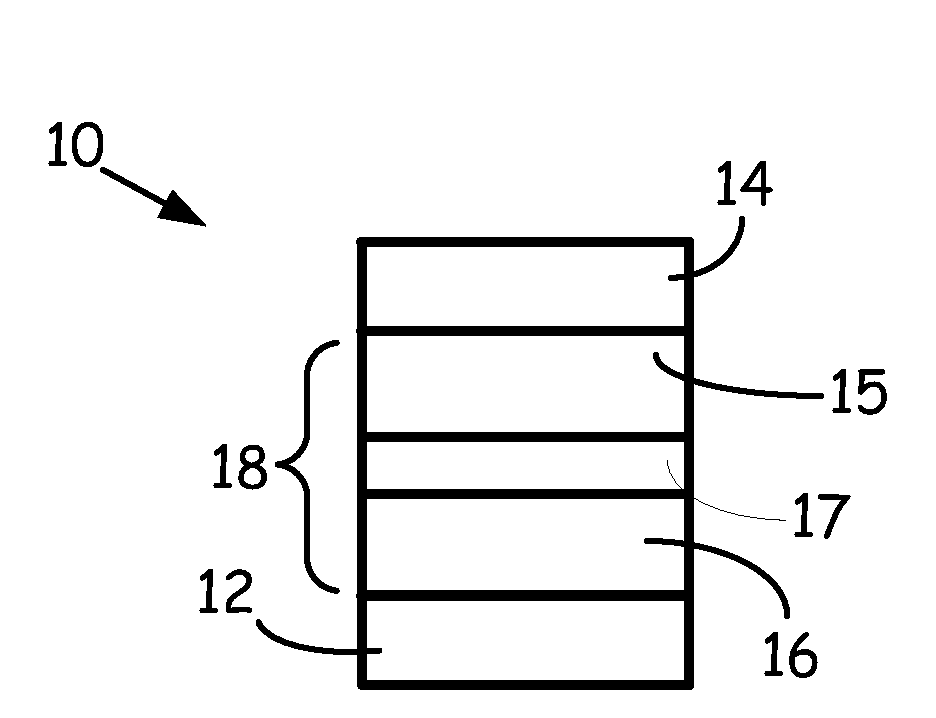
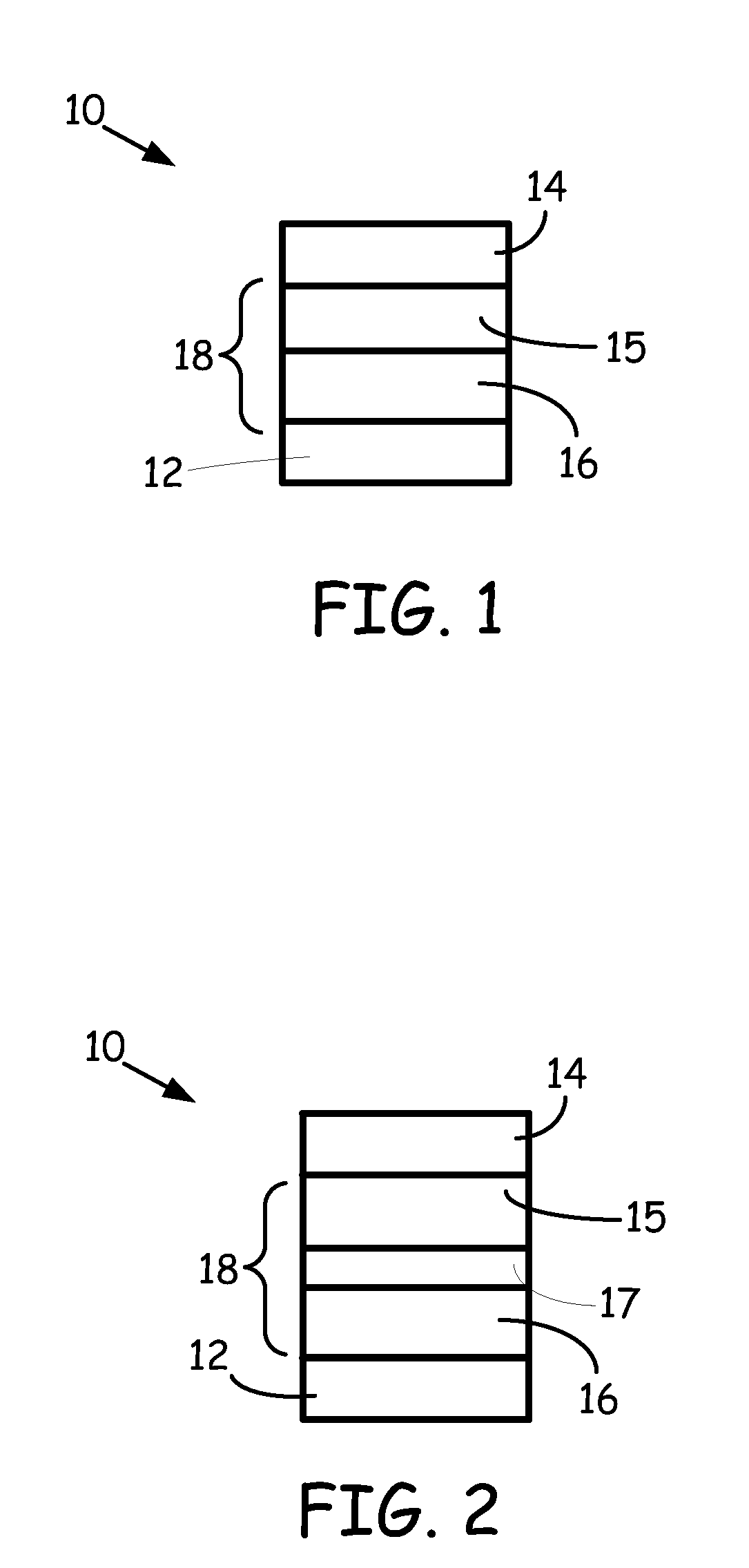
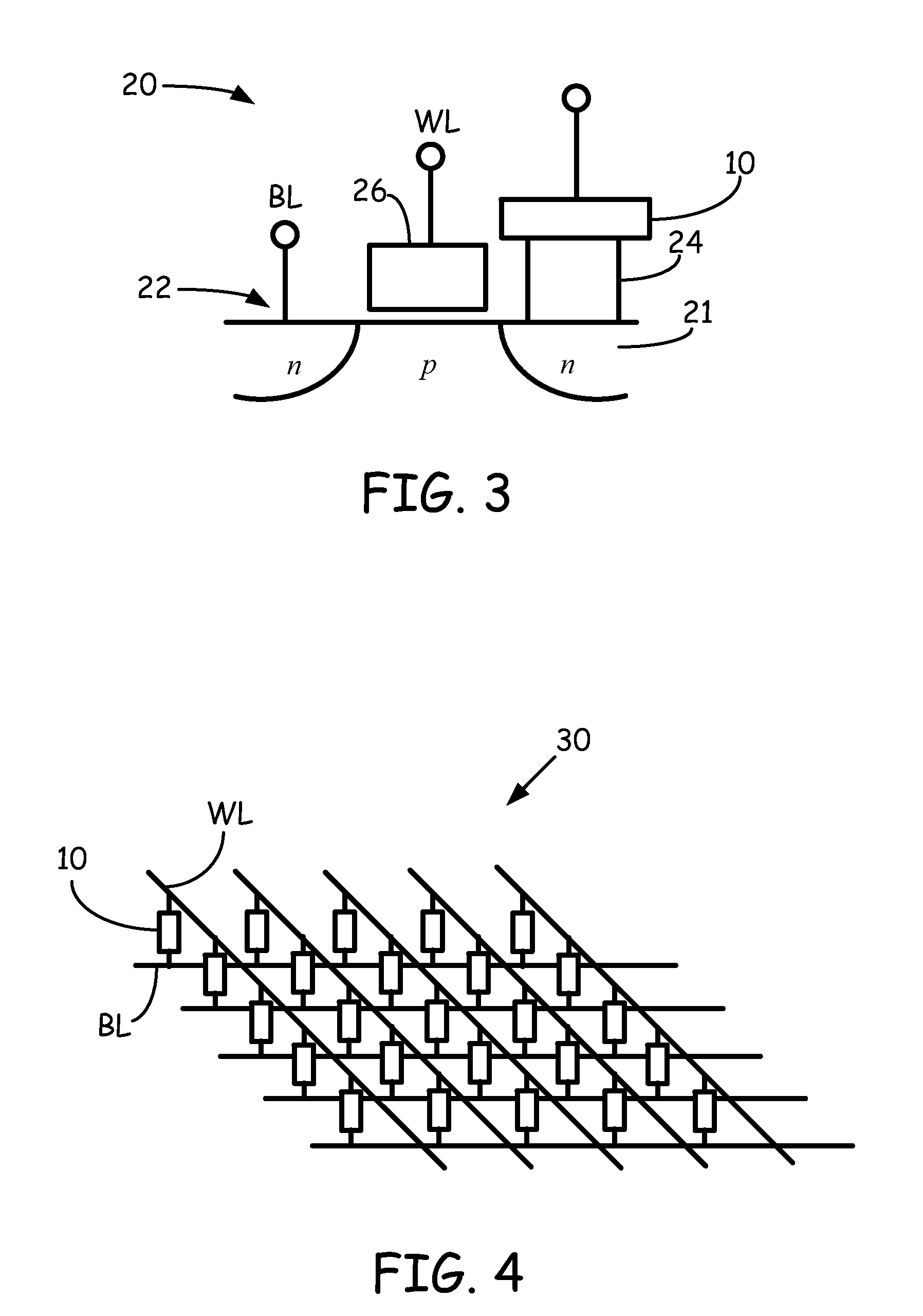
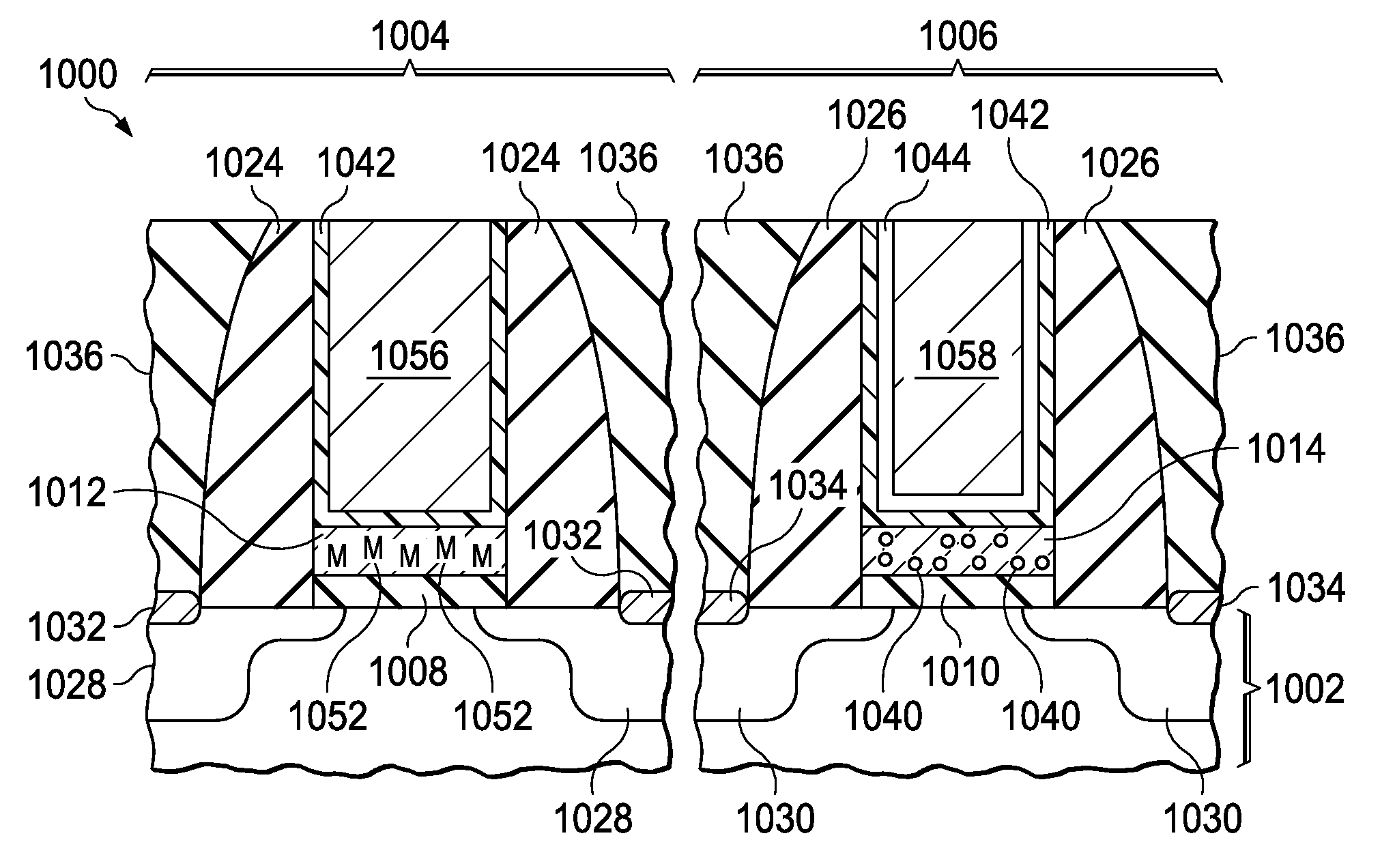
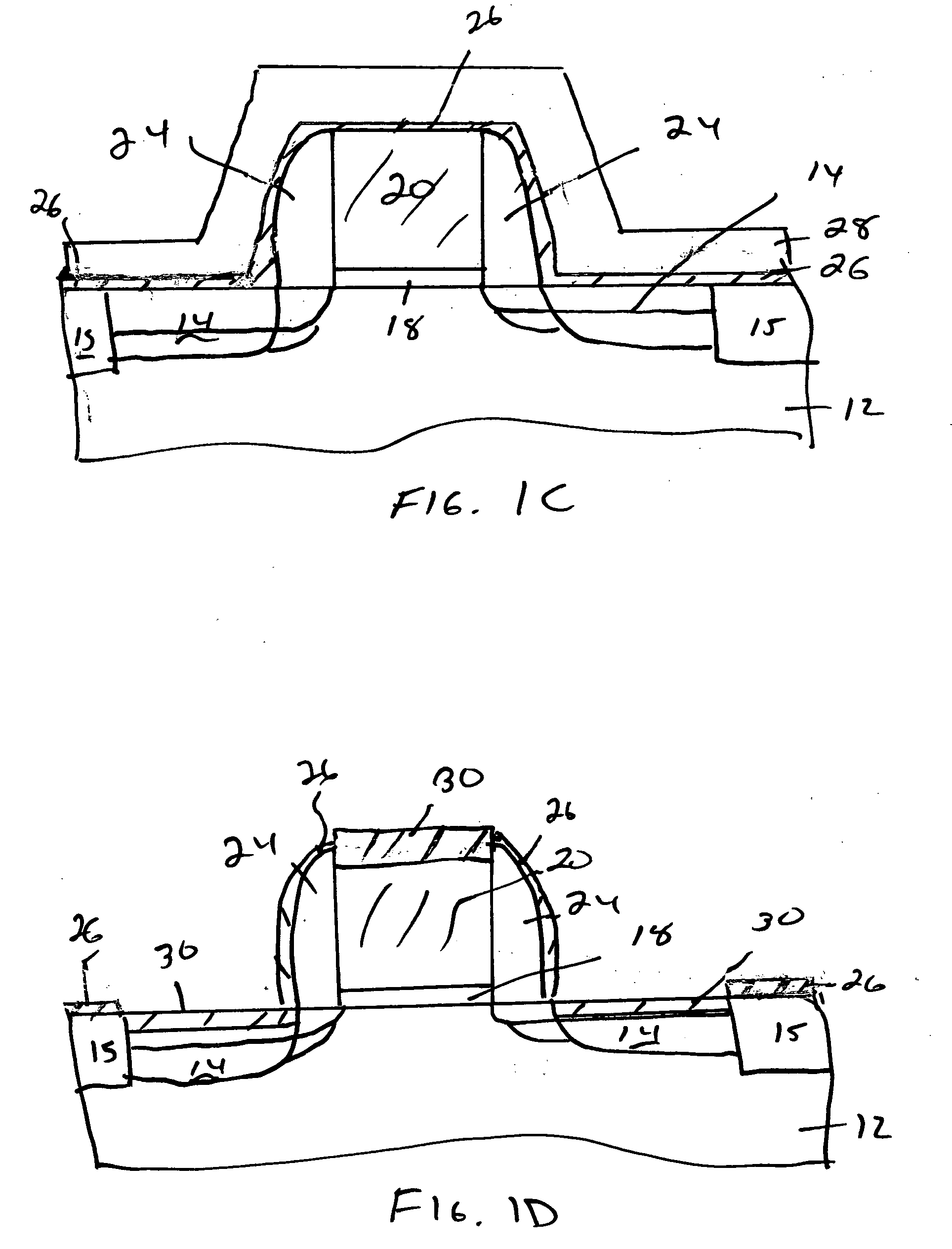
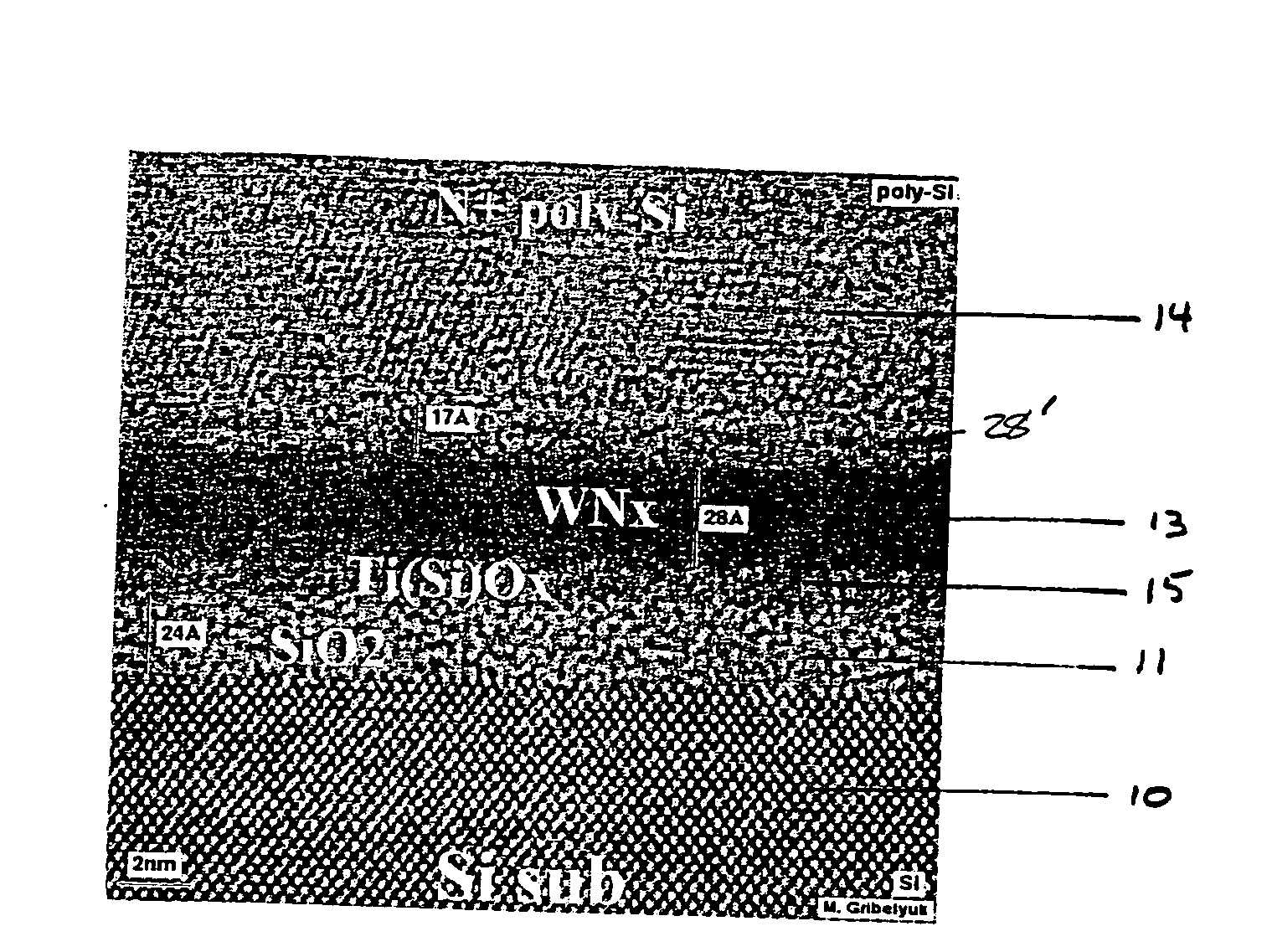
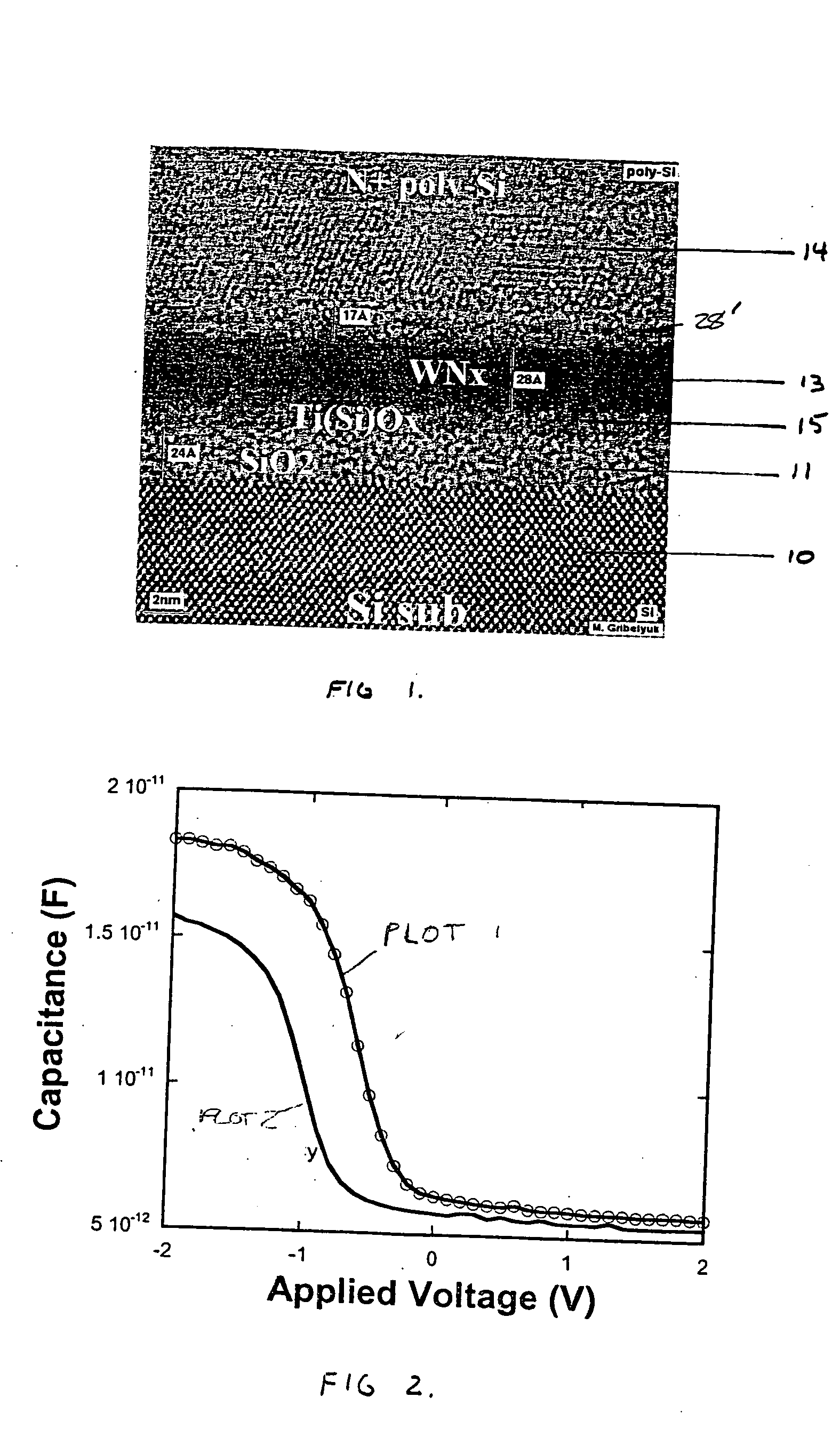
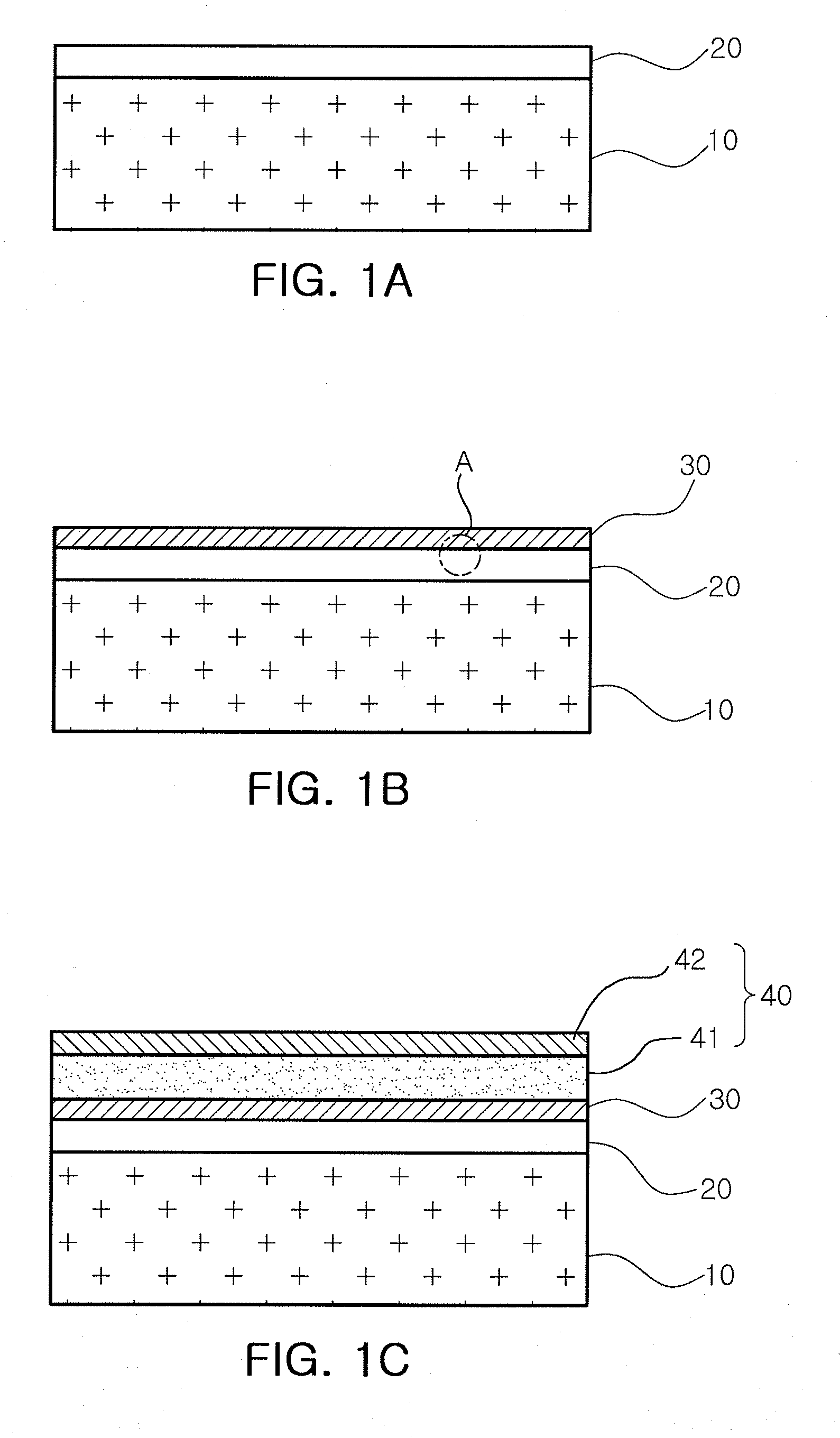
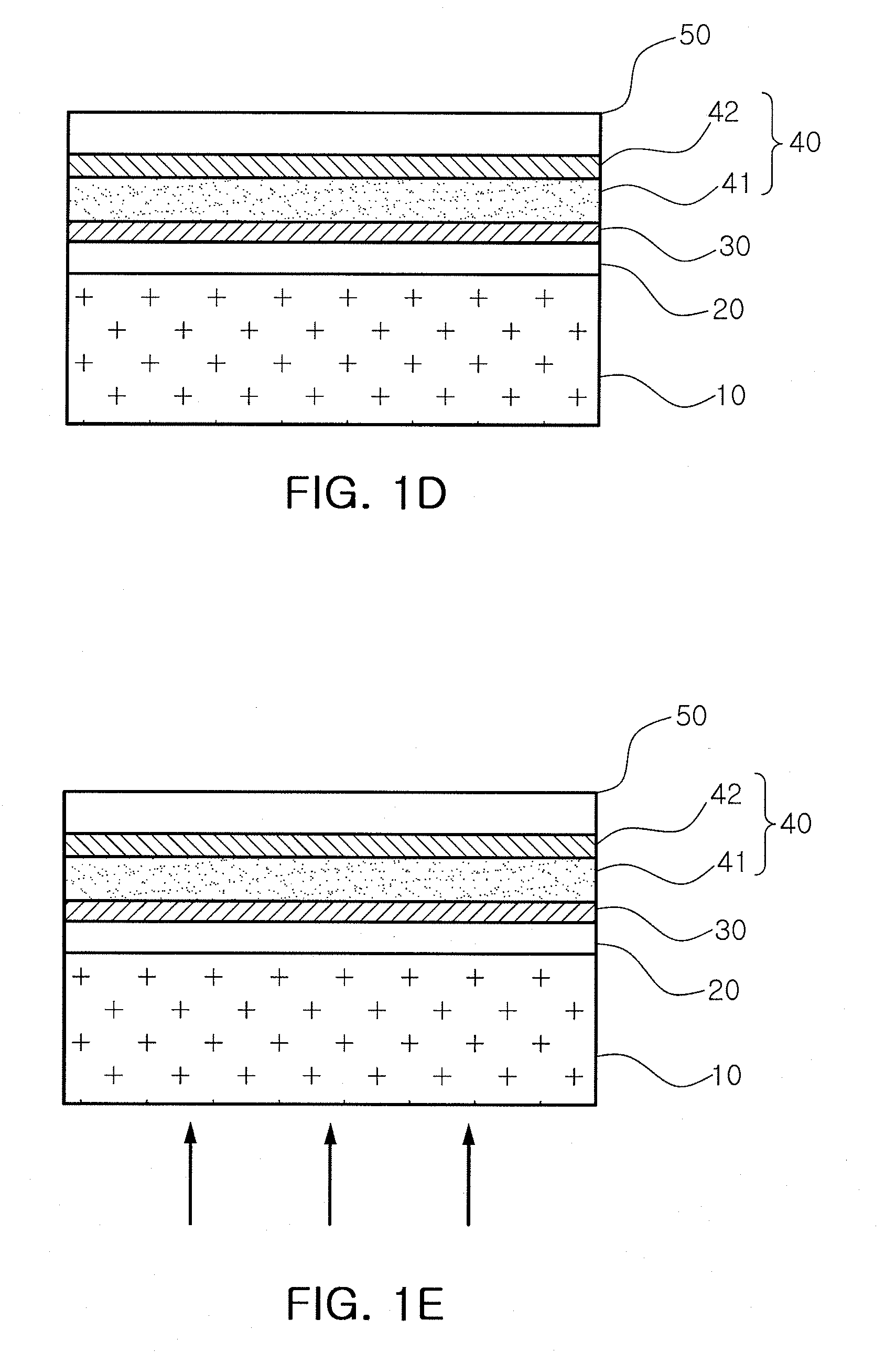
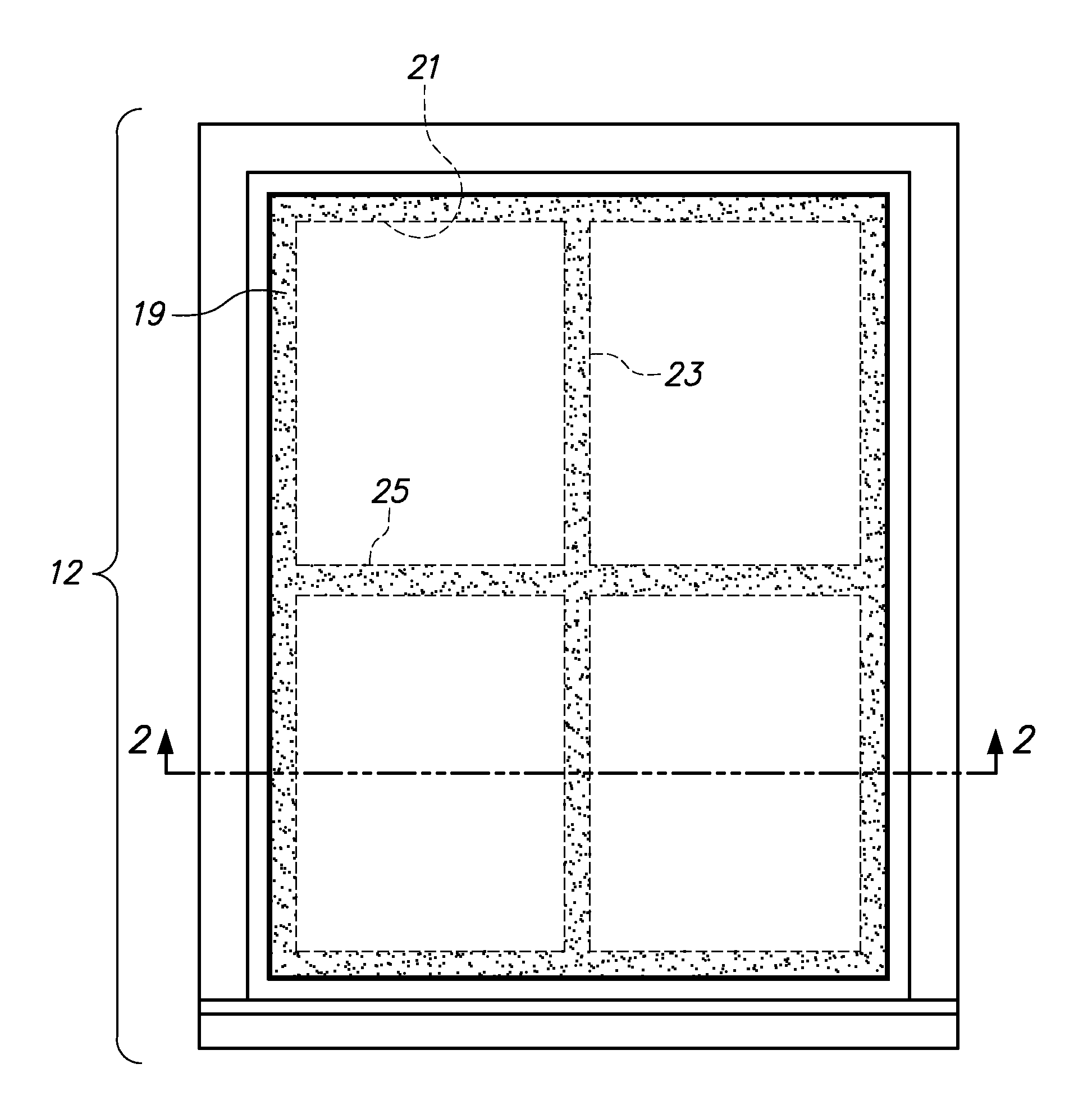
