Preparation method for lithium ion secondary battery positive pole active substance lithium iron phosphate
A cathode active material, lithium iron phosphate technology, applied in the field of preparation of lithium iron phosphate cathode active material for lithium ion secondary batteries, can solve the problem that lithium iron phosphate cannot take into account high mass specific capacity and volume specific capacity, battery Can not take into account the problems of high capacity, high current discharge performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
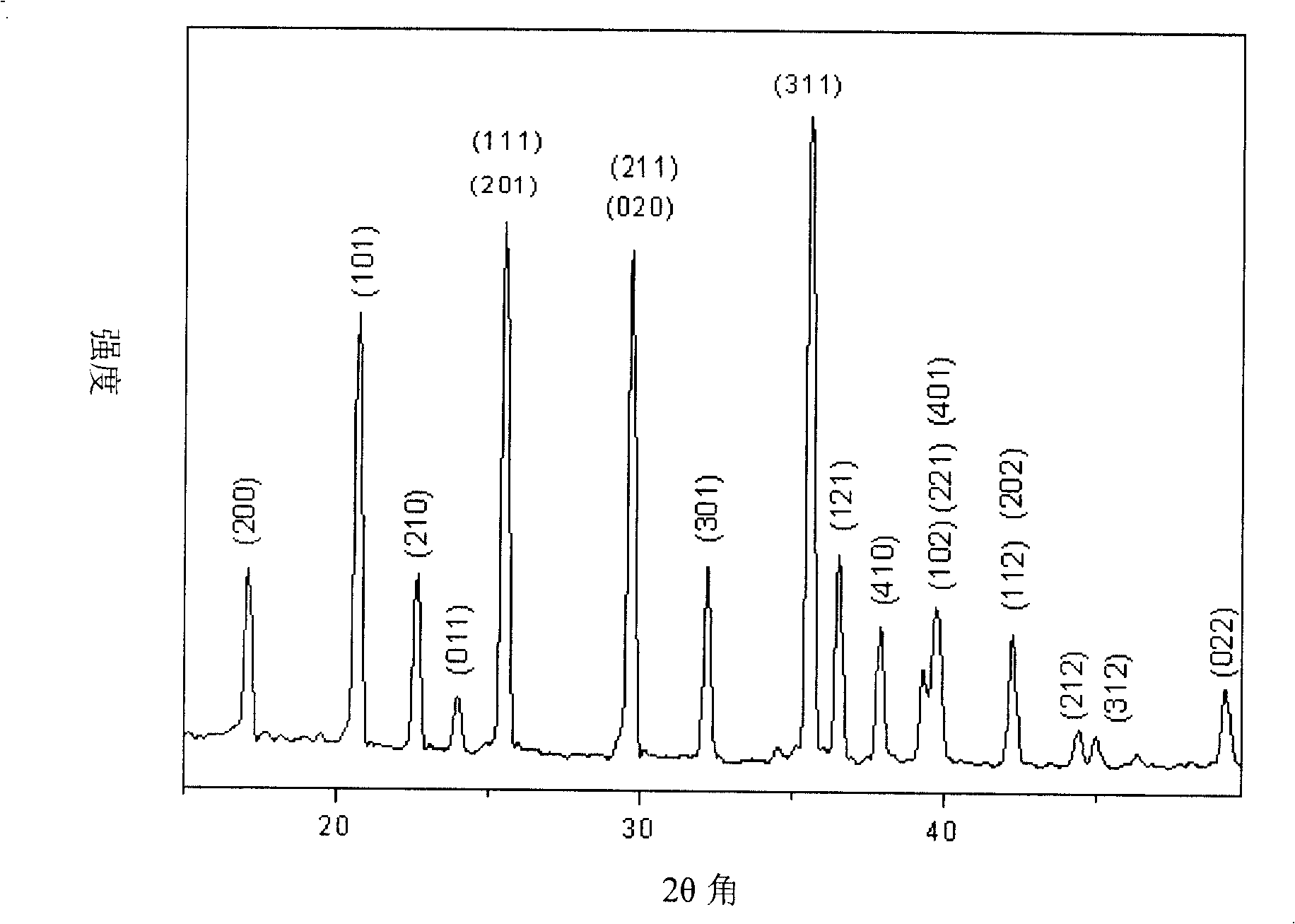
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] This embodiment illustrates the preparation of the positive electrode active material lithium iron phosphate provided by the invention
[0029] (1) 369.5 grams of Li 2 CO 3 , 798.5 g Fe 2 o 3 , 1150.2 g NH 4 h 2 PO 4 , 80 grams of graphite mixed with 2500 milliliters of absolute ethanol (Li: Fe: P molar ratio is 1: 1: 1), ball milled on a planetary ball mill for 0.5 hour, took out and dried;
[0030] (2) Under the protection of argon gas at 350° C. and a flow rate of 10 liters / min, the mixture in step (1) was sintered at a constant temperature for 6 hours, and naturally cooled to room temperature;
