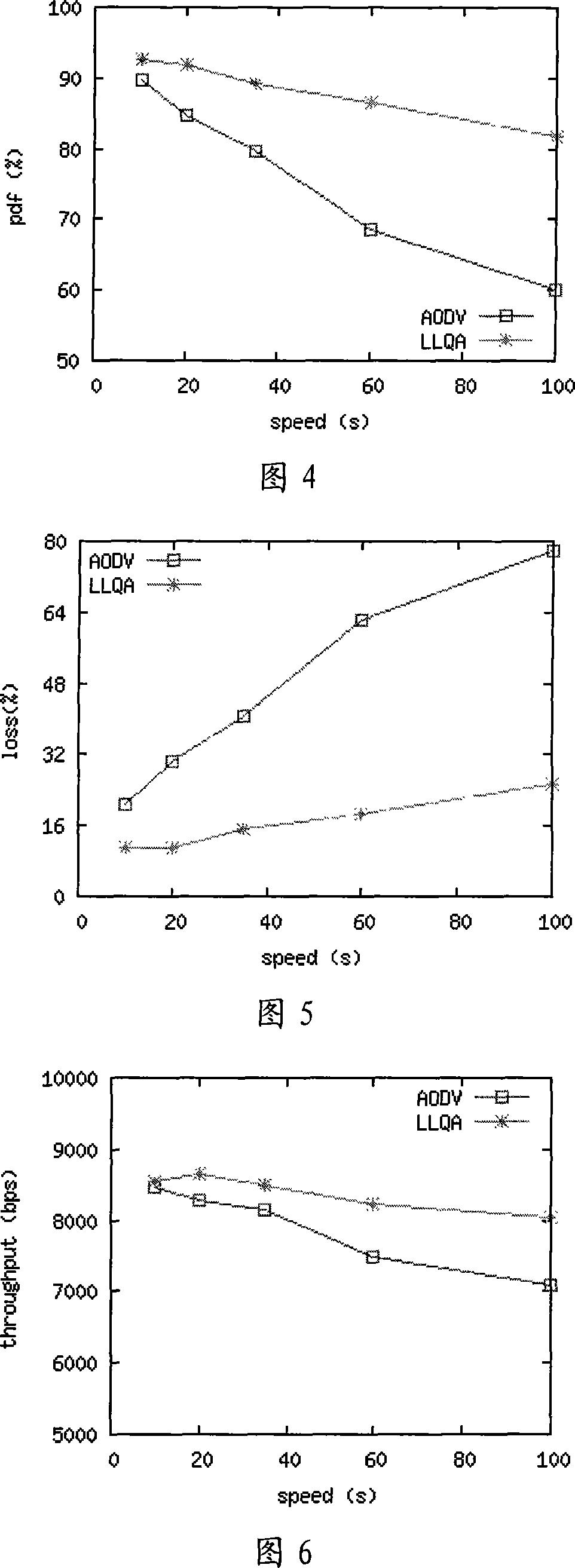
[0017] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
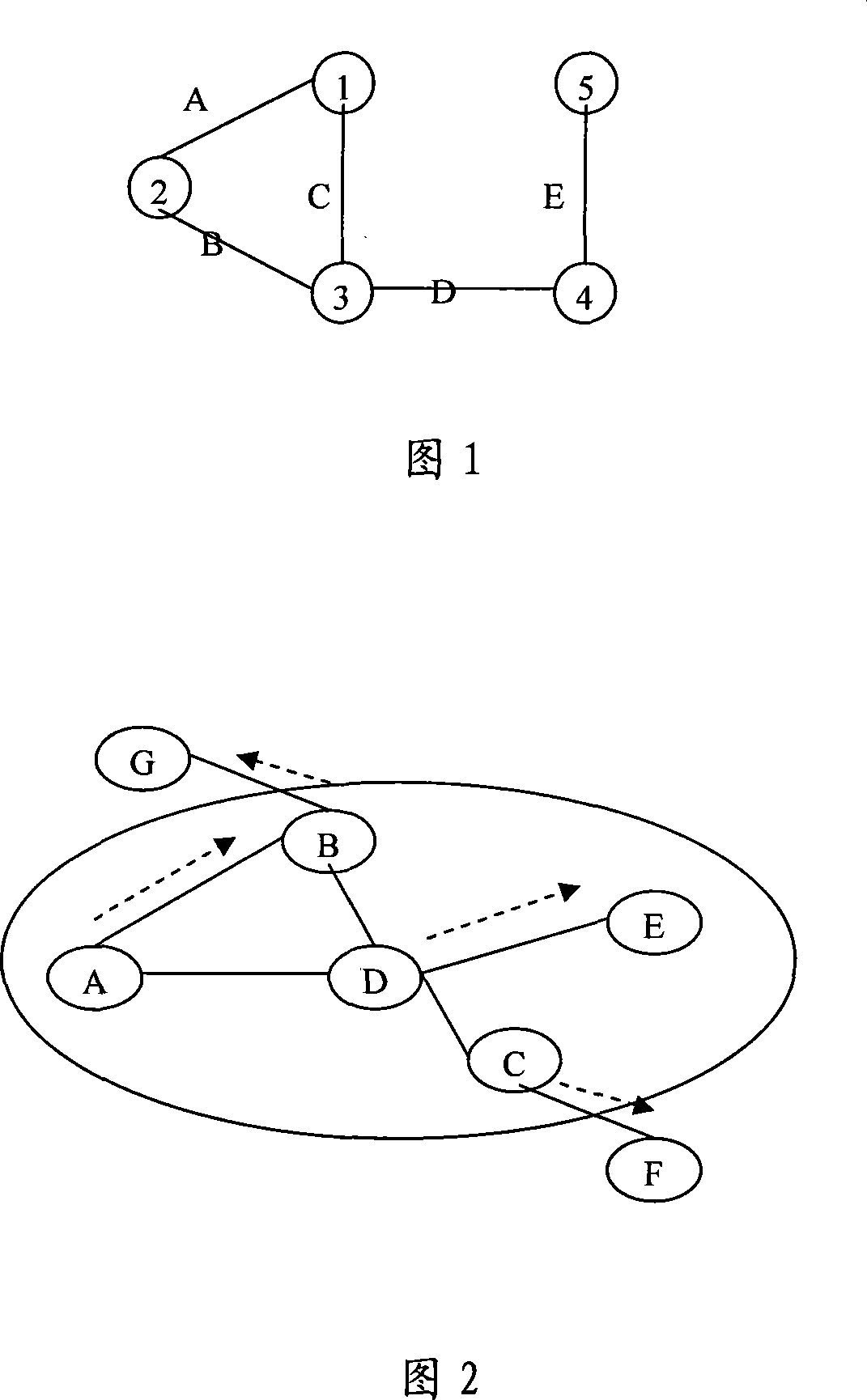
[0018] The shared transmission medium between nodes in the mobile ad hoc network is one of the remarkable characteristics of wireless networks. This characteristic causes the signals between adjacent nodes to interfere with each other, thus affecting the normal transmission of information. Through a simple example, it is indeed possible to improve the performance of the network by considering the bandwidth factor. Figure 1 is a connected graph of five nodes. The points in the graph represent the nodes in the network, and the edges in the graph represent the wireless links between nodes. Assume that the capacity of the channel is C. When node 1 and node 5 want to communicate, the traditional path selection method based on the shortest path will choose the path C-D-E. It can be seen from the figure that since link C receives interference from links A, B, D, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com