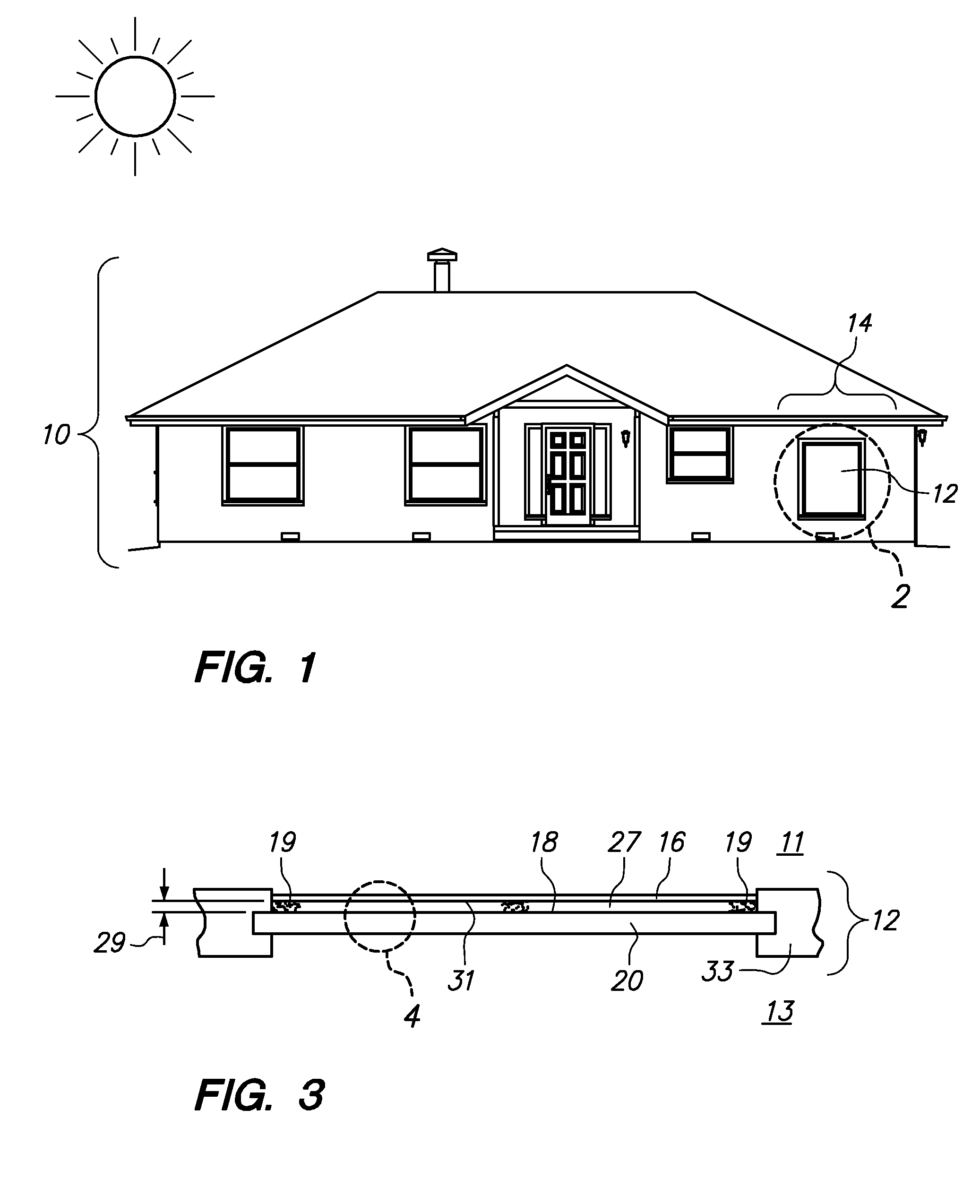
Patents
Literature
269 results about "Oxygen diffusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
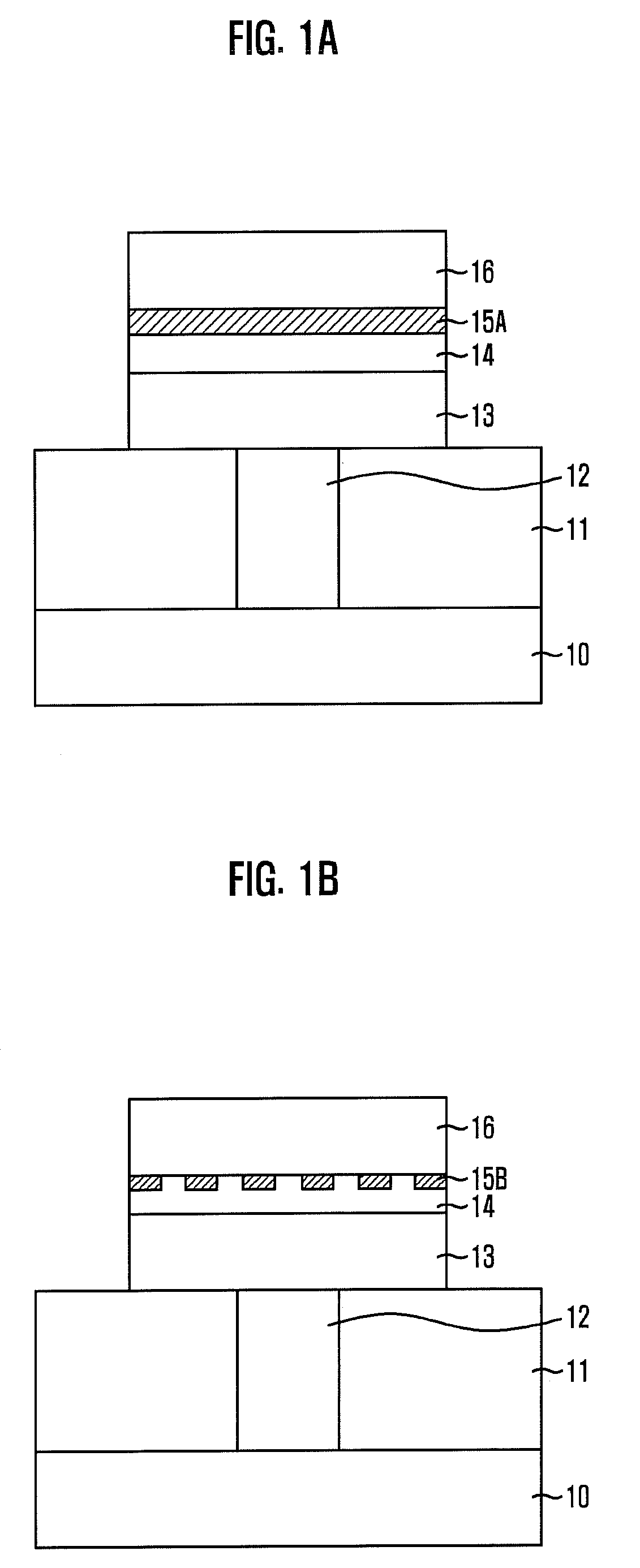
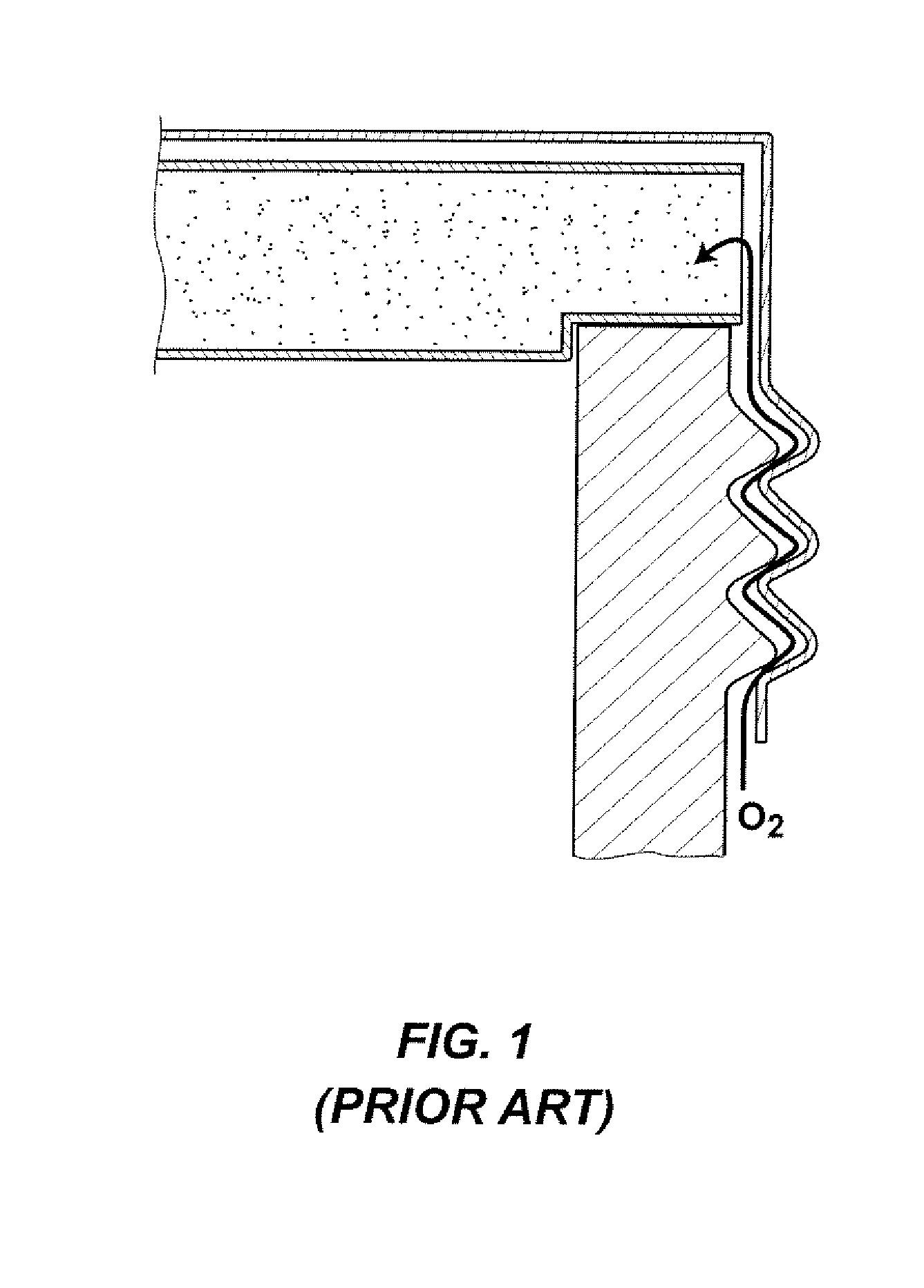
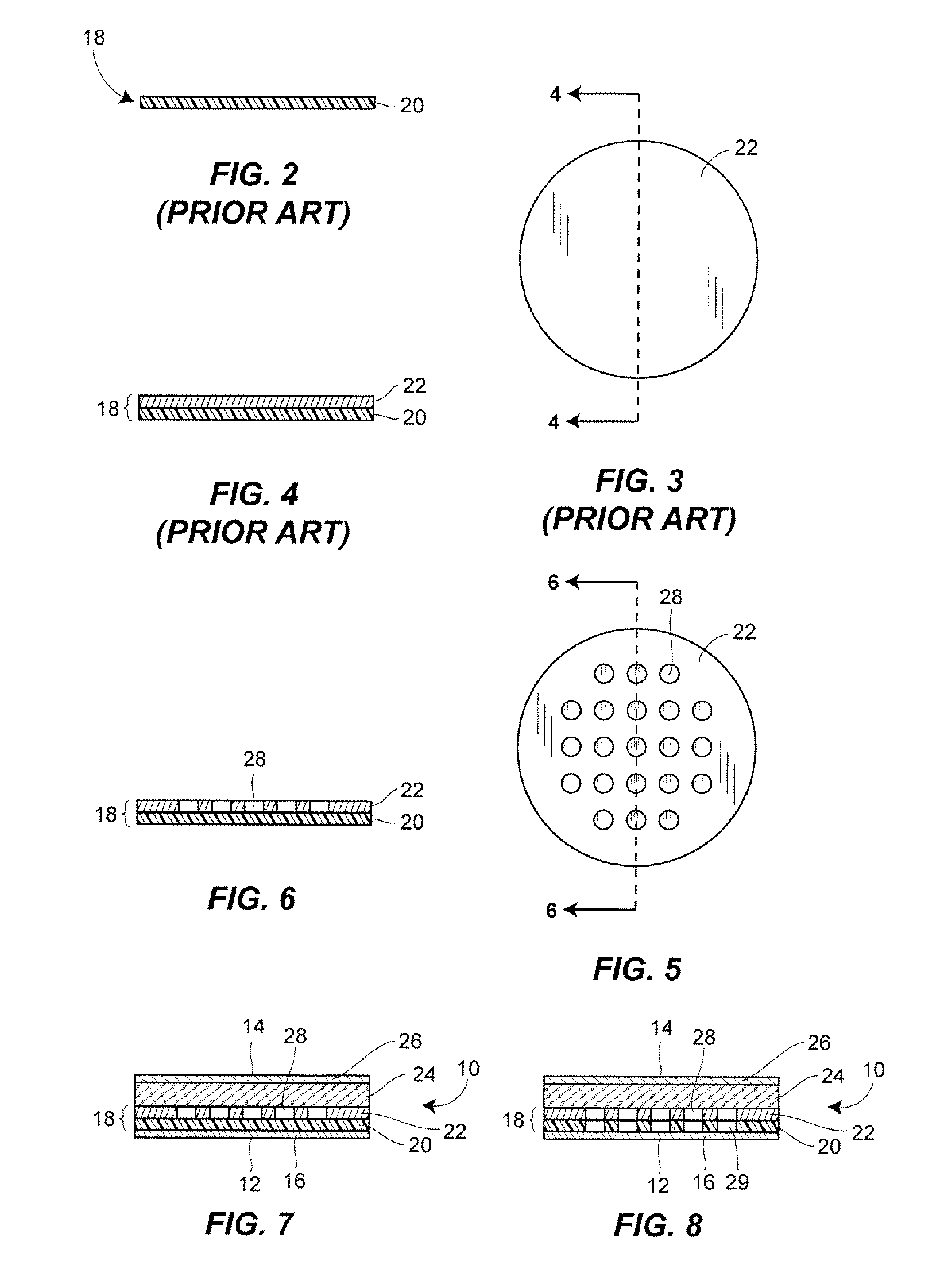
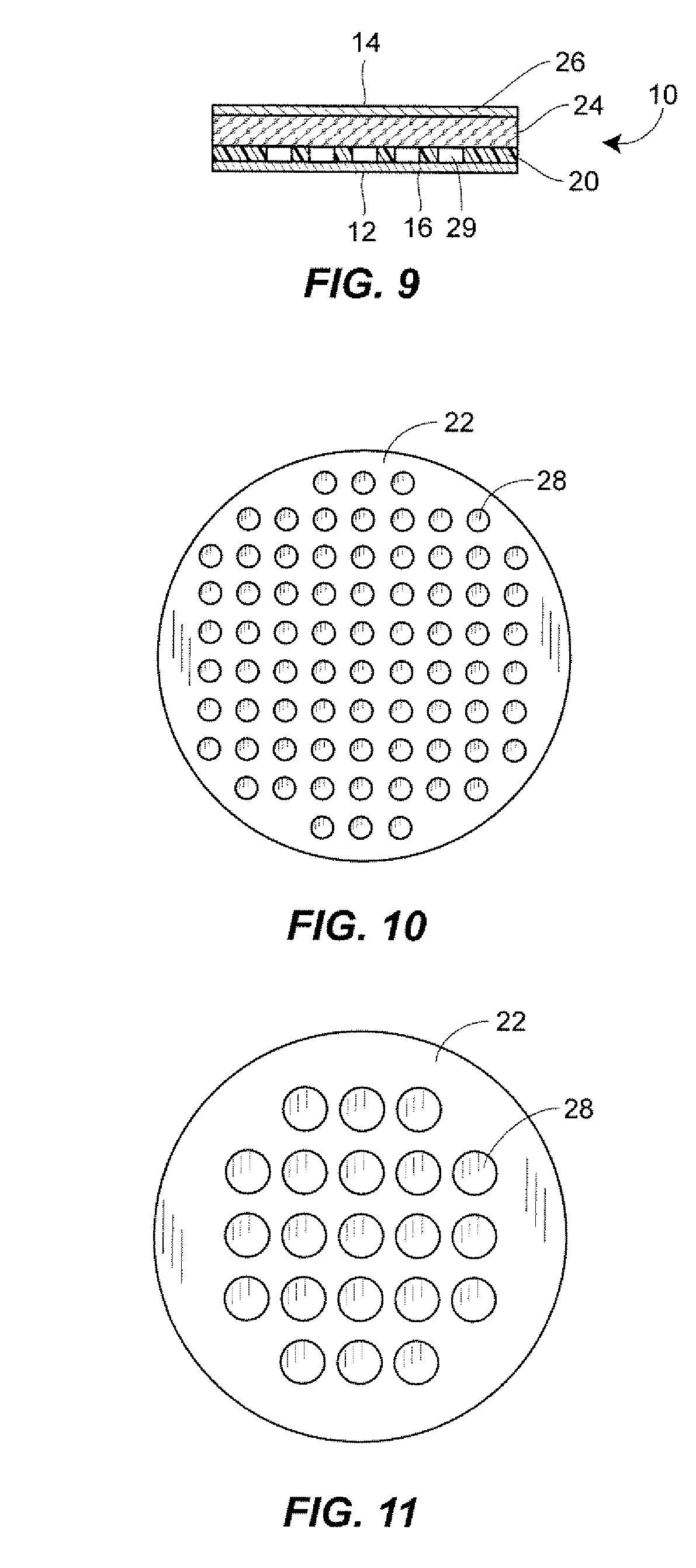
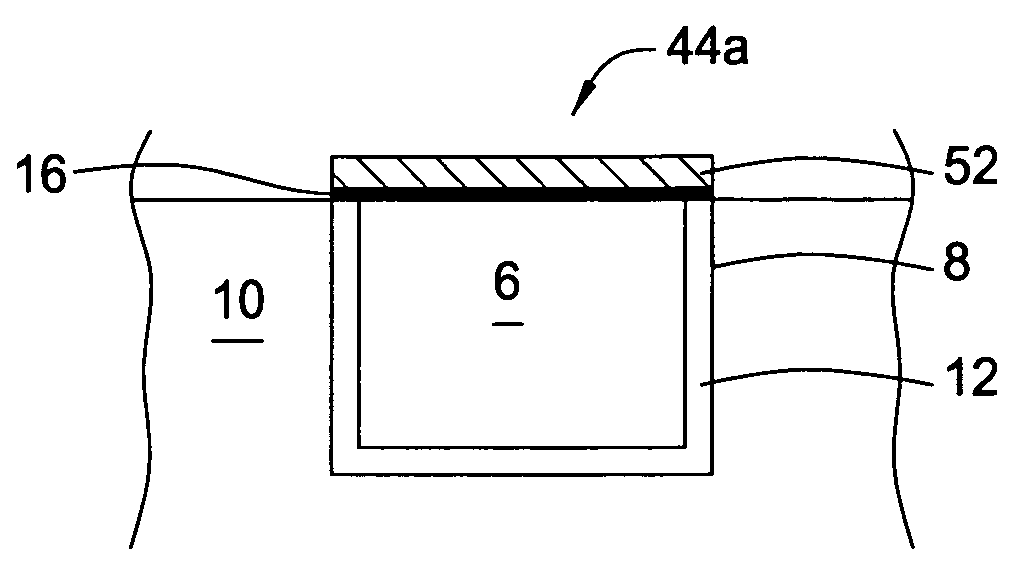
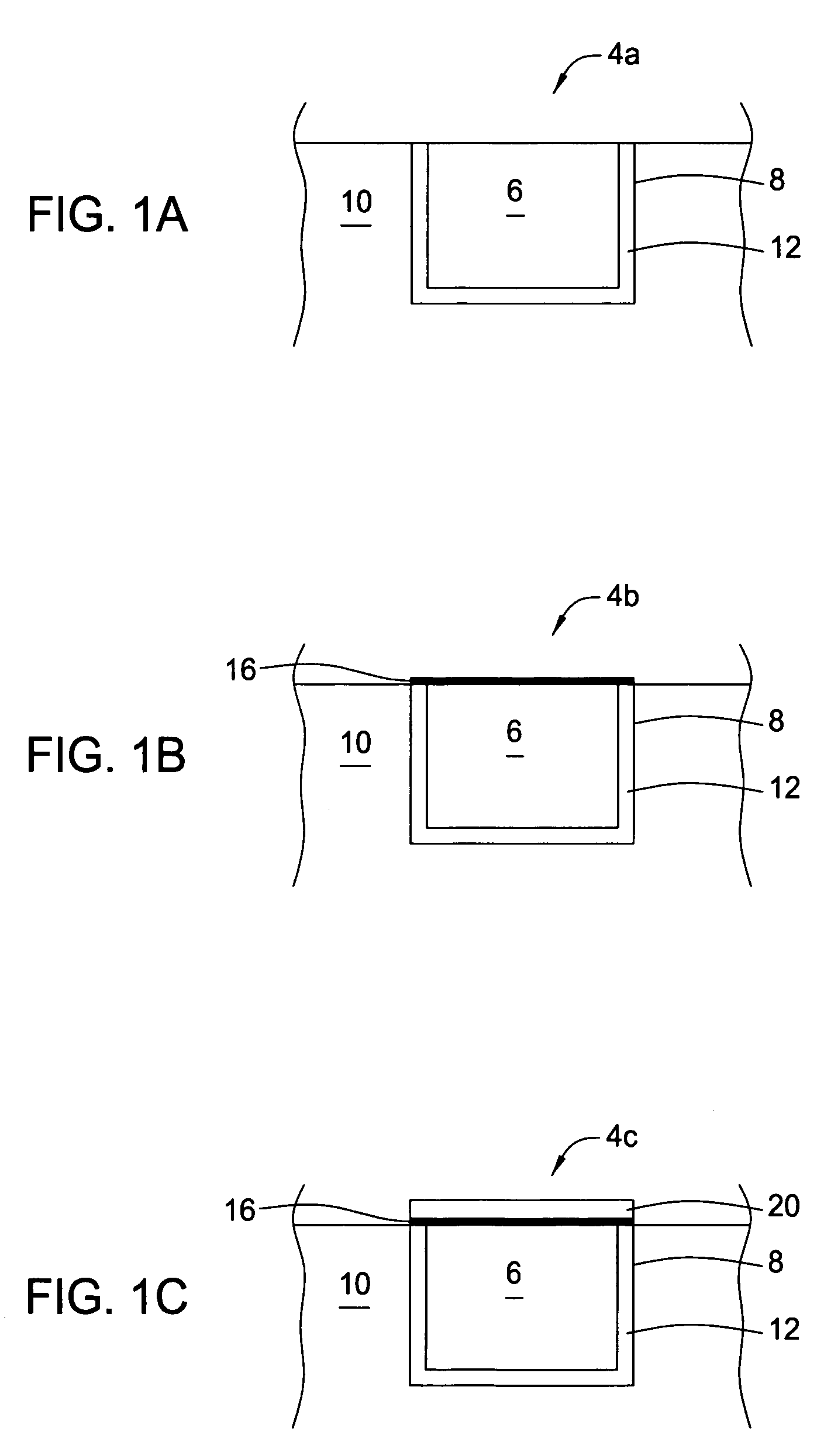
