Method for implementing shared risk link circuit group separation crossing field path
A technology of shared risk link and group separation, applied in the field of realizing cross-domain path shared risk link group separation, which can solve the problem that SRLG does not have global uniqueness, and cannot realize cross-domain path shared risk link group separation, etc. , to avoid physical topology risks and improve survivability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1 of the present invention implements SRLG separation of cross-domain paths based on a PCS serial computing manner. The technical solution specifically includes the following steps.
[0047] S101. The network manager configures the SRLG association mapping table based on the network for the PCS corresponding to each domain in the network.
[0048] S102. The service source node initiates a cross-domain path calculation request for N (N is an integer greater than 1) SRLG separation from the source node to the destination node to the PCS of its domain (the first domain).
[0049] S103. After receiving the path calculation request, the PCS in the domain where the source node is located completes the path calculation in the domain, obtains the SRLG information used by the path at the same time, and then combines the calculated path segment information with the path calculation The request is also sent to the PCS of the next domain (the second domain), wherein the...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2 of the present invention implements SRLG separation of cross-domain paths based on a PCS parallel computing manner. The technical solution specifically includes the following steps.
[0062] S201. The network manager configures the SRLG association mapping table based on the network for the PCS corresponding to each domain in the network.
[0063] S202. The service source node initiates a cross-domain path calculation request for N (N is an integer greater than 1) SRLG separation from the source node to the destination node to the PCS of its domain (the first domain).
[0064] S203. After receiving the path calculation request, the PCS in the domain where the service source node is located calculates M1 (M1 and N are integers greater than 1, and M1 is not less than N) SRLG separated path sections in the domain, and obtains the path at the same time The SRLG information used by the section, and then send the calculated path section information together with...
Embodiment 3
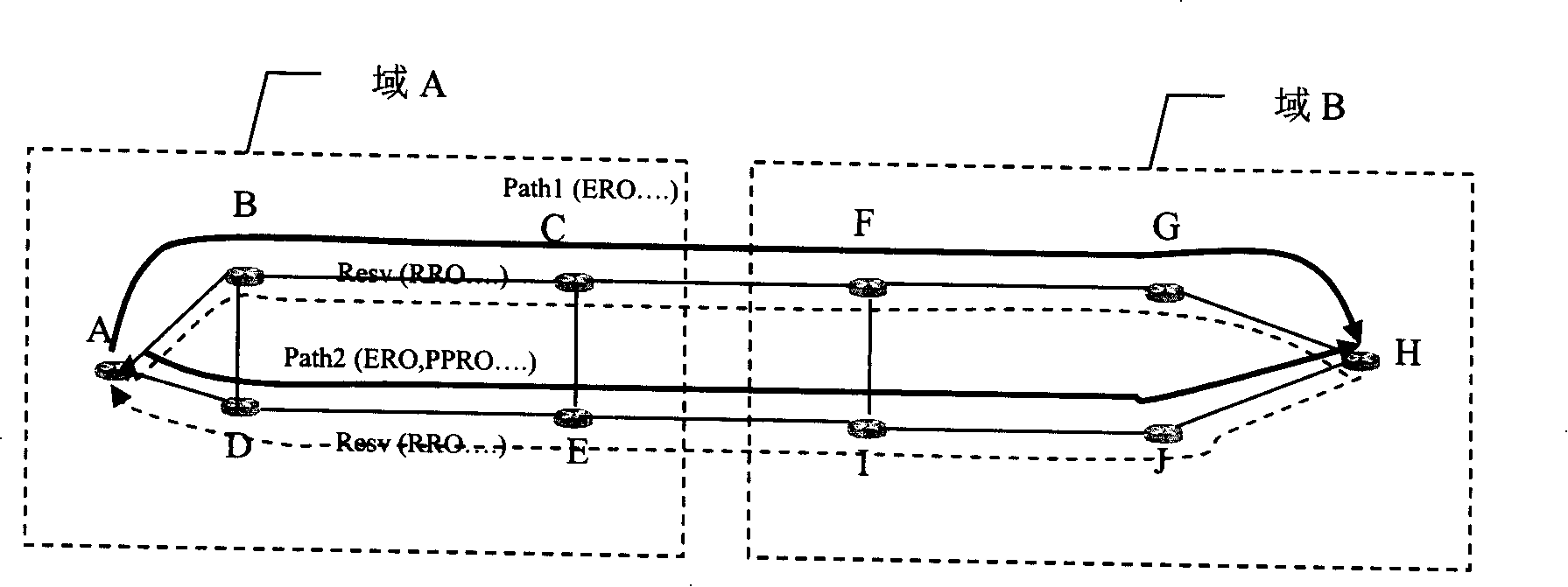
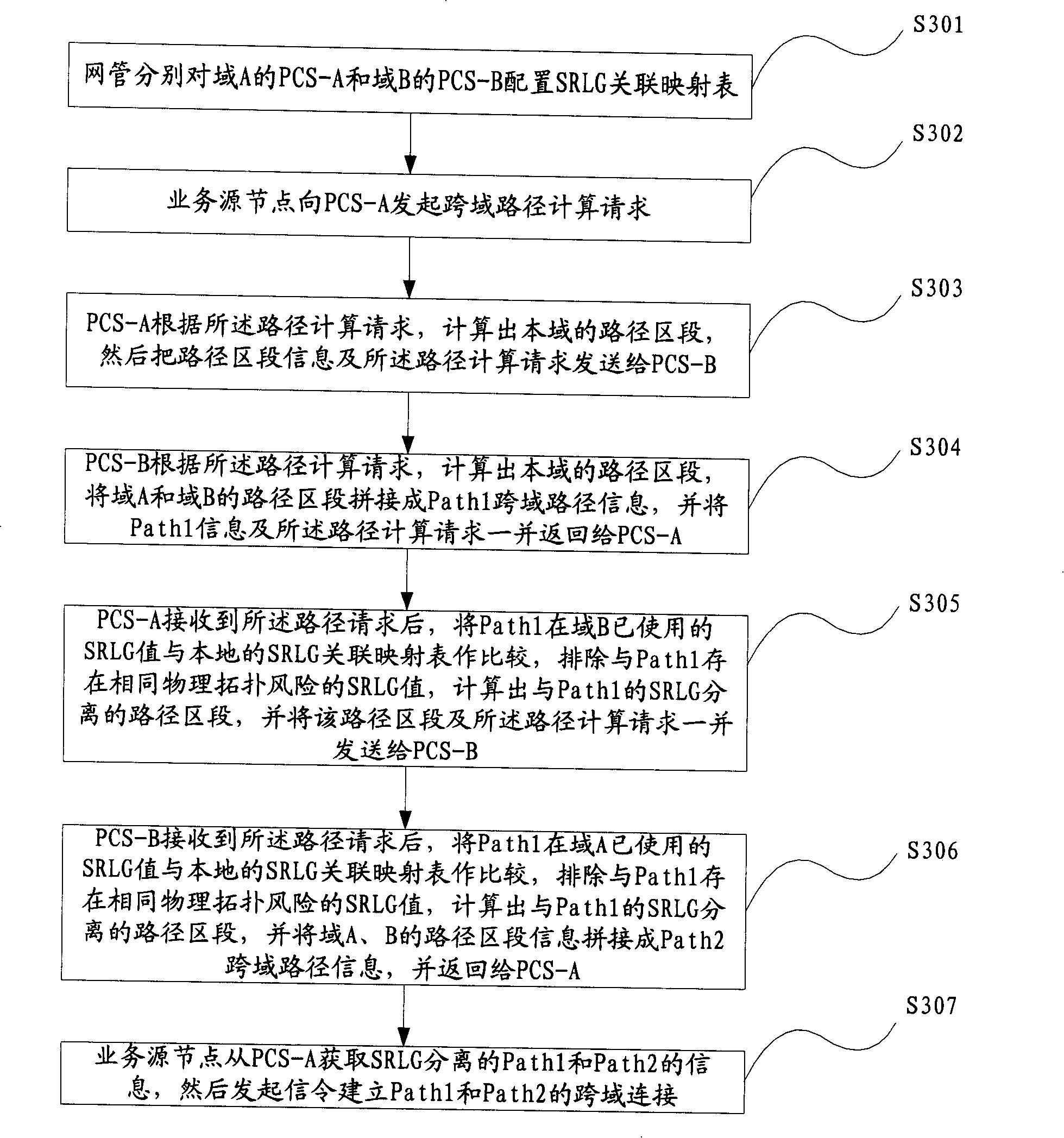
[0078] Such as image 3 as shown, image 3 It is a flow chart of implementing SRLG separation of cross-domain paths based on PCS serial computing in an embodiment of the present invention. The technical solution of Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be further elaborated below.