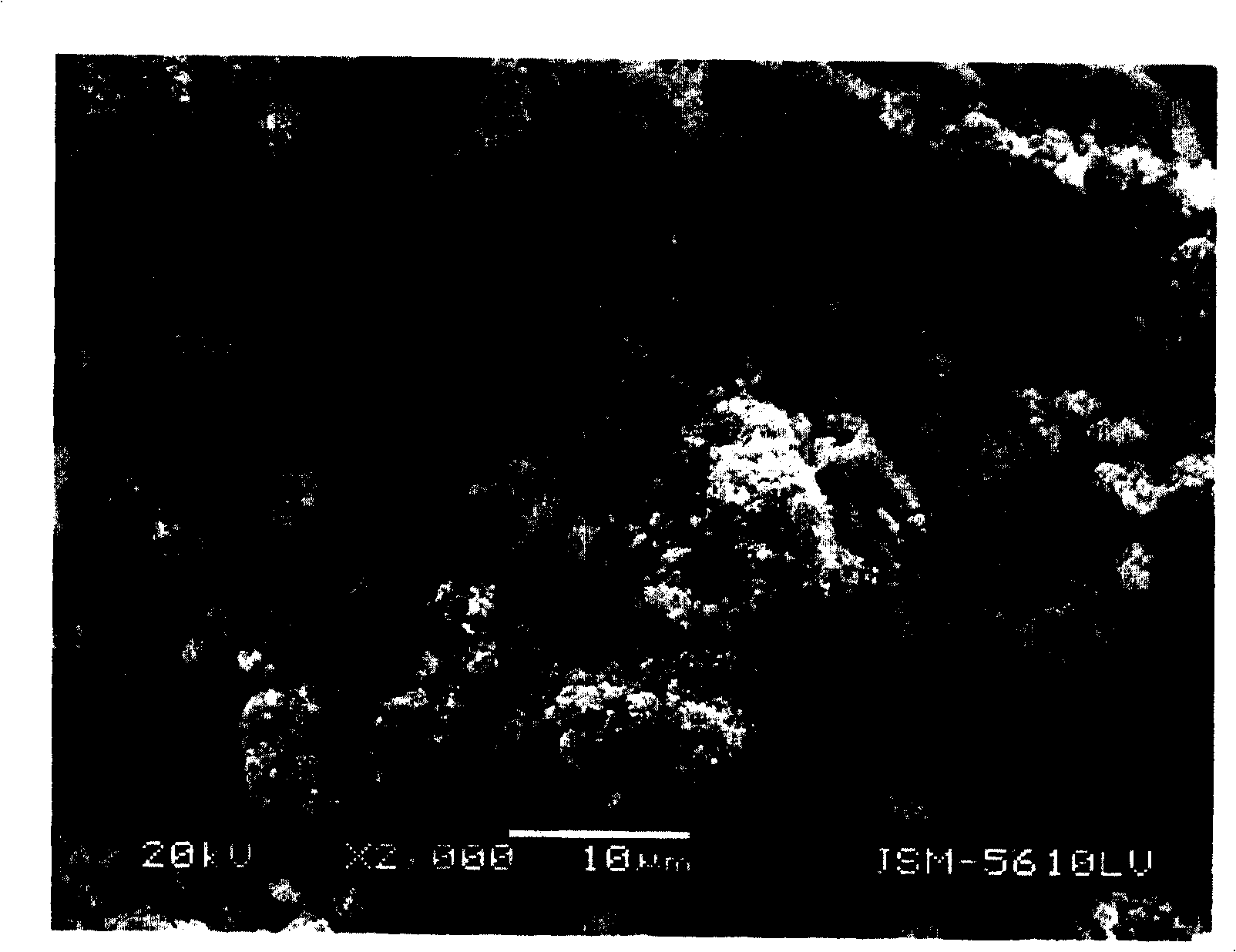
[0031] (3) The sintered product obtained in step (2) was continued to be high-energy ball milled on a planetary ball mill for 6 hours at a speed of 900 rpm, and the median particle diameter D of the obtained sintered product was 50 1.90 microns; D 95 7.74 microns; then, under the protection of argon at 650°C and a flow rate of 10 liters / min, the above-mentioned sinte...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment illustrates the preparation of the positive electrode active material lithium iron phosphate provided by the invention
[0034] (1) 369.5 grams of Li 2 CO 3 , 758.5 g Fe 2 o 3 , 20 grams of MgO, 1150.2 grams of NH 4 h 2 PO 4 , 228.6 grams of glucose mixed with 2500 milliliters of absolute ethanol (Li: Fe: Mg: P molar ratio is 1: 0.95: 0.05: 1), ball milled on a planetary ball mill for 0.5 hour, took out and dried;
[0035] (2) Under the protection of argon gas at 350° C. and a flow rate of 10 liters / min, the mixture in step (1) was sintered at a constant temperature for 6 hours, and naturally cooled to room temperature;
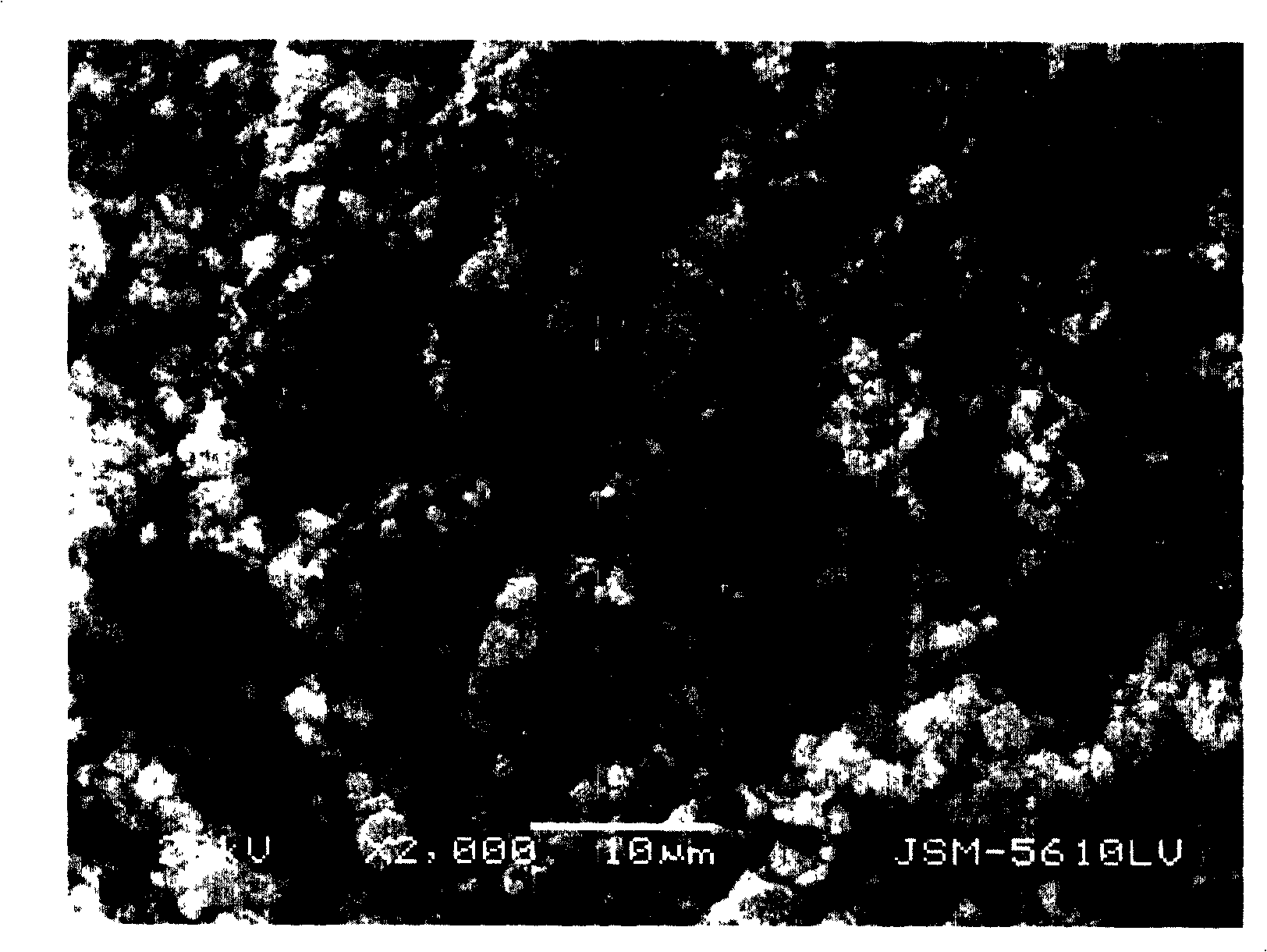