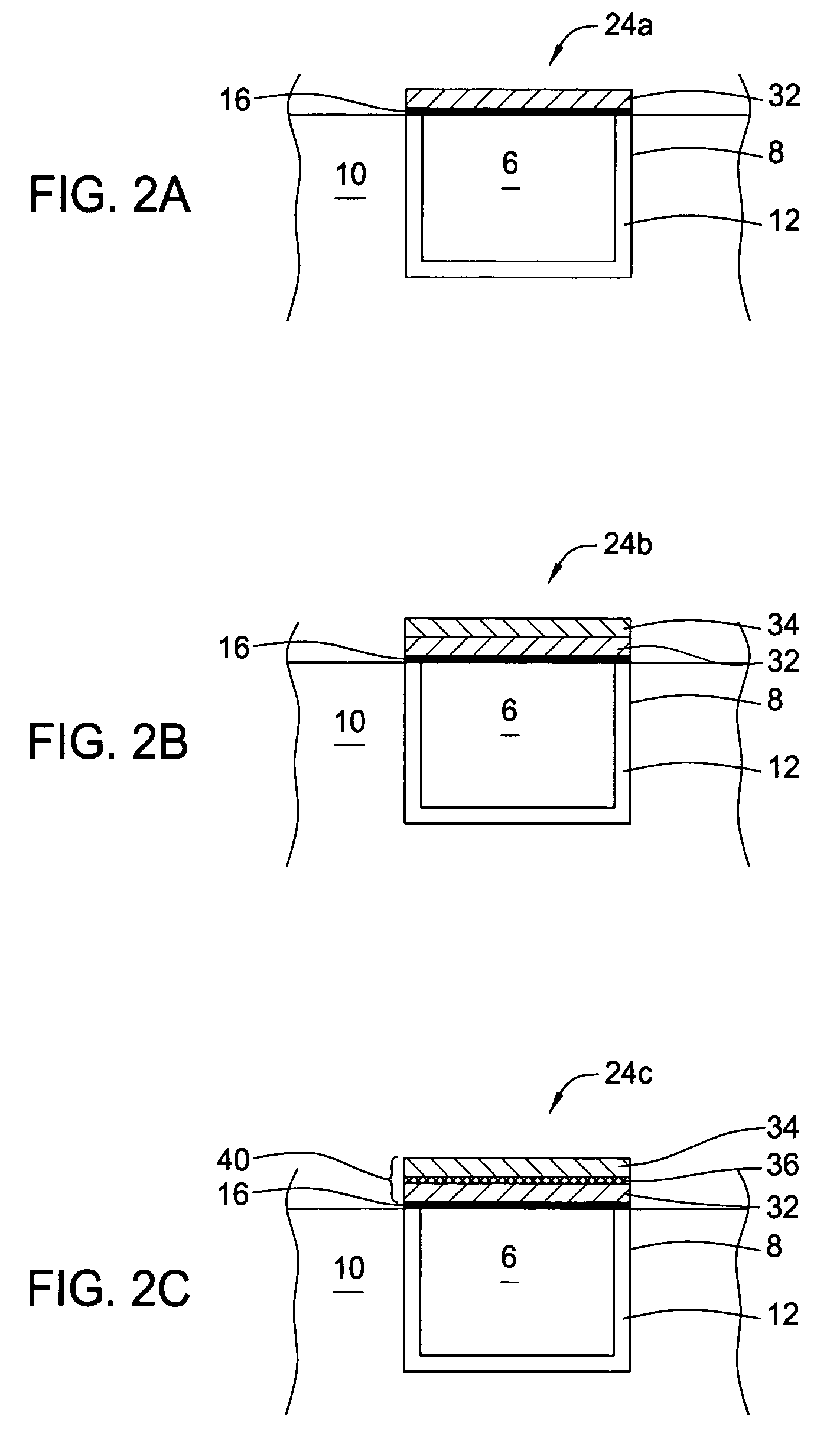
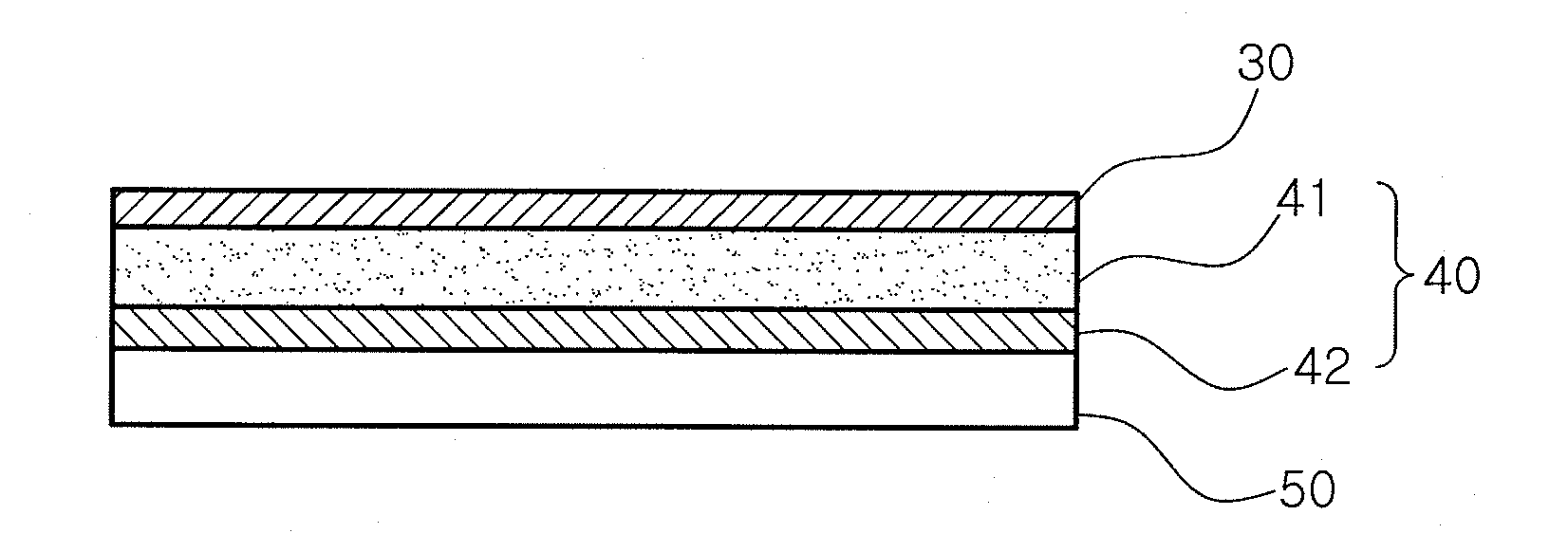
From the alveoli, the oxygen from the air you breathe enters your blood in nearby blood vessels. This is a process called oxygen diffusion. Once your blood is oxygenated, it carries oxygen throughout your body. Another form of diffusion occurs when blood containing carbon dioxide travels back to your lungs.
