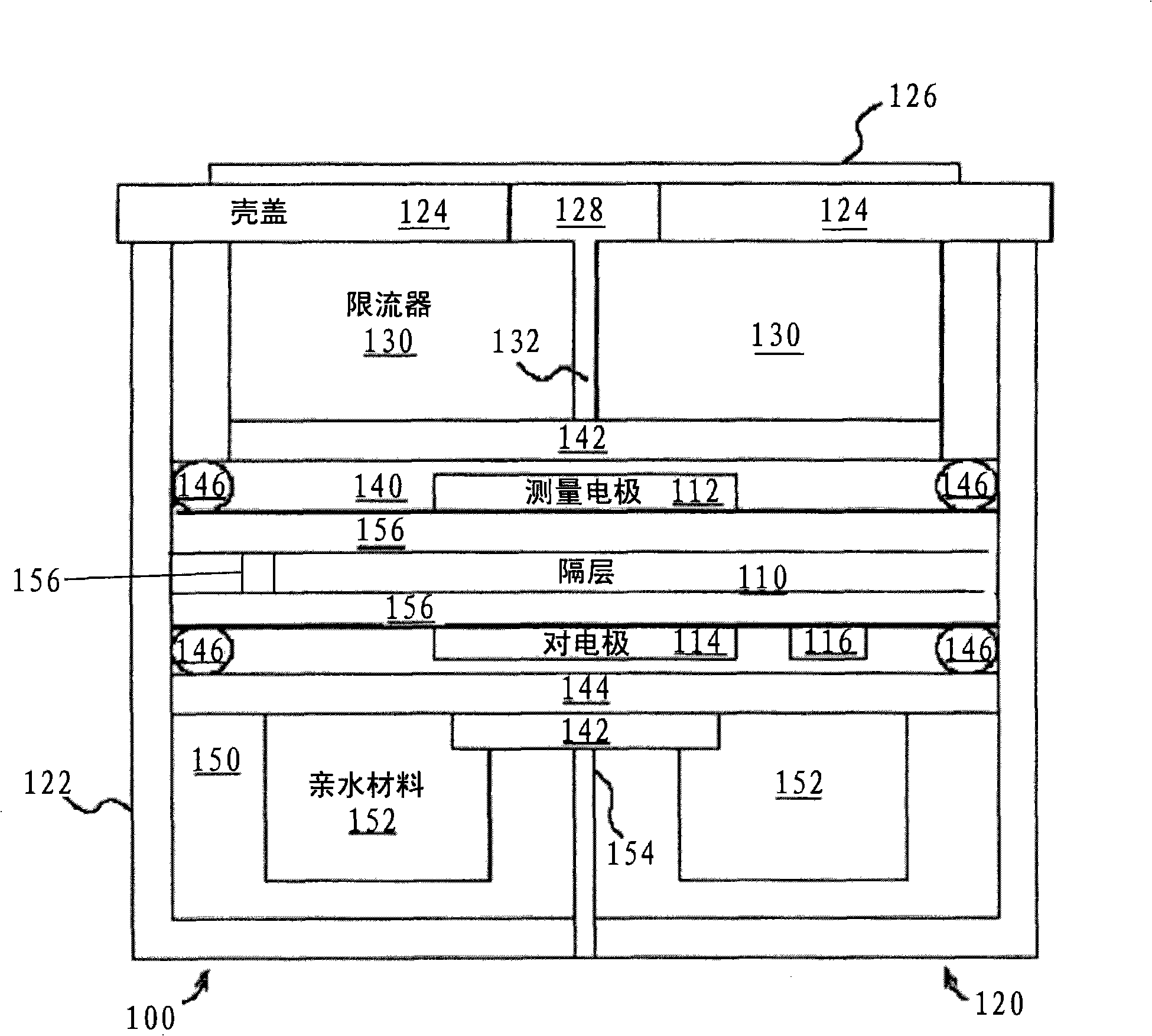
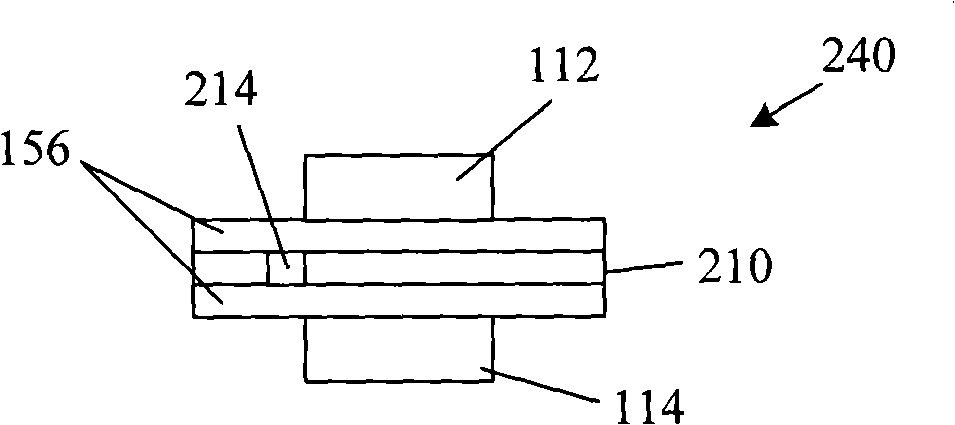
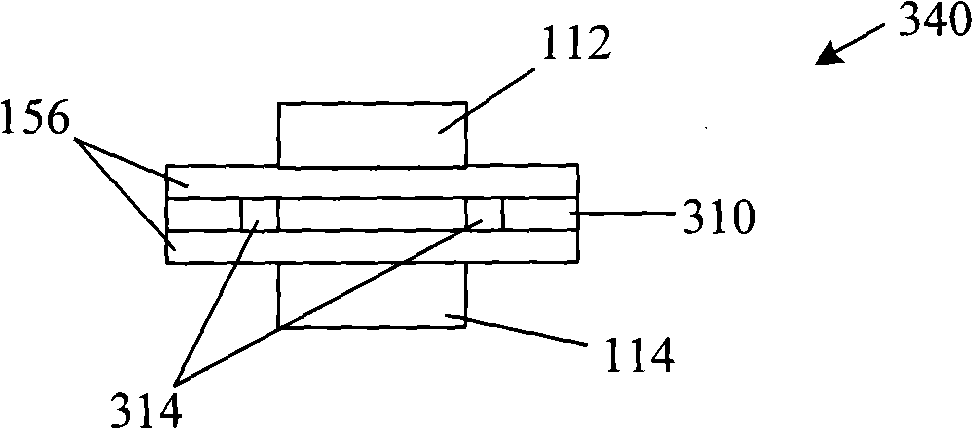
Gas sensor
An oxygen sensor and oxygen technology, applied in the direction of instruments, scientific instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problem of large sensor size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0106] Example 1: For a 4R sensor, its cross section is 8×10 -5 m 2 , when the liquid electrolyte, that is, the pore cross-sectional area of the interlayer occupies 50% of the cross-sectional area of the sensor, A 液相 =4×10 -5 m 2 , using formula (17)A 液相 / l 隔层 入口 / l 入口 )6.5×10 3 Calculated
[0107] 4×10 -5 / l 隔层 -6 ×6.5×10 3
[0108] as long as l 隔层 >7.7×10 -4 m, that is, the thickness of the liquid electrolyte is greater than 0.77 mm, and the oxygen diffused to the measuring electrode through the liquid layer can be neglected.
example 2
[0109] Example 2: For a 4R sensor, its cross section is 8×10 -5 m 2 , when the liquid electrolyte, that is, the pore cross-sectional area of the interlayer accounts for 1% of the cross-section of the sensor, it can be calculated using formula (17)
[0110] 0.01×8×10 -5 / l 隔层 -6 ×6.5×10 3
[0111] as long as l 隔层 >1.5×10 -5 m, that is, the thickness of the liquid electrolyte is greater than 15 microns, and the oxygen diffusion through the liquid layer to the measuring electrode can be neglected.
[0112] (b) Regarding the second term A in formula (16) 泄漏 / l 隔层