[0036] (3) The sintered product obtained in step (2) was continued to be high-energy ball milled on a planetary ball mill for 8 hours at a speed of 900 rpm, and the median particle diameter D of the obtained sintered product was 50 1.89 microns; D 95 7.56 microns; then, under the protection of argon at 650°C and a flow rate of...
Embodiment 3
[0038] This embodiment illustrates the preparation of the positive electrode active material lithium iron phosphate provided by the invention
[0039] (1) 419.6 g of LiOH·H 2 O, 798.5 g Fe 2 o 3 , 1150.2 g NH 4 h 2 PO 4 , 228.6 grams of glucose mixed with 3500 milliliters of absolute ethanol (Li: Fe: P molar ratio is 1: 1: 1), ball milled on a planetary ball mill for 0.5 hour, took out and dried;
[0040] (2) Under the protection of argon gas at 400°C and a flow rate of 8 liters / min, the mixture in step (1) was sintered at a constant temperature for 10 hours, and cooled naturally to room temperature;
[0041] (3) The median diameter D of the sintered product obtained by step (2) continued to be high-energy ball milled on a planetary ball mill for 10 hours at a speed of 1000 rpm 50 1.63 microns; D 95 6.52 microns; then, under the protection of argon at 700°C and a flow rate of 8 liters / min, the above-mentioned sintered product was sintered at a constant temperature for 1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com