Medical devices comprising a reticulated composite material
A technology of composite materials and medical devices, applied in medical science, thin material processing, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, and achieve the effect of easy realization and easy biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0117] According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the at least one reticulating agent is combined with, eg embedded in, a matrix material to form a composite material comprised in a medical device. The composite can be produced in the presence or absence of a suitable solvent or solvent mixture, wherein the matrix material can be combined with a selected reticulating agent or mixture thereof to form a porous reticulated composite.
[0118]The matrix material may comprise the form of polymers, oligomers, monomers or prepolymers, optionally of synthetic origin, and the polymers may be used in the same manner as mentioned above for reticulation agents or in references for encapsulation. The polymeric material of the reticulating agent is the same as the material which can be synthesized as prepolymerized, partially polymerized or polymerized or which is already present as such, in particular also a polymer composite. Polymer composites can already exist as nan...
Embodiment 1
[0230]A solution of soot, lamp black with a primary particle size of about 90 to 120 nm (Degussa, Germany) and a block copolymer in phenyl-1-methyl ethyl acetate, Byk-Chemie, Germany) was prepared and oxygen resin (Beckopox(R) EP 401, a homogeneous suspension of Cytec). First, a stock solution of methyl ethyl ketone (31 g), 3.1 g of Beckopox(R) EP 401 and 0.4 g of glycerol (Sigma Aldrich) (crosslinker) was prepared. Soot was prepared from 1.65 g of lamp black and 1.65 g of dispersing additive (Disperbyk 2150, 2-methoxy-1-methyl ethyl ketone mid-block copolymer solution, Byk-Chemie, Germany) by adding part of the mother liquor of methyl ethyl ketone / Beckopox(R) EP 401 paste. Subsequently, the paste was converted into a dispersion using a Pentraulik(R) dissolver for 15 minutes by adding the rest of the mother liquor to obtain a homogeneous suspension.
[0231] The suspension has a total solids content of about 3.5%, determined by means of a moisture measuring device (Sartorius...
Embodiment 2
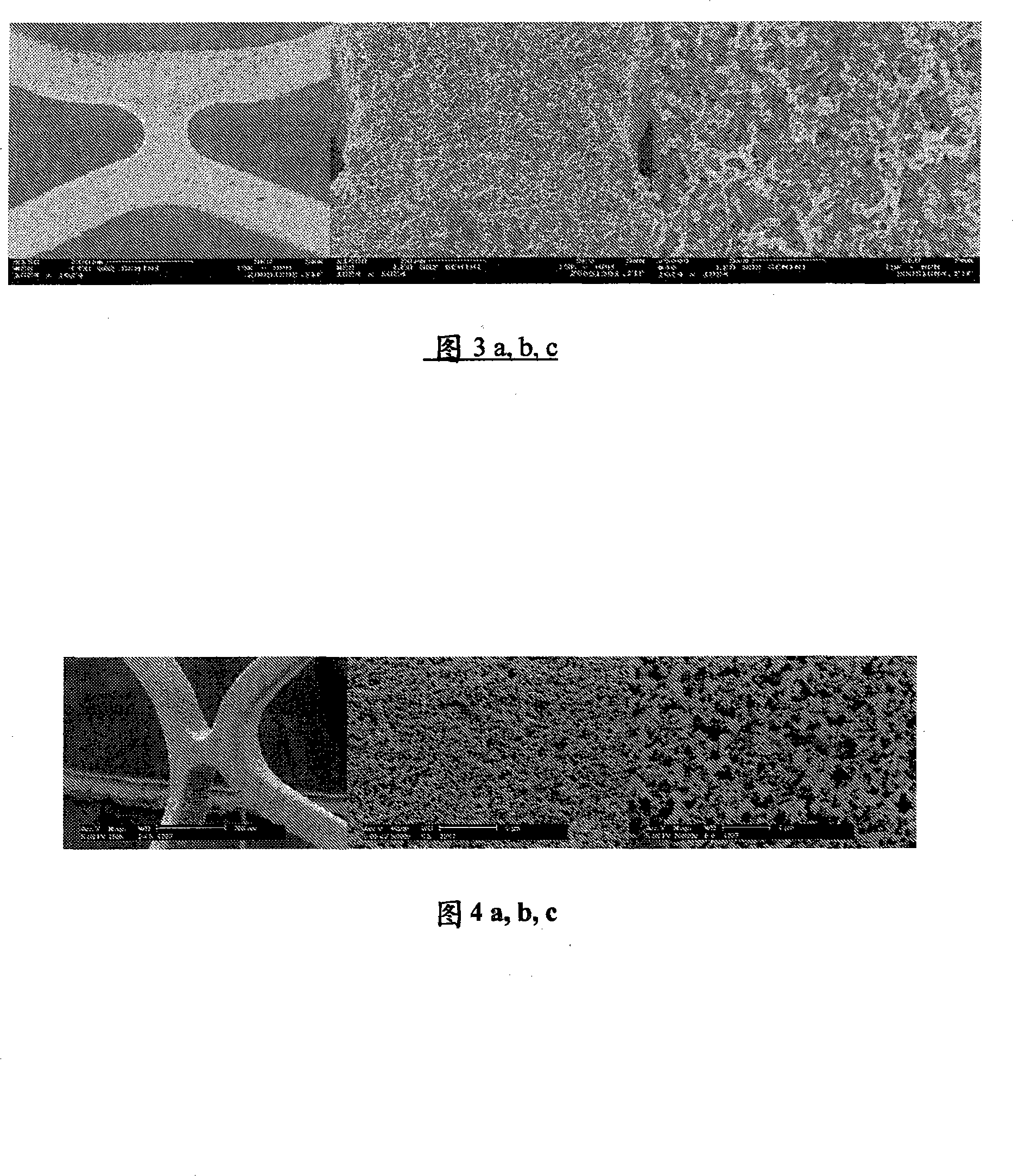
[0234] A homogeneous dispersion was prepared by using the same amounts of ingredients as described in Example 1. Instead of soot, however, 1.6 g of silica (Aerosil R972, Degussa, Germany) was used. The dispersion has a total solids content of about 3.2% and an average particle size distribution of D50 = 150 nm. The dispersion is 3.3g / m 2 The average specific surface weight of is sprayed onto the steel substrate and dried with hot air for 2 minutes. The heat treatment was the same as that described in Example 1.
[0235] The 2000 times magnified scanning electron micrograph in Fig. 2 shows the formed porous composite material with an average pore diameter of 150 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com