[0113] In addition, it is also necessary to consider that the oxygen from the counter electrode side penetrates the liquid layer in the form of bubbles and reaches the measurement electrode. Generally speaking, if the resistance of the liquid layer to the gas is greater than the gas pressure on the side of the counter electrode, the gas will not penetrate the liquid layer to reach the measuring electrode, an...
example 1
[0125] Example 1: In an extreme case, if the cross-sectional area of the hole, that is, the exposed area of the liquid layer accounts for 50% of the cross-sectional area of the sensor, that is, the diameter of the hole is 7 mm, and the thickness of the liquid layer is 0.77 mm, then
[0126] l 出气孔 / d 出气孔 4 8
[0127] Assuming that the length of the vent hole is 1 mm, the diameter of the vent hole needs to be greater than 1.5 mm.
[0128] Example 2: In another extreme case, if the cross-sectional area of the hole, that is, the exposed area of the liquid layer accounts for 1% of the cross-sectional area of the sensor, that is, when the diameter of the hole on the interlayer is 1 mm and the thickness of the liquid layer is 15 microns,
[0129] l 出气孔 / d 出气孔 4 10
[0130] At this time, when the length of the air outlet is 1 mm, the diameter of the air outlet needs to be greater than 0.56 mm.
[0131] It can be seen that when using a liquid electrolyte as an elect...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com