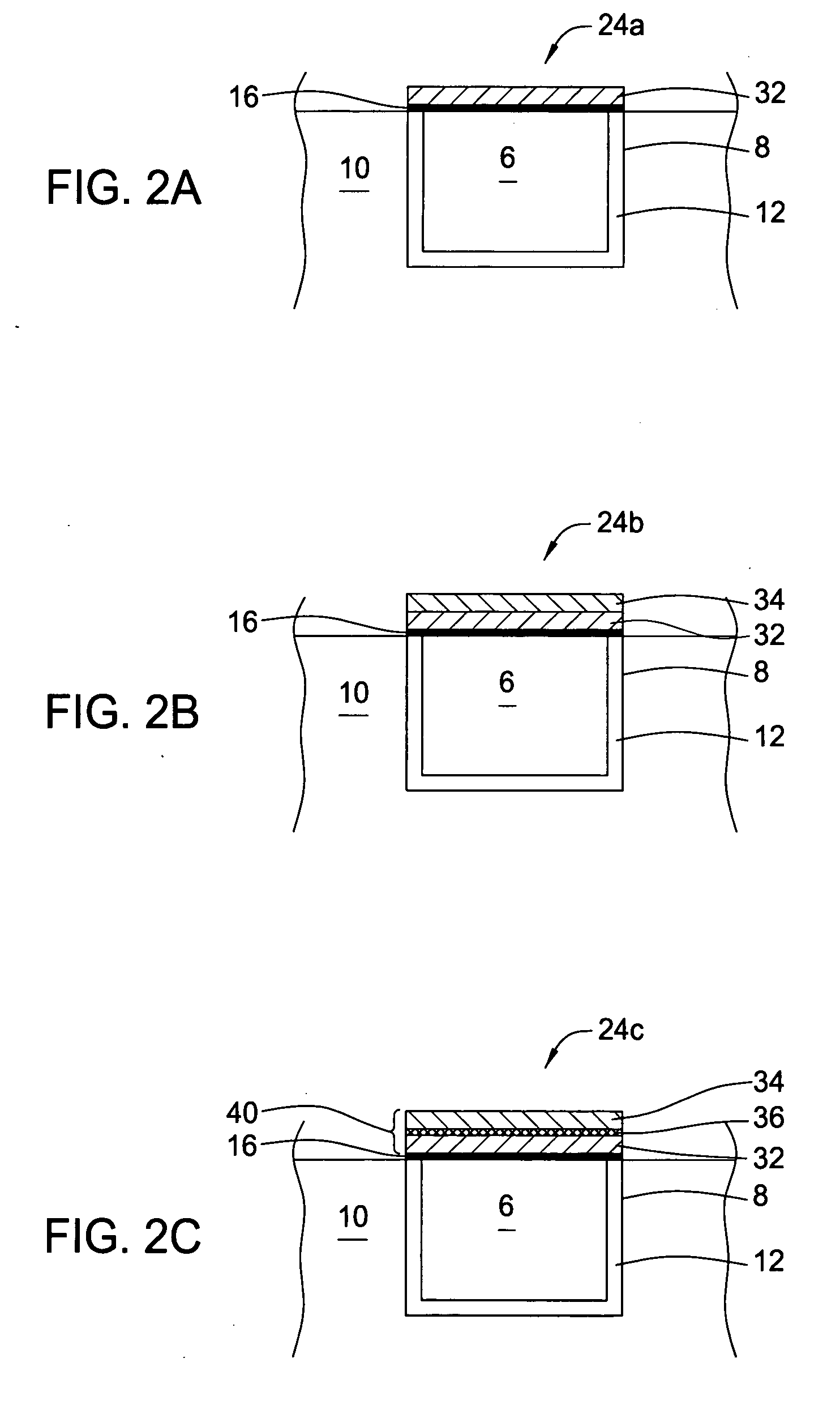
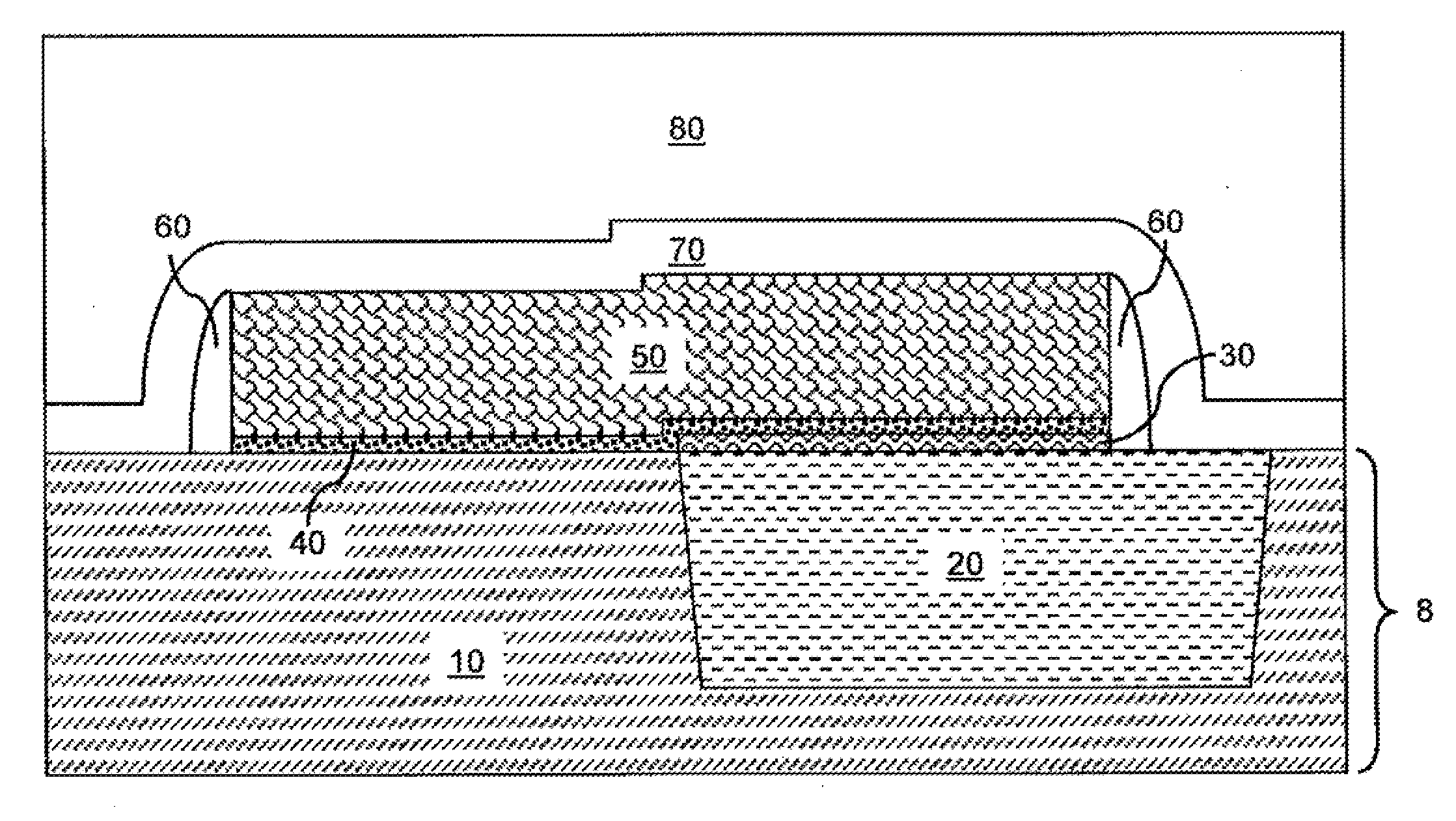
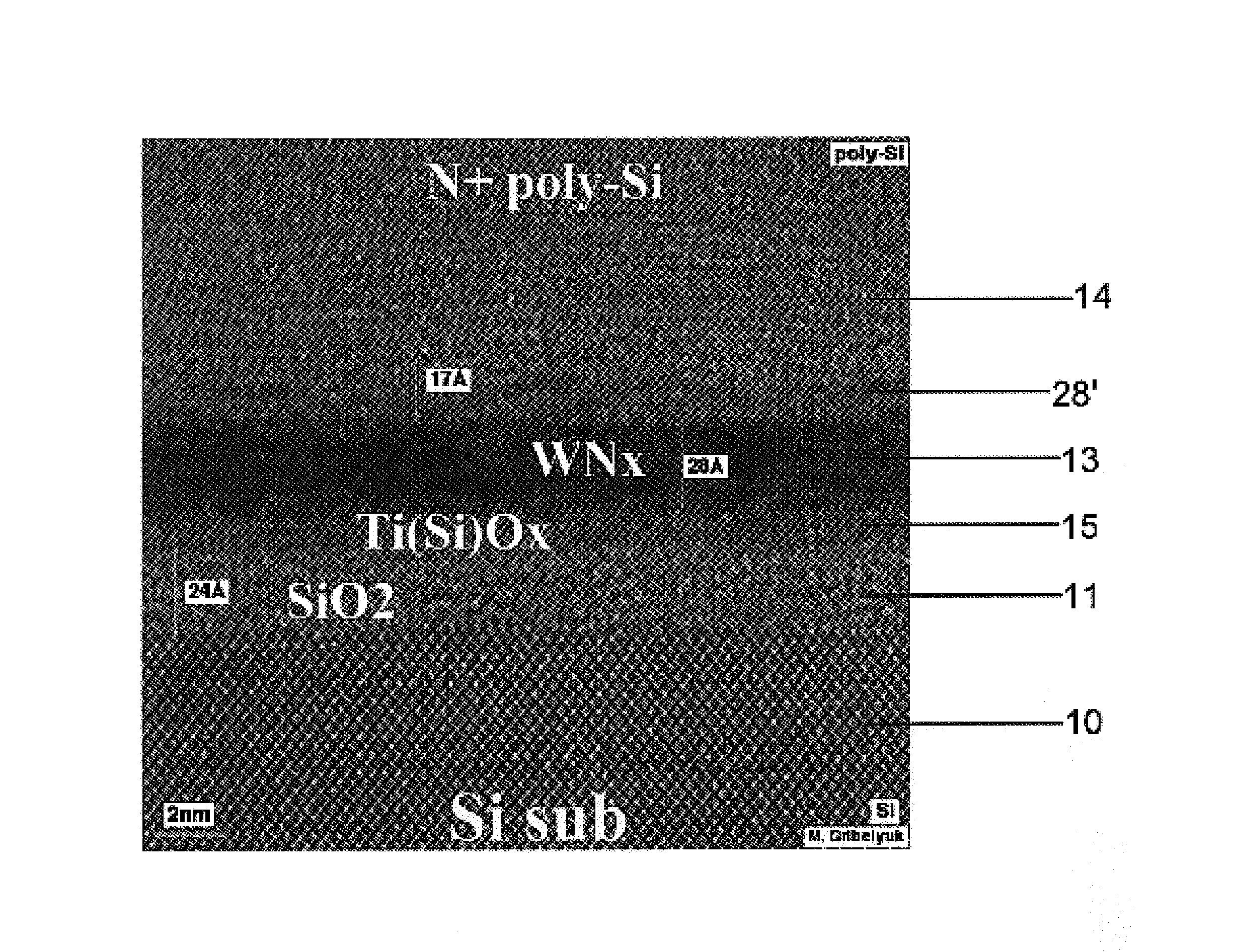
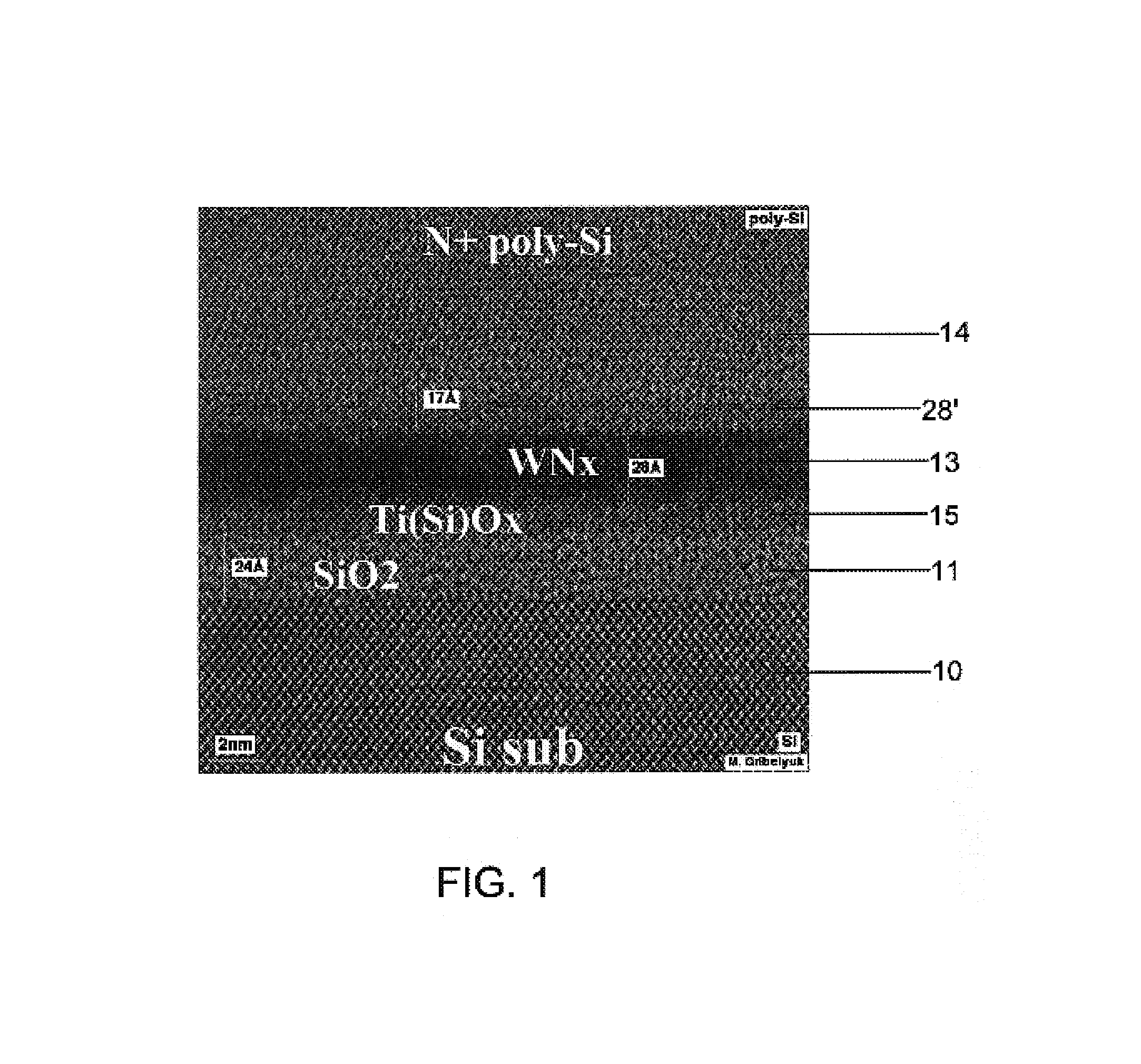
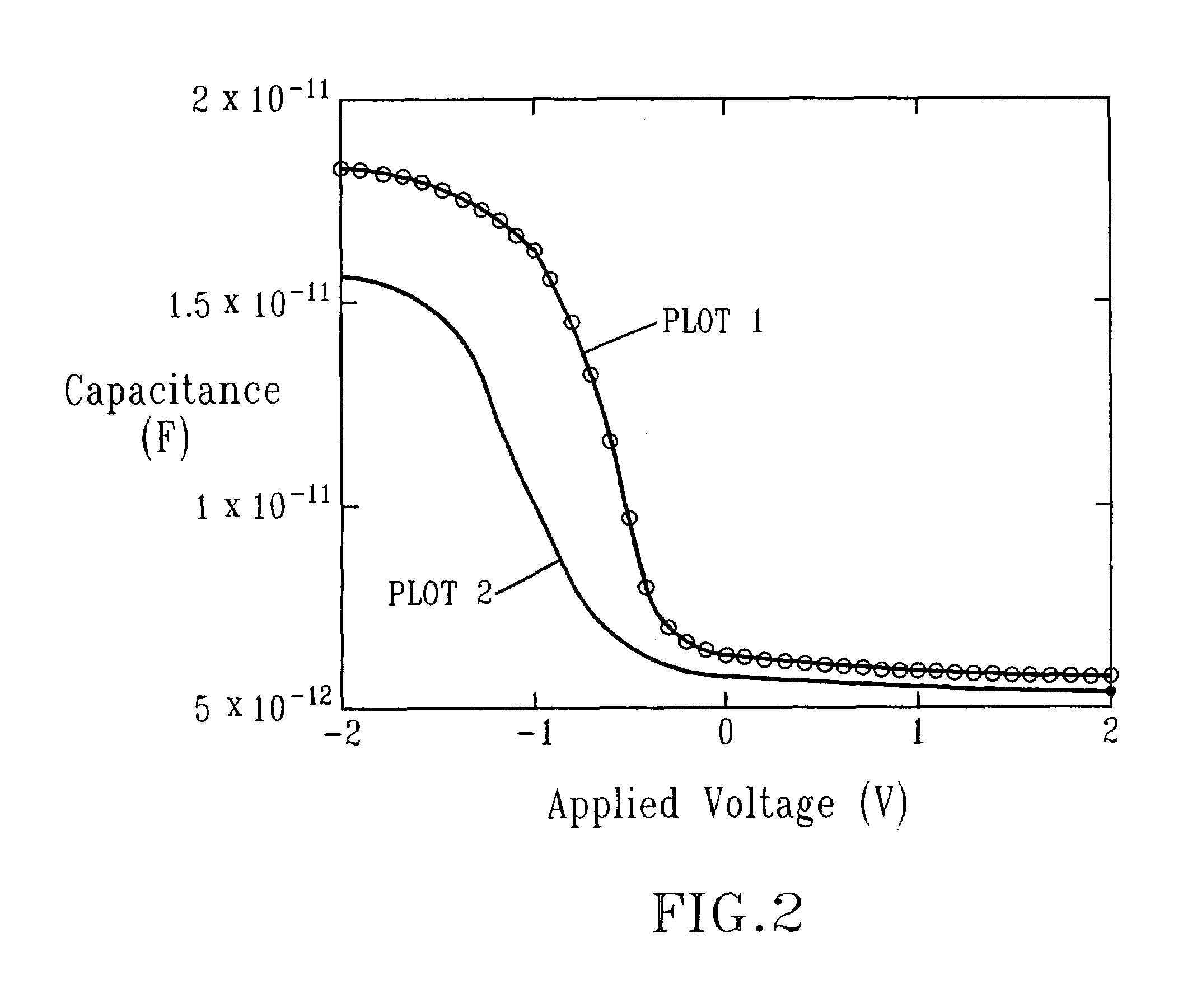
Methods of atomic layer deposition of hafnium oxide / erbium oxide bi-layer as advanced gate dielectrics
InactiveUS20130313656A1Improve electrical performanceFew defectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGate dielectricHafnium
Provided is a two-step ALD deposition process for forming a gate dielectric involving an erbium oxide layer deposition followed by a hafnium oxide layer deposition. Hafnium oxide can provide a high dielectric constant, high density, large bandgap and good thermal stability. Erbium oxide can act as a barrier against oxygen diffusion, which can lead to increasing an effective oxide thickness of the gate dielectric and preventing hafnium-silicon reactions that may lead to higher leakage current.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
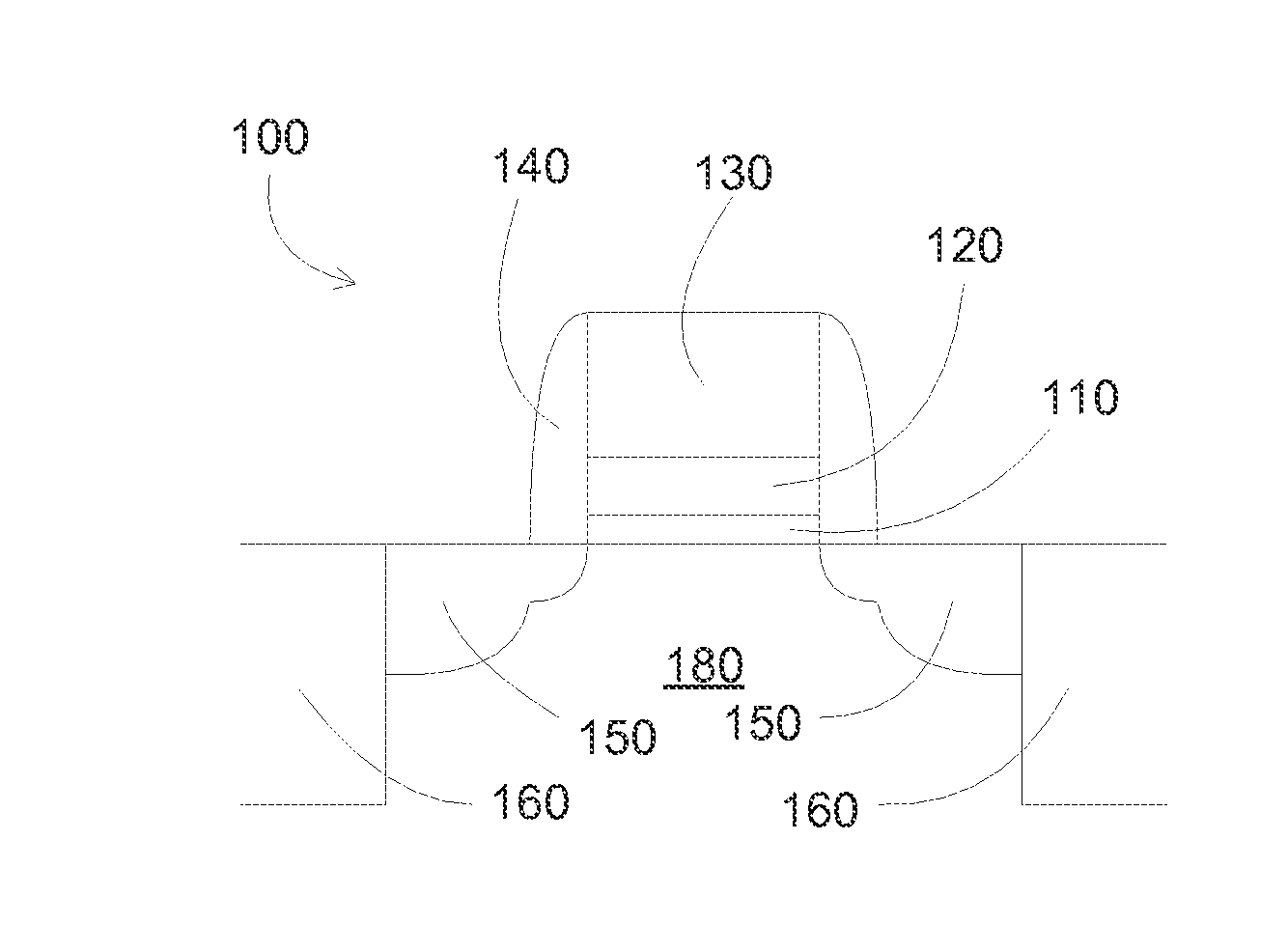
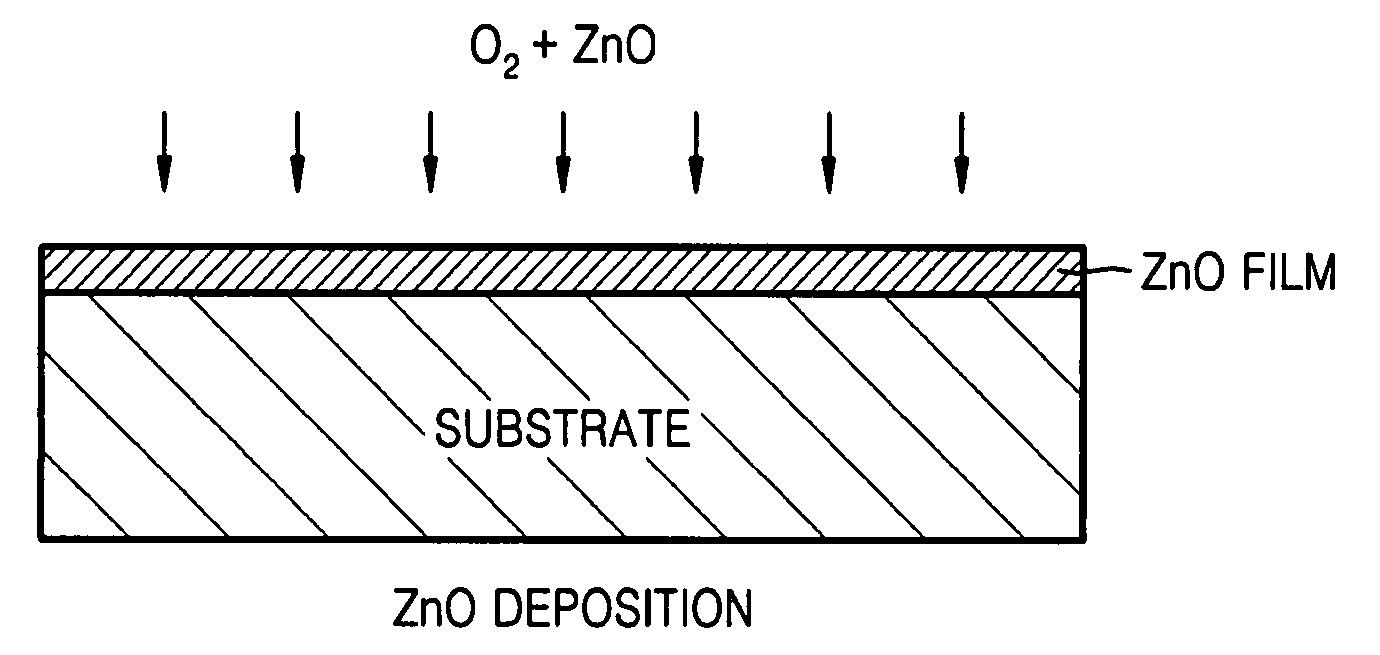
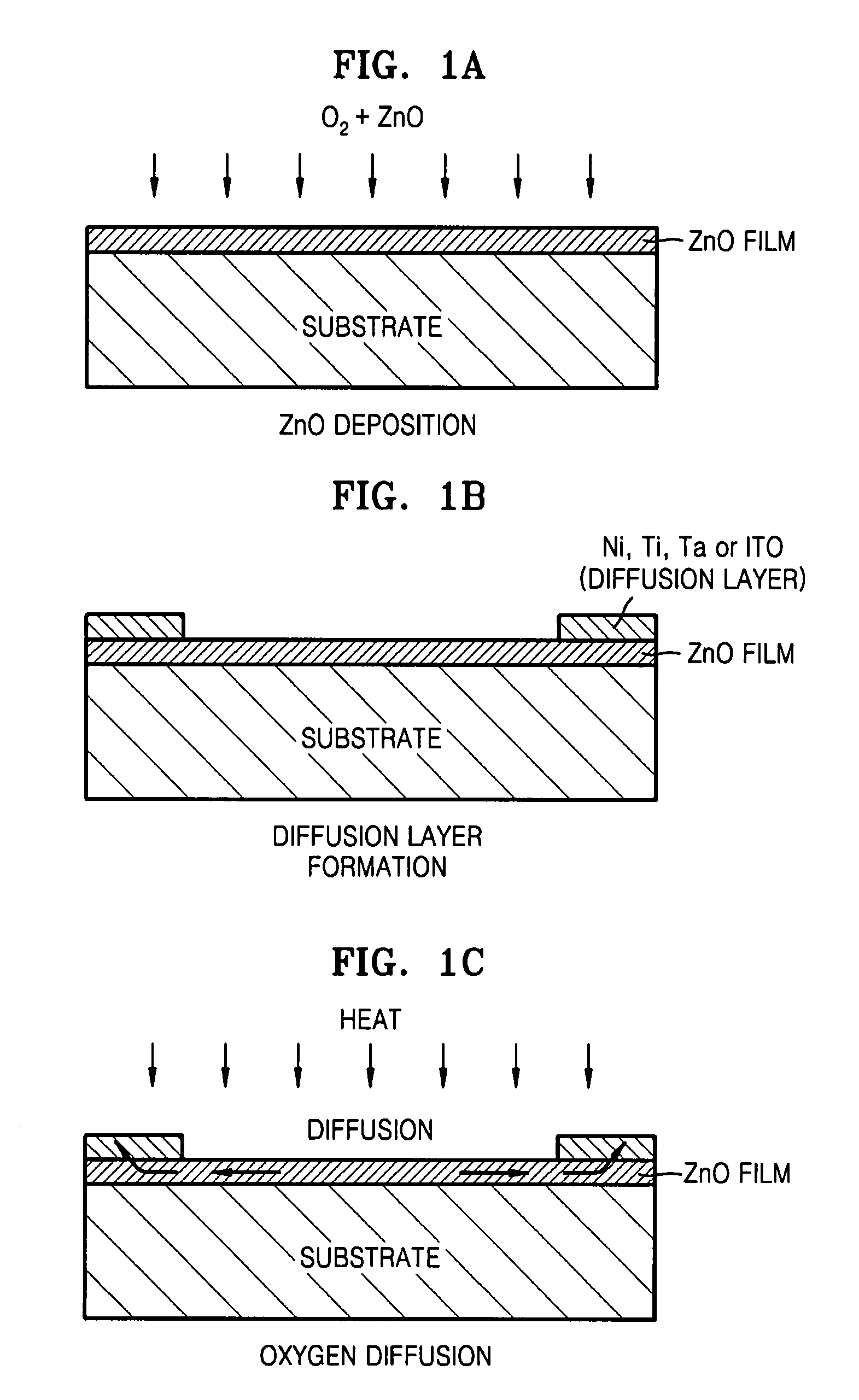
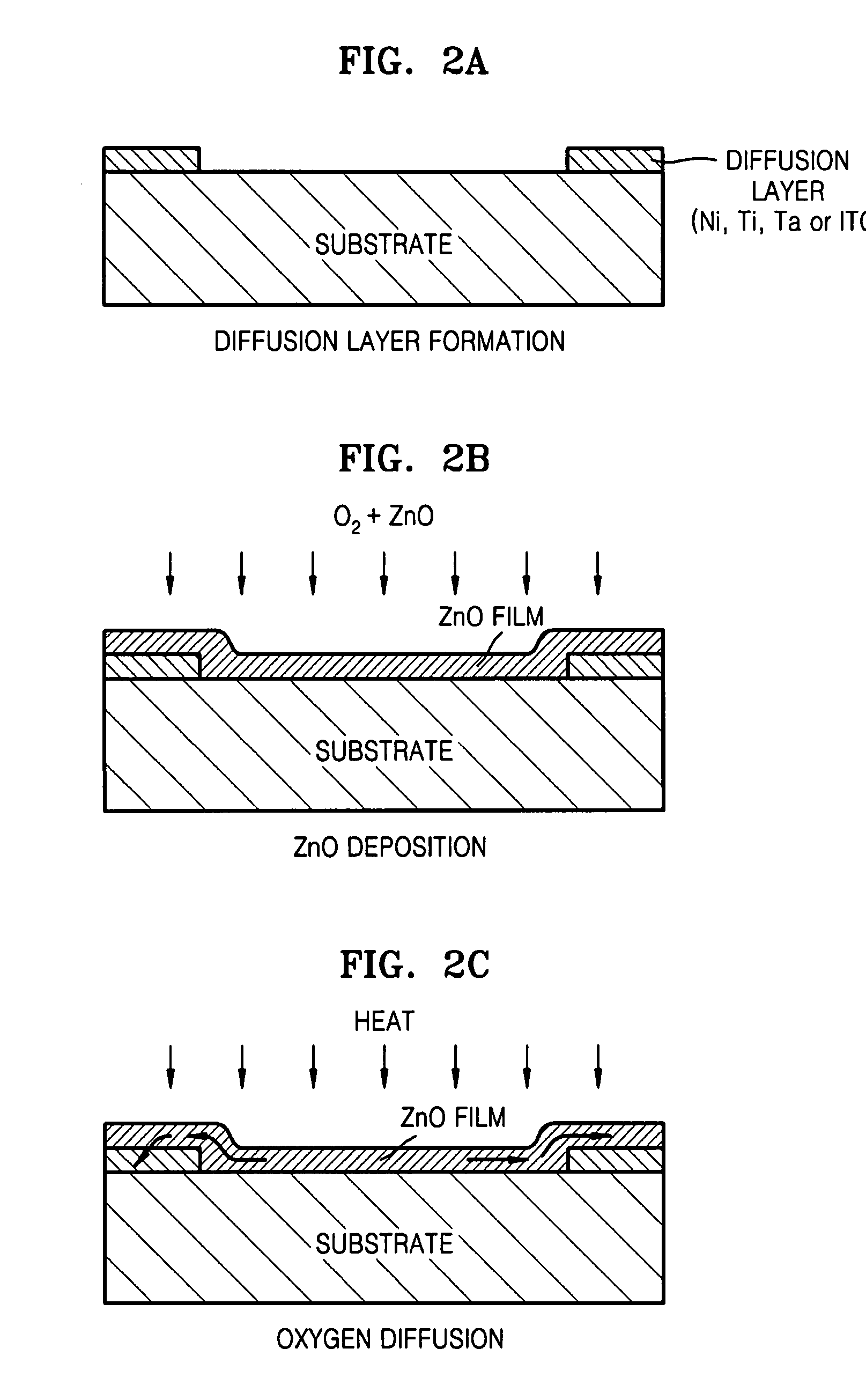
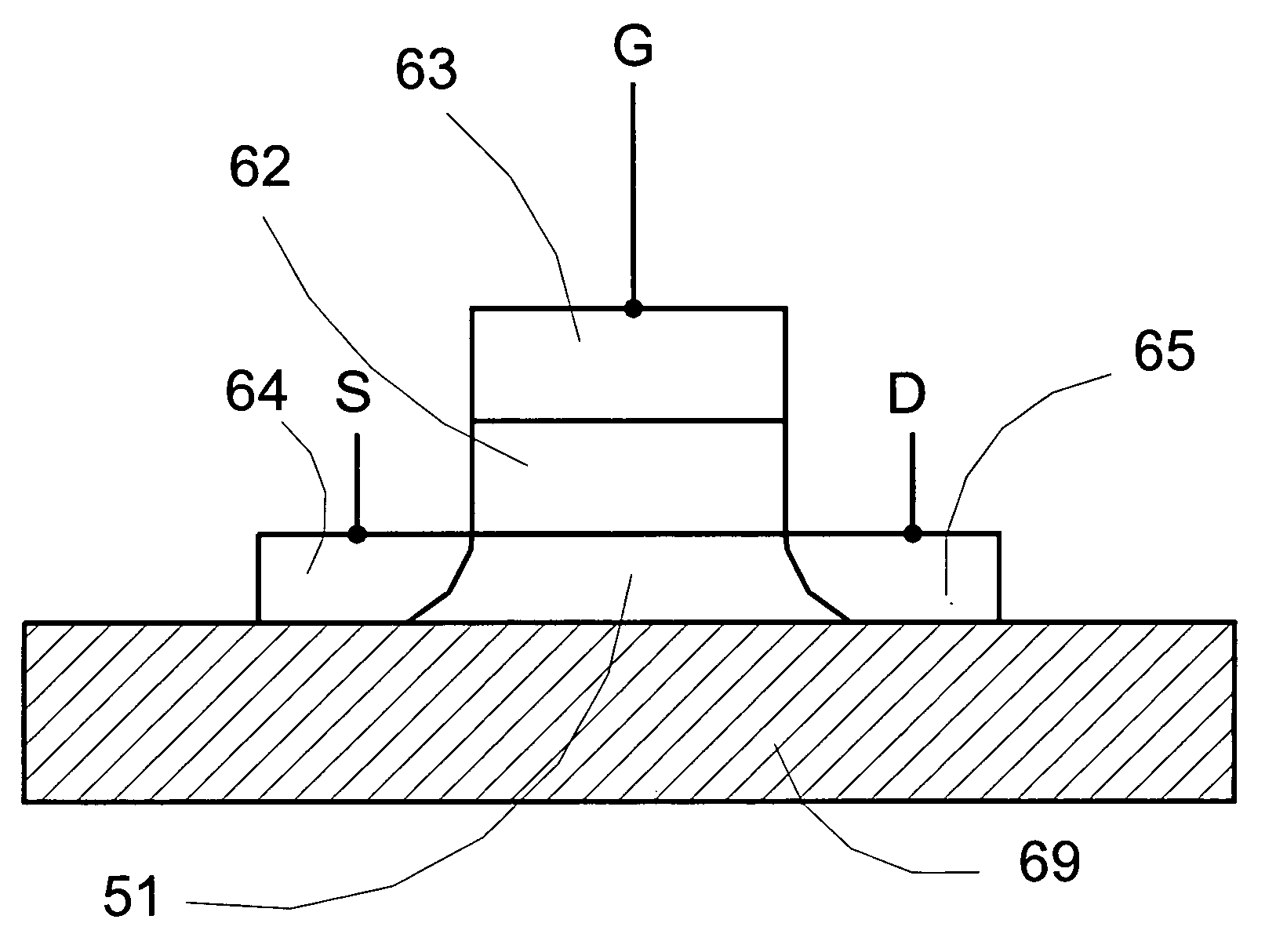
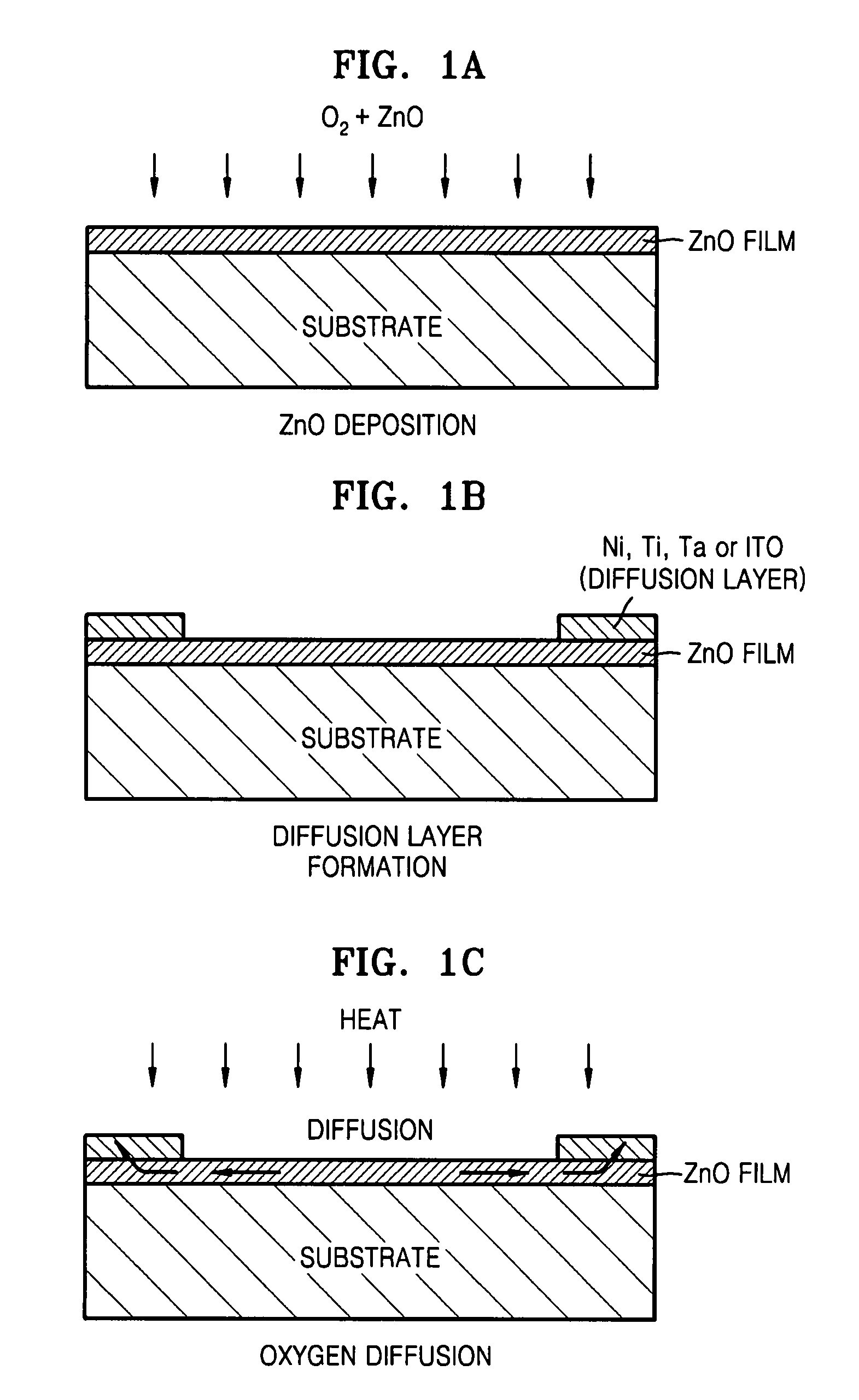
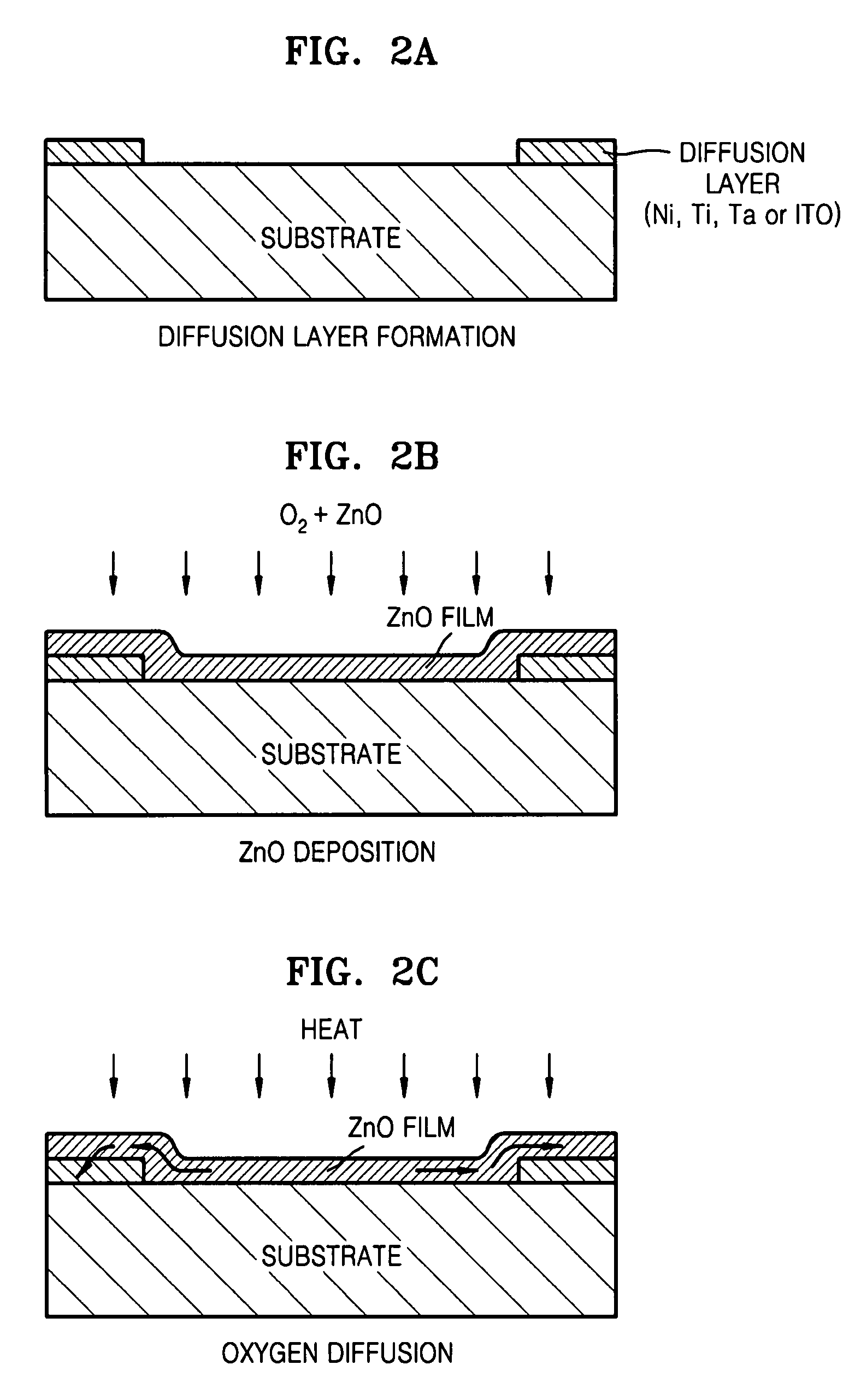
Fabrication methods of a ZnO thin film structure and a ZnO thin film transistor, and a ZnO thin film structure and a ZnO thin film transistor
ActiveUS20070241327A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsFilm structure
Provided is a method of fabricating a ZnO thin film structure and a ZnO thin film transistor (TFT), and a ZnO thin film structure and a ZnO thin film transistor. The method of fabricating a ZnO thin film structure may include forming a ZnO thin film on a substrate in an oxygen atmosphere, forming oxygen diffusion layers of a metal having an affinity for oxygen on the ZnO thin film and heating the ZnO thin film and the oxygen diffusion layers to diffuse oxygen of the ZnO thin film into the oxygen diffusion layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductive metal oxide thin film ferroelectric memory transistor
InactiveUS20060038242A1Simplify the manufacturing processHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricGate dielectric
The present invention discloses a novel transistor structure employing semiconductive metal oxide as the transistor conductive channel. By replacing the silicon conductive channel with a semiconductive metal oxide channel, the transistors can achieve simpler fabrication process and could realize 3D structure to increase circuit density. The disclosed semiconductive metal oxide transistor can have great potential in ferroelectric non volatile memory device with the further advantages of good interfacial properties with the ferroelectric materials, possible lattice matching with the ferroelectric layer, reducing or eliminating the oxygen diffusion problem to improve the reliability of the ferroelectric memory transistor. The semiconductive metal oxide film is preferably a metal oxide exhibiting semiconducting properties at the transistor operating conditions, for example, In2O3 or RuO2. The present invention ferroelectric transistor can be a metal-ferroelectric-semiconductive metal oxide FET having a gate stack of a top metal electrode disposed on a ferroelectric layer disposed on a semiconductive metal oxide channel on a substrate. Using additional layer of bottom electrode and gate dielectric, the present invention ferroelectric transistor can also be a metal-ferroelectric-metal (optional)-gate dielectric (optional)-semiconductive metal oxide FET.
Owner:SHARP KK
Non-volatile resistive sense memory
ActiveUS20110006275A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsManganese oxide
A resistive sense memory cell includes a layer of crystalline praseodymium calcium manganese oxide and a layer of amorphous praseodymium calcium manganese oxide disposed on the layer of crystalline praseodymium calcium manganese oxide forming a resistive sense memory stack. A first and second electrode are separated by the resistive sense memory stack. The resistive sense memory cell can further include an oxygen diffusion barrier layer separating the layer of crystalline praseodymium calcium manganese oxide from the layer of amorphous praseodymium calcium manganese oxide a layer. Methods include depositing an amorphous praseodymium calcium manganese oxide disposed on the layer of crystalline praseodymium calcium manganese oxide forming a resistive sense memory stack.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
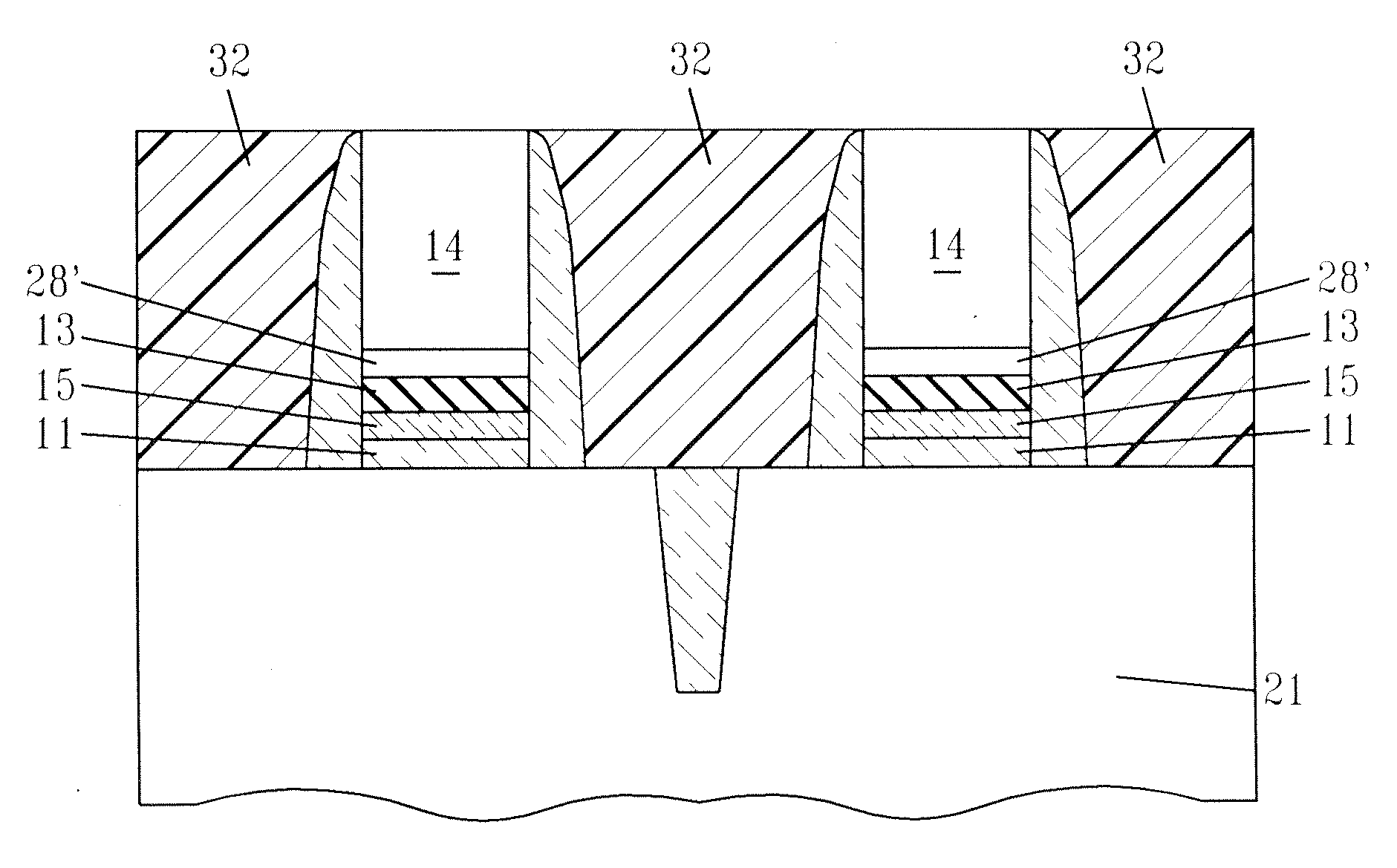
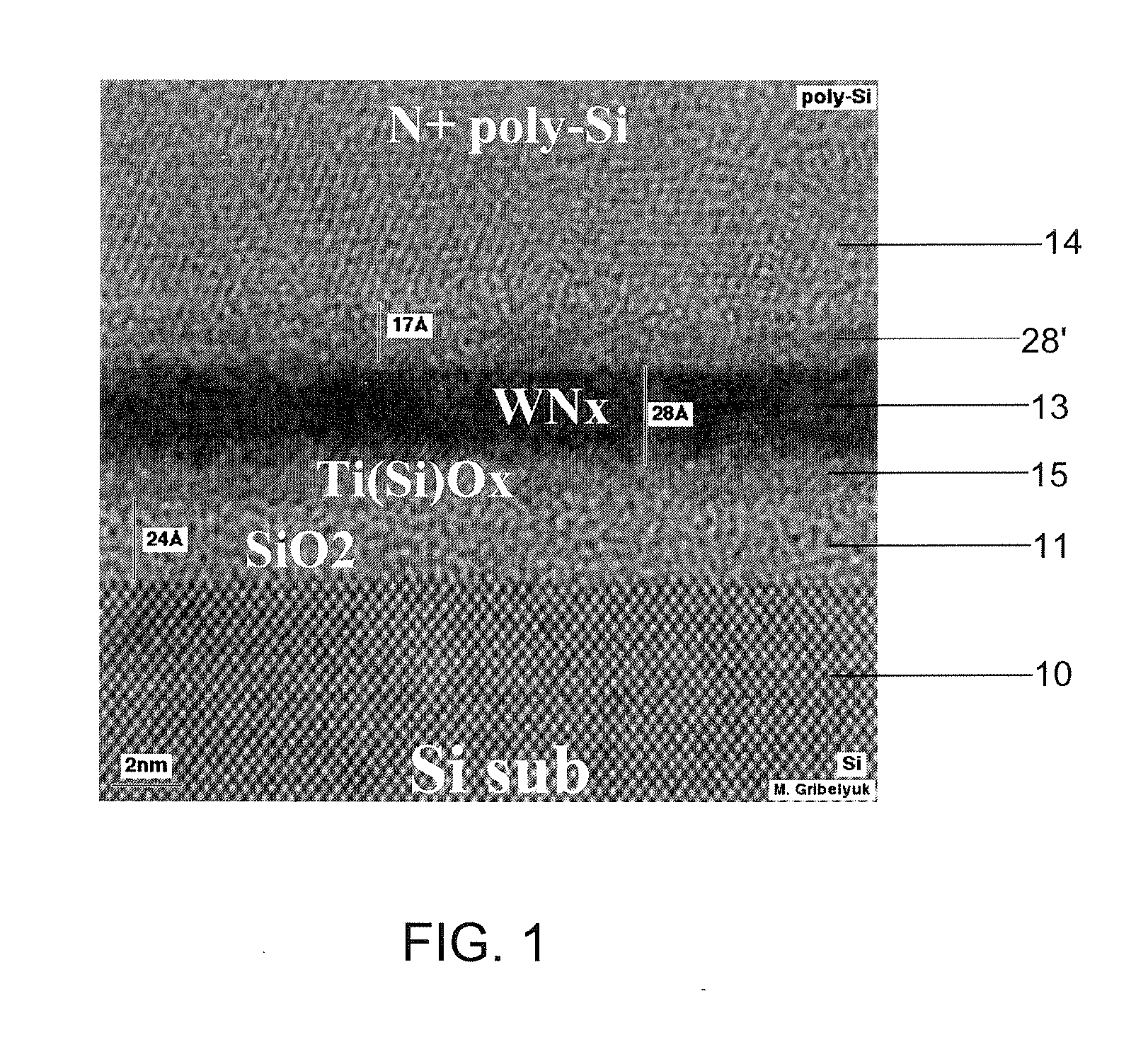
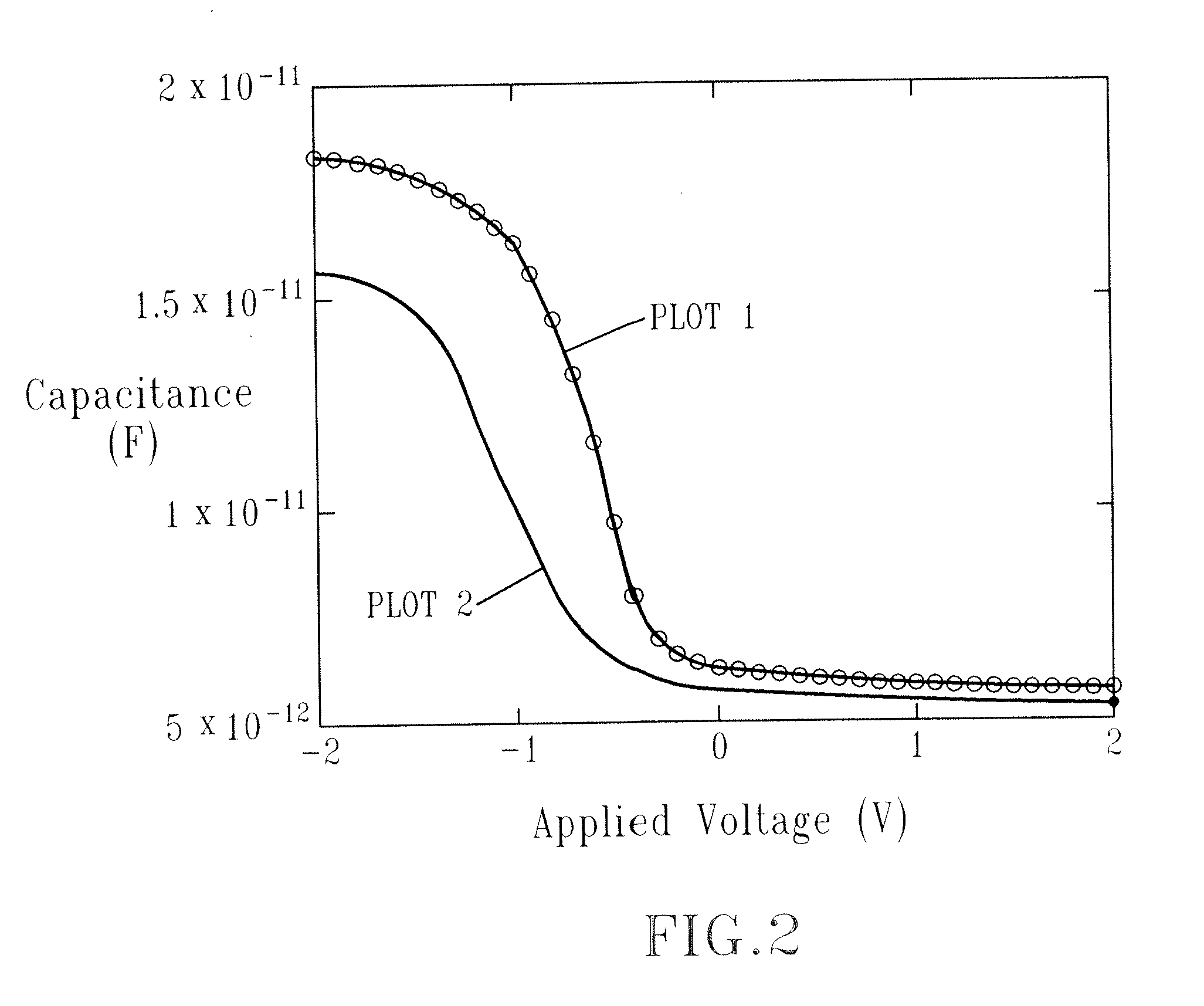
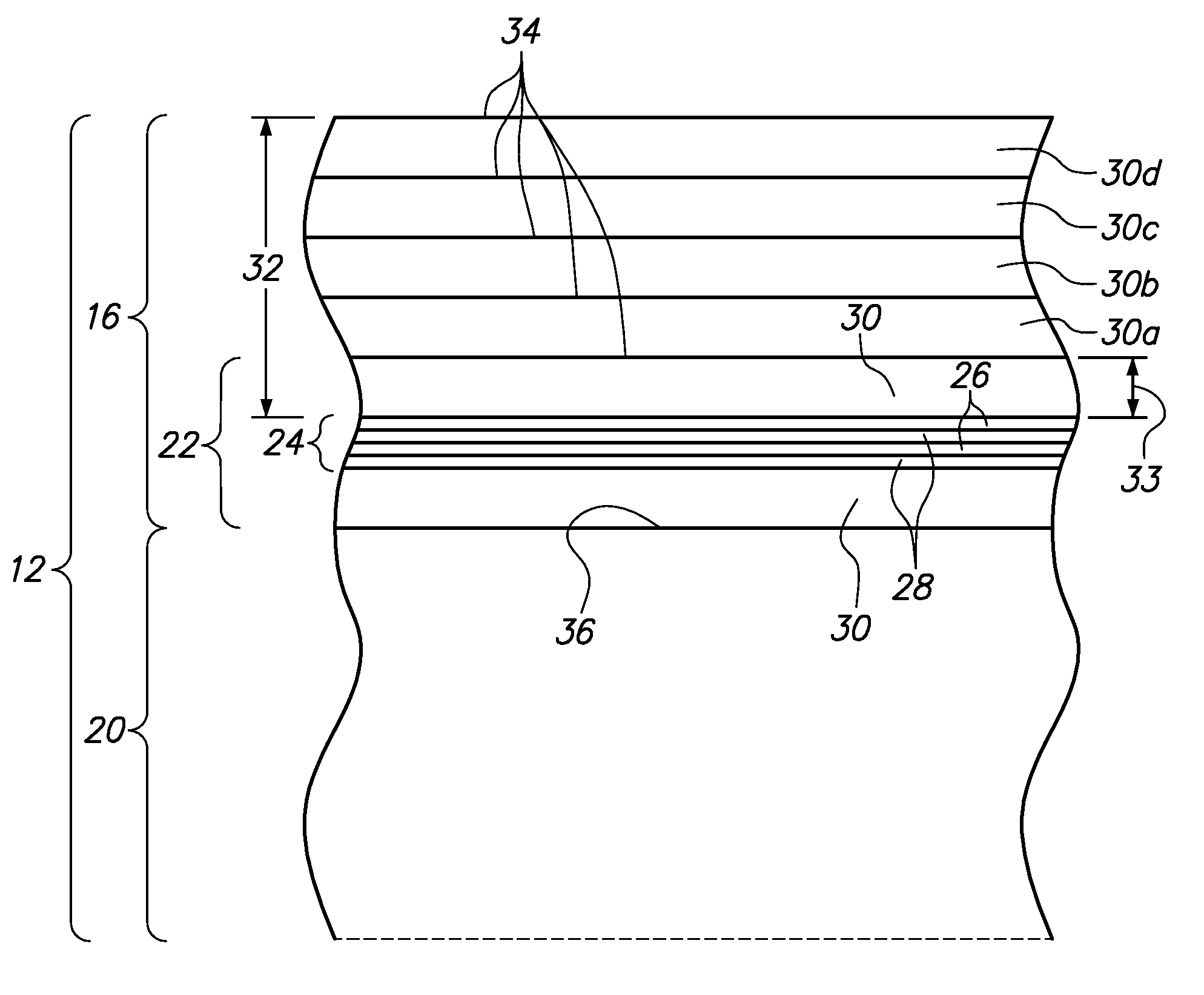
Structure and method for metal gate stack oxygen concentration control using an oxygen diffusion barrier layer and a sacrificial oxygen gettering layer
ActiveUS20100127336A1Increase their effective work functionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWork functionDiffusion barrier
A process is disclosed of forming metal replacement gates for NMOS and PMOS transistors with oxygen in the PMOS metal gates and metal atom enrichment in the NMOS gates such that the PMOS gates have effective work functions above 4.85 eV and the NMOS gates have effective work functions below 4.25 eV. Metal work function layers in both the NMOS and PMOS gates are oxidized to increase their effective work functions to the desired PMOS range. An oxygen diffusion blocking layer is formed over the PMOS gate and an oxygen getter is formed over the NMOS gates. A getter anneal extracts the oxygen from the NMOS work function layers and adds metal atom enrichment to the NMOS work function layers, reducing their effective work functions to the desired NMOS range. Processes and materials for the metal work function layers, the oxidation process and oxygen gettering are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
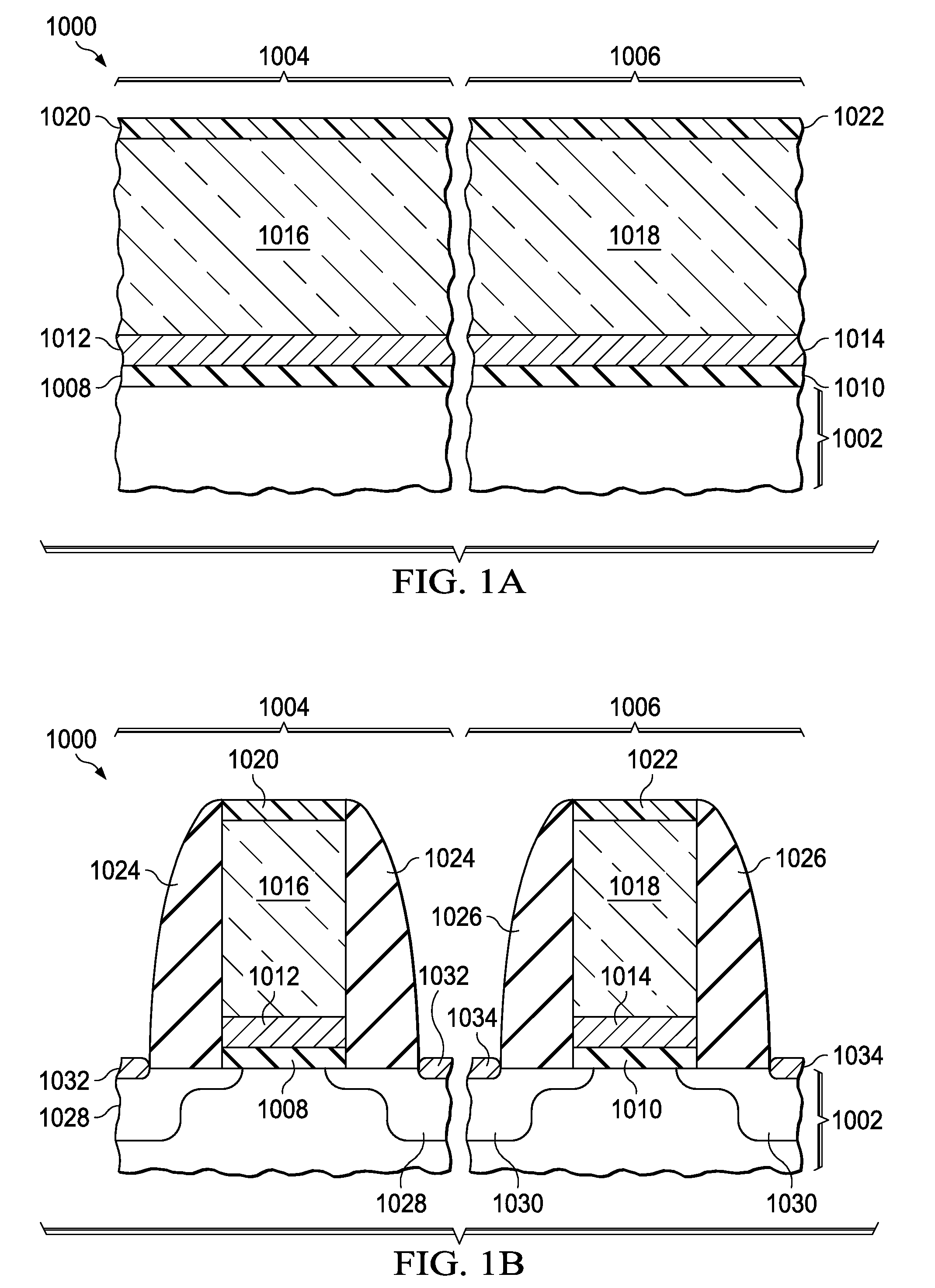
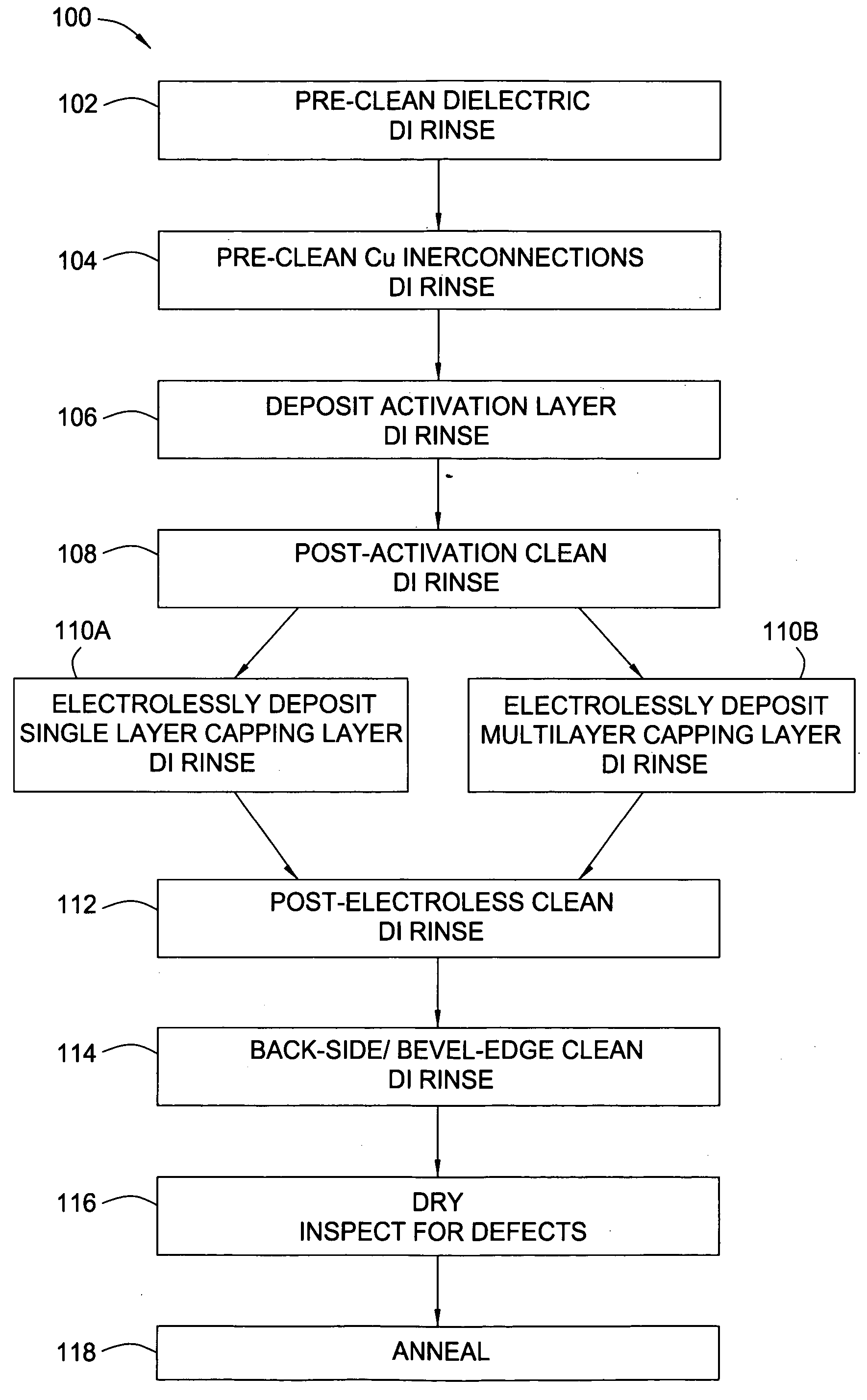
Method and tool of chemical doping CoW alloys with Re for increasing barrier properties of electroless capping layers for IC Cu interconnects
InactiveUS20050101130A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingRheniumAlloy
A method for fabricating a capping layer with enhanced barrier resistance to both copper and oxygen diffusion, comprises forming a capping layer on a conductive surface of an interconnect, wherein the capping layer comprises cobalt (Co), tungsten (W), rhenium (Re), and at least one of phosphorus (P) and boron (B). In an embodiment of the invention, forming the capping layer comprises exposing the conductive surface to an electroless capping solution comprising a cobalt source, a tungsten source, a rhenium source, and at least one of a phosphorus source and a boron source, and annealing the capping layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductive metal oxide thin film ferroelectric memory transistor
InactiveUS7378286B2Simplify the manufacturing processHigh densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricGate dielectric
The present invention discloses a novel transistor structure employing semiconductive metal oxide as the transistor conductive channel. By replacing the silicon conductive channel with a semiconductive metal oxide channel, the transistors can achieve simpler fabrication process and could realize 3D structure to increase circuit density. The disclosed semiconductive metal oxide transistor can have great potential in ferroelectric non volatile memory device with the further advantages of good interfacial properties with the ferroelectric materials, possible lattice matching with the ferroelectric layer, reducing or eliminating the oxygen diffusion problem to improve the reliability of the ferroelectric memory transistor. The semiconductive metal oxide film is preferably a metal oxide exhibiting semiconducting properties at the transistor operating conditions, for example, In2O3 or RuO2. The present invention ferroelectric transistor can be a metal-ferroelectric-semiconductive metal oxide FET having a gate stack of a top metal electrode disposed on a ferroelectric layer disposed on a semiconductive metal oxide channel on a substrate. Using additional layer of bottom electrode and gate dielectric, the present invention ferroelectric transistor can also be a metal-ferroelectric-metal (optional)-gate dielectric (optional)-semiconductive metal oxide FET.
Owner:SHARP KK
Selectively self-assembling oxygen diffusion barrier
ActiveUS20100237442A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricMonomer
A shallow trench isolation structure is formed in a semiconductor substrate adjacent to an active semiconductor region. A selective self-assembling oxygen barrier layer is formed on the surface of the shallow trench isolation structure that includes a dielectric oxide material. The formation of the selective self-assembling oxygen barrier layer is selective in that it is not formed on the surface the active semiconductor region having a semiconductor surface. The selective self-assembling oxygen barrier layer is a self-assembled monomer layer of a chemical which is a derivative of alkylsilanes including at least one alkylene moiety. The silicon containing portion of the chemical forms polysiloxane, which is bonded to surface silanol groups via Si—O—Si bonds. The monolayer of the chemical is the selective self-assembling oxygen barrier layer that prevents diffusion of oxygen to a high dielectric constant material layer that is subsequently deposited as a gate dielectric.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Fabrication methods of a ZnO thin film structure and a ZnO thin film transistor, and a ZnO thin film structure and a ZnO thin film transistor
Provided is a method of fabricating a ZnO thin film structure and a ZnO thin film transistor (TFT), and a ZnO thin film structure and a ZnO thin film transistor. The method of fabricating a ZnO thin film structure may include forming a ZnO thin film on a substrate in an oxygen atmosphere, forming oxygen diffusion layers of a metal having an affinity for oxygen on the ZnO thin film and heating the ZnO thin film and the oxygen diffusion layers to diffuse oxygen of the ZnO thin film into the oxygen diffusion layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and process for forming a self-aligned silicide contact
ActiveUS20060051961A1Short lifeGood removal effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureMetal alloy
The present invention provides a method for forming a self-aligned Ni alloy silicide contact. The method of the present invention begins by first depositing a conductive Ni alloy with Pt and optionally at least one of the following metals Pd, Rh, Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, W or Re over an entire semiconductor structure which includes at least one gate stack region. An oxygen diffusion barrier comprising, for example, Ti, TiN or W is deposited over the structure to prevent oxidation of the metals. An annealing step is then employed to cause formation of a NiSi, PtSi contact in regions in which the metals are in contact with silicon. The metal that is in direct contact with insulating material such as SiO2 and Si3N4 is not converted into a metal alloy silicide contact during the annealing step. A selective etching step is then performed to remove unreacted metal from the sidewalls of the spacers and trench isolation regions.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
High-temperature stable gate structure with metallic electrode
InactiveUS20050282341A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMetallic electrodeElectrical conductor
The present invention provides a method for depositing a dielectric stack comprising forming a dielectric layer atop a substrate, the dielectric layer comprising at least oxygen and silicon atoms; forming a layer of metal atoms atop the dielectric layer within a non-oxidizing atmosphere, wherein the layer of metal atoms has a thickness of less than about 15 Å; forming an oxygen diffusion barrier atop the layer of metal atoms, wherein the non-oxidizing atmosphere is maintained; forming a gate conductor atop the oxygen diffusion barrier; and annealing the layer of metal atoms and the dielectric layer, wherein the layer of metal atoms reacts with the dielectric layer to provide a continuous metal oxide layer having a dielectric constant ranging from about 25 to about 30 and a thickness less than about 15 Å.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
High-temperature stable gate structure with metallic electrode
InactiveUS7279413B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMetallic electrodeElectrical conductor
The present invention provides a method for depositing a dielectric stack comprising forming a dielectric layer atop a substrate, the dielectric layer comprising at least oxygen and silicon atoms; forming a layer of metal atoms atop the dielectric layer within a non-oxidizing atmosphere, wherein the layer of metal atoms has a thickness of less than about 15 Å; forming an oxygen diffusion barrier atop the layer of metal atoms, wherein the non-oxidizing atmosphere is maintained; forming a gate conductor atop the oxygen diffusion barrier; and annealing the layer of metal atoms and the dielectric layer, wherein the layer of metal atoms reacts with the dielectric layer to provide a continuous metal oxide layer having a dielectric constant ranging from about 25 to about 30 and a thickness less than about 15 Å.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Engineered oxygen profile in metal gate electrode and nitrided high-k gate dielectrics structure for high performance pmos devices
ActiveUS20100052071A1Reduce diffuseImprove work functionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenLow oxygen
A PMOS transistor is disclosed which includes a nitrogen containing barrier to oxygen diffusion between a gate dielectric layer and a metal gate in the PMOS transistor, in combination with a low oxygen region of the metal gate in direct contact with the nitrogen containing barrier and an oxygen rich region of the metal gate above the low oxygen content metal region. The nitrogen containing barrier may be formed by depositing nitrogen containing barrier material on the gate dielectric layer or by nitridating a top region of the gate dielectric layer. The oxygen rich region of the metal gate may be formed by depositing oxidized metal on the low oxygen region of the metal gate or by oxidizing a top region of the low oxygen region of the metal gate.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
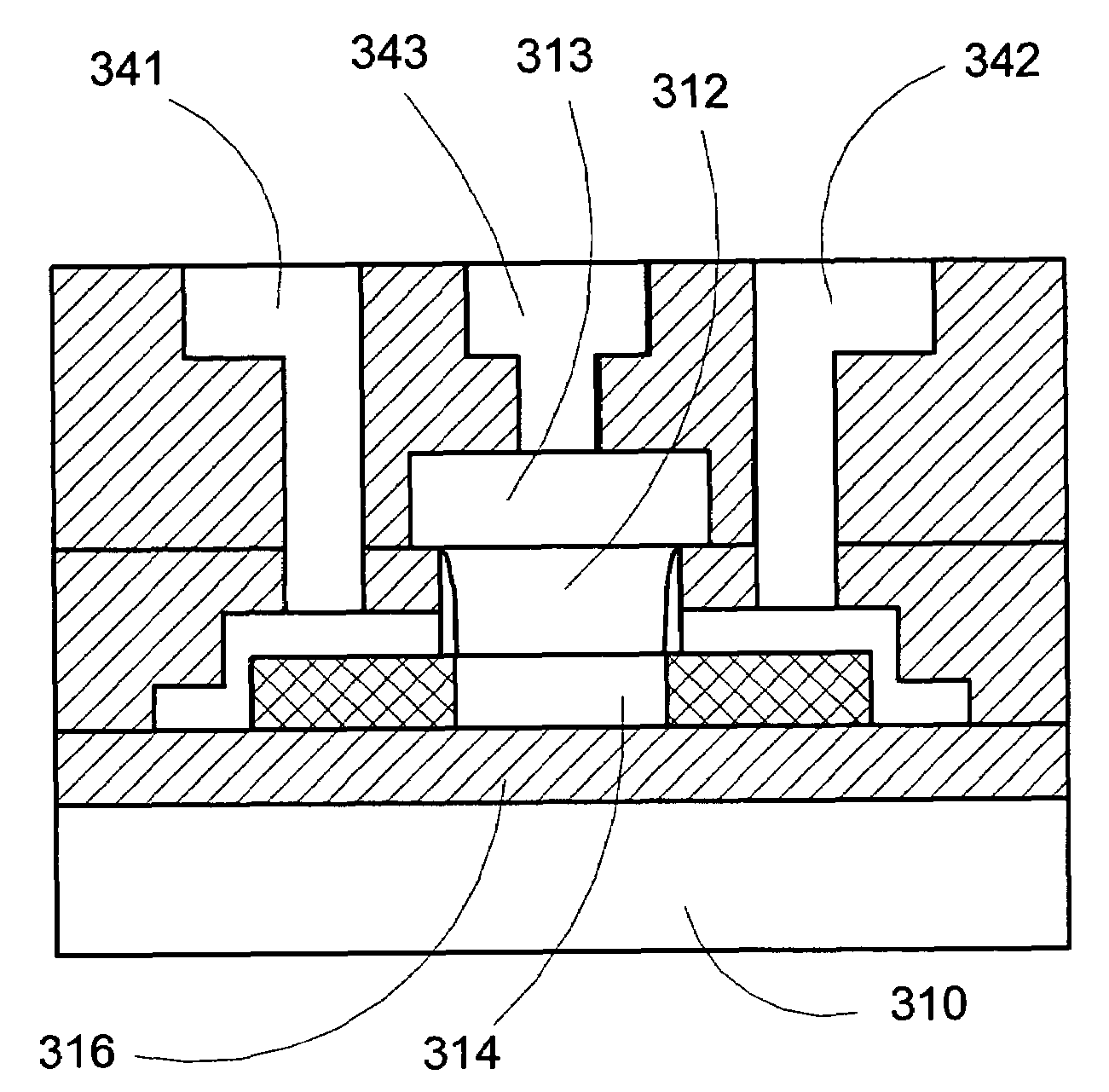
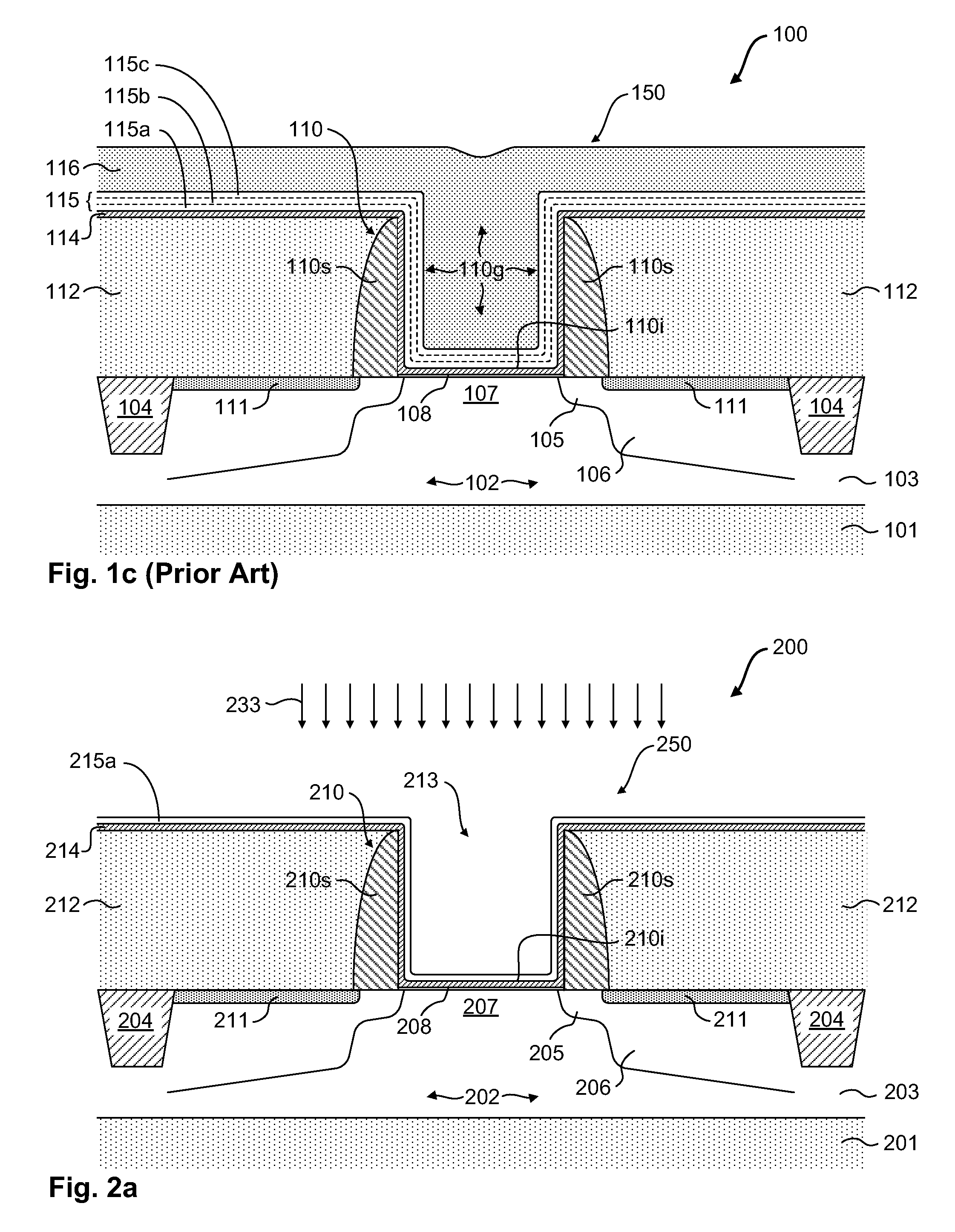
Metal Gate Stack Formation for Replacement Gate Technology
ActiveUS20120315749A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringConcentration gradient
Generally, the subject matter disclosed herein relates to modern sophisticated semiconductor devices and methods for forming the same, wherein a reduced threshold voltage (Vt) may be achieved in HK / MG transistor elements that are manufactured based on replacement gate electrode integrations. One illustrative method disclosed herein includes forming a first metal gate electrode material layer above a gate dielectric material layer having a dielectric constant of approximately 10 or greater. The method further includes exposing the first metal gate electrode material layer to an oxygen diffusion process, forming a second metal gate electrode material layer above the first metal gate electrode material layer, and adjusting an oxygen concentration gradient and a nitrogen concentration gradient in at least the first metal gate electrode material layer and the gate dielectric material layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Micro-nano-structure anode material for Li-air battery and preparation method of micro-nano-structure anode material
The invention relates to a micro-nano-structure anode material for a Li-air battery and a preparation method of the micro-nano-structure anode material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparation of hollow composite precursor fibers through electrostatic spinning by blending a metal nitride catalyst precursor with a high-carbon polymer in an organic solvent, preprocessing of the precursor fiber material, nitridation of complex fibers, and pore-forming and pore-expansion through activation. The preparation method is simple in technique and convenient to operate and is easy to realize the uniform distribution of nanoscale catalyst particles in hollow carbon fibers. A prepared anode material tube is hollow internally, a plurality of holes are formed on the wall of the tube, and metal nitride catalysts are uniformly distributed in the three-dimensional holes of the wall of the tube, so that high specific surface area provides a sufficient place for the reaction of the battery, and the hollow pore passage in the tube can ensure an oxygen diffusion channel to be smooth and has good ion transport capacity and electrical conductivity. According to the invention, the charge-discharge capacity of the Li-air battery can be improved effectively, the power multiplying performance and the power density of the Li-air battery can be improved, the internal resistance of the battery can be reduced, and the charge-discharge polarization can be lessened through the uniform distribution of the nanoscale metal nitride, therefore, the micro-nano-structure anode material has good industrialization prospect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Resistive memory device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100019219A1Improve staminaOut diffusionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A resistive memory device and a method for manufacturing the same are disclosed. The resistive memory device includes a lower electrode formed over a substrate, a resistive layer disposed over the lower electrode, an upper electrode formed over the resistive layer, and an oxygen-diffusion barrier pattern provided in an interface between the resistive layer and the upper electrode. The above-described resistive memory device and a method for manufacturing the same may prevent the out diffusion of oxygen in the interface of the upper electrode to avoid set-stuck phenomenon occurring upon the operation of the resistive memory device, thereby improving the endurance of the resistive memory device.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Modified barrier layers in liners for container closures, capable of providing varible, controlled oxygen ingress
InactiveUS20090123766A1Shortened shelf-life issuesFacilitated DiffusionDomestic sealsBottlesMetal foilCork stopper
A liner for bottle caps and method for controlling the oxygen diffusion rate of closures. The oxygen barrier layer of a laminated cap liner or seal over cork stopper for a container closure, such as a metal foil or PVDC, is provided with perforations, formed, for example, by laser. Perforations permit an increased oxygen diffusion rate as compared to conventional barrier layers having imperforate metal foil, while permitting the liner or seal to retain a lower oxygen diffusion rate as compared to other conventional liners having no oxygen barrier. The oxygen diffusion rate can be further adjusted by changing the cumulative area of perforations in the metal foil of the barrier laminate, by varying the number of perforations, or by varying the size of the individual perforations.
Owner:G3 ENTERPRISES
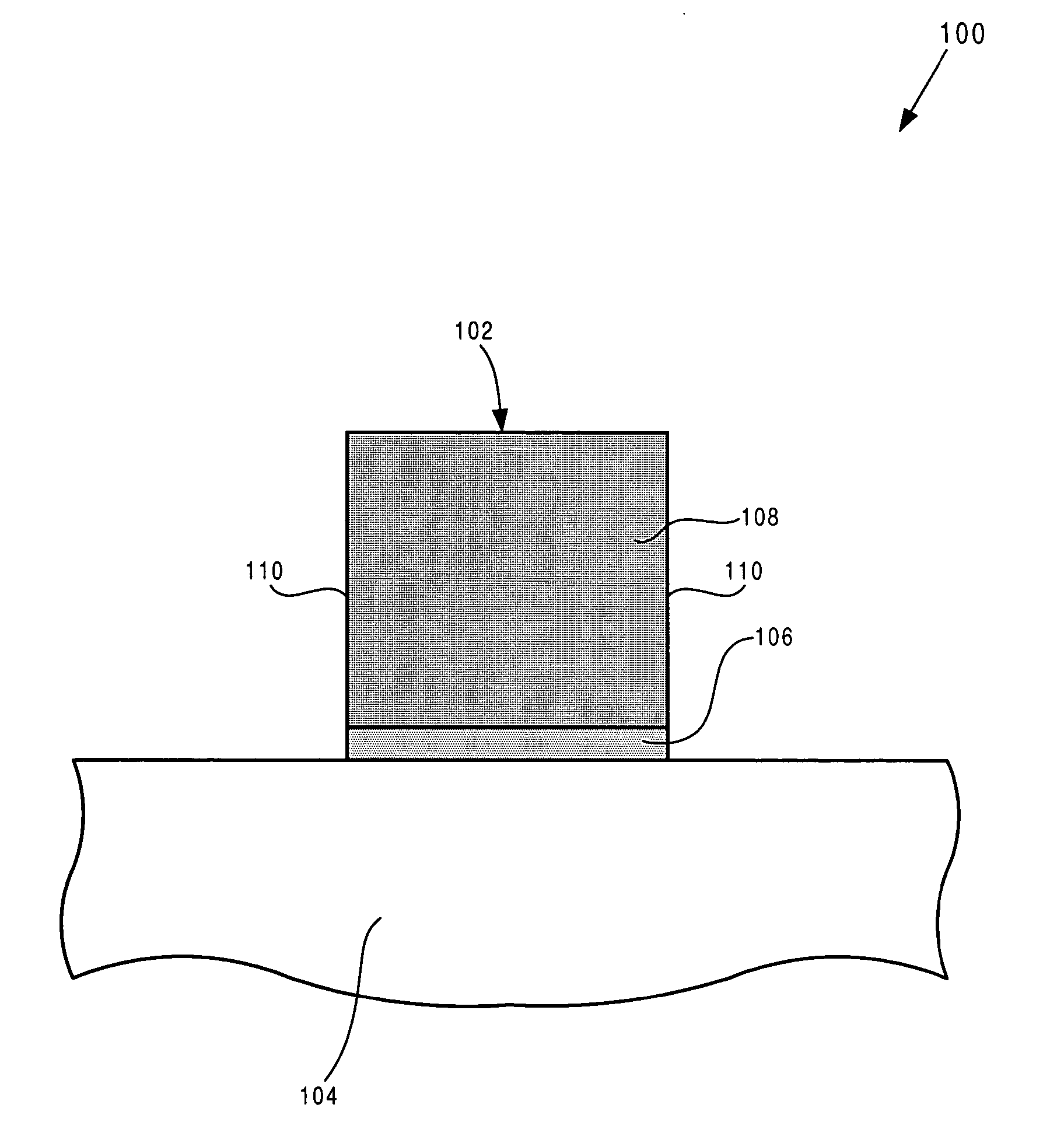
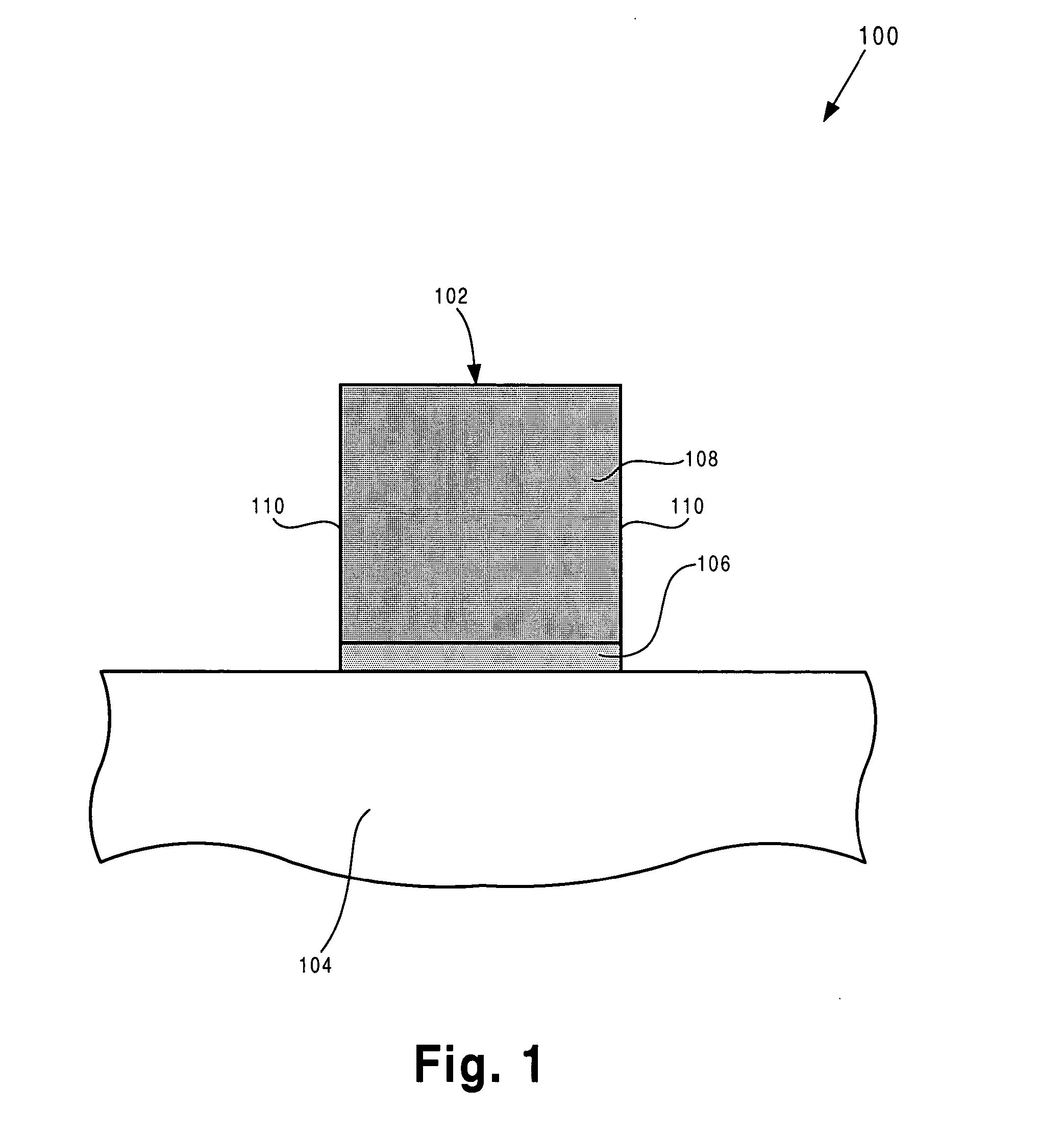
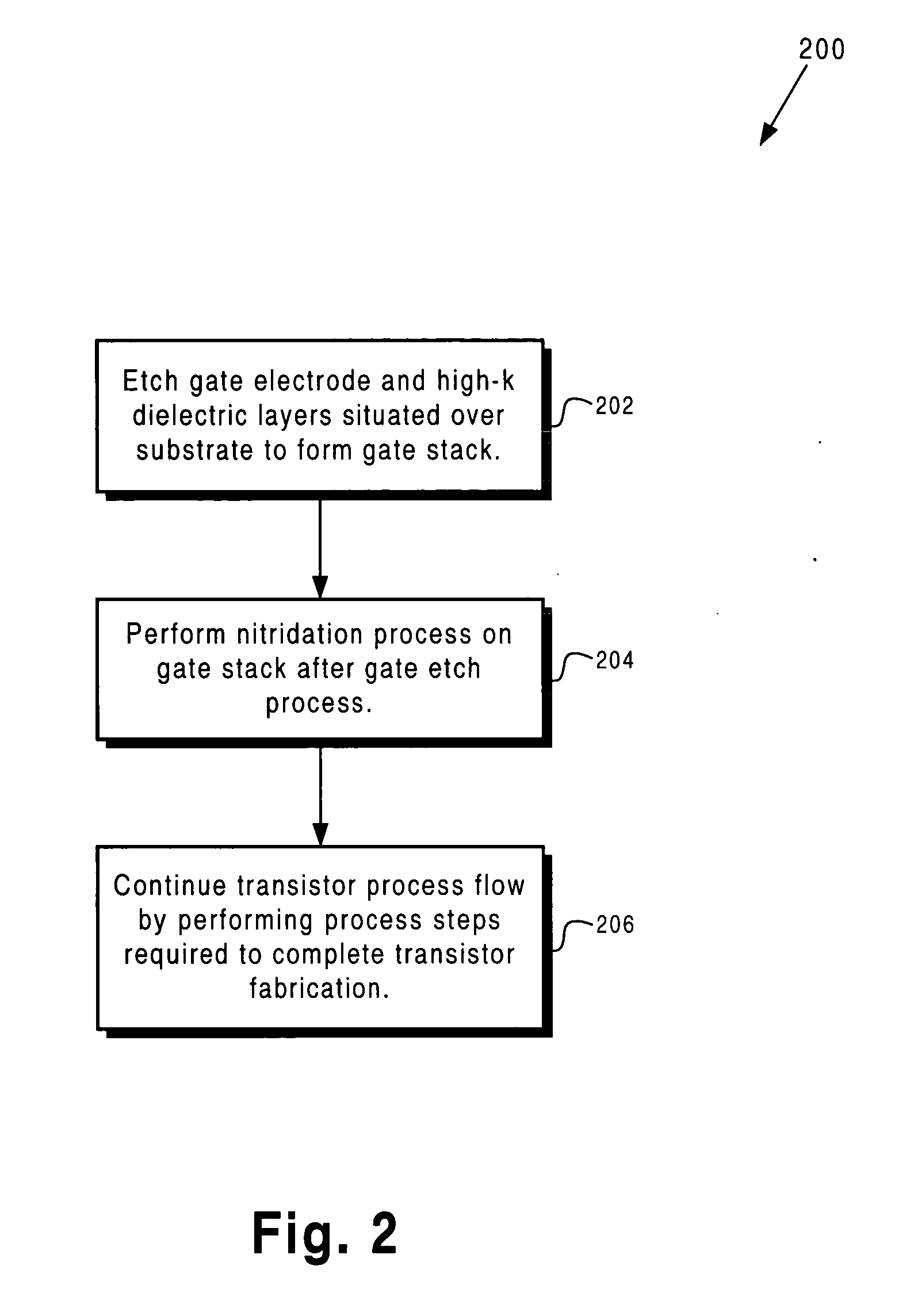
Method for integrating a high-k gate dielectric in a transistor fabrication process
InactiveUS20050101147A1Efficient integrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricNitrogen
According to one exemplary embodiment, a method for forming a field-effect transistor on a substrate, where the substrate includes a high-k dielectric layer situated over the substrate and a gate electrode layer situated over the high-k dielectric layer, comprises a step of etching the gate electrode layer and the high-k dielectric layer to form a gate stack, where the gate stack comprises a high-k dielectric segment situated over the substrate and a gate electrode segment situated over the high-k dielectric segment. According to this exemplary embodiment, the method further comprises performing a nitridation process on the gate stack. The nitridation process can be performed by, for example, utilizing a plasma to nitridate sidewalls of the gate stack, where the plasma comprises nitrogen. The nitridation process can cause nitrogen to enter the high-k dielectric segment and form an oxygen diffusion barrier in the high-k dielectric segment, for example.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
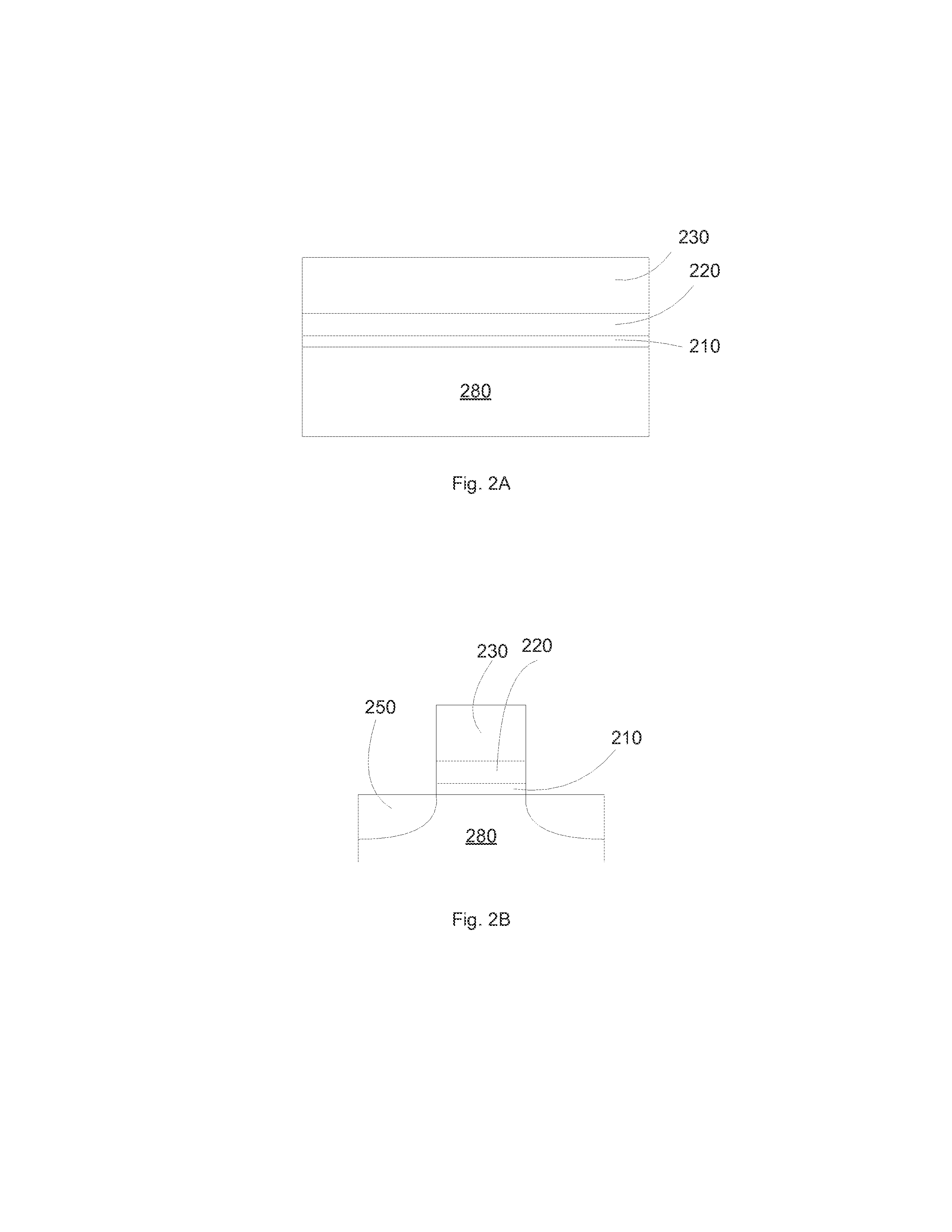