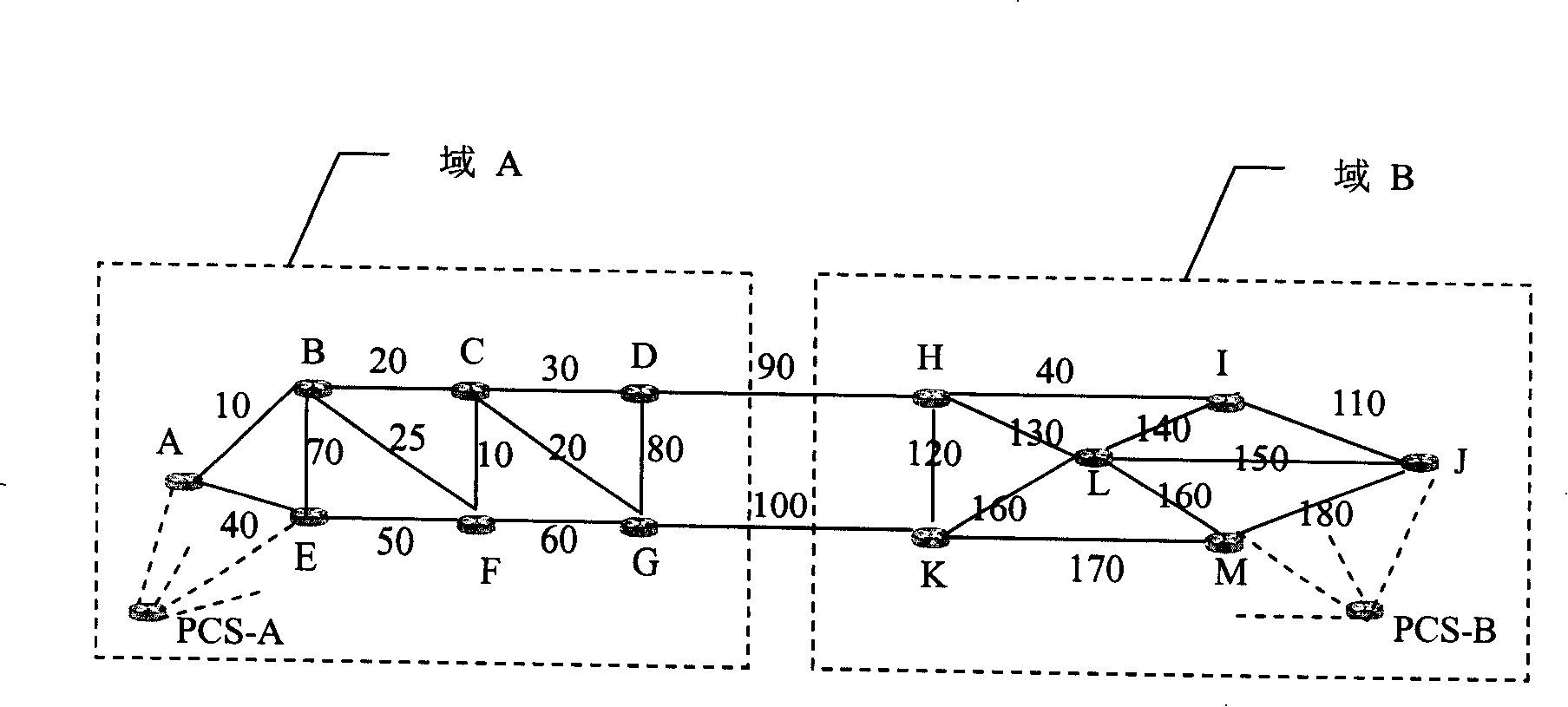
[0079] S301. The network management configures the SRLG association mapping table for the PCS-A of domain A and the PCS-B of domain B respectively, wherein the information of the SRLG association mapping table stored in PCS-A and PCS-B is as follows:
[0080] Table 2 is the SRLG association mapping table configured by the network management for PCS-A
[0081] associated domain
The SRLG value of the associated domain
Associated domain
The SRLG value of the associated domain
A
30
B
170
A
70
B
40
A
60
B
190
[0082] Table 3 is the SRLG association mapping table configured by the network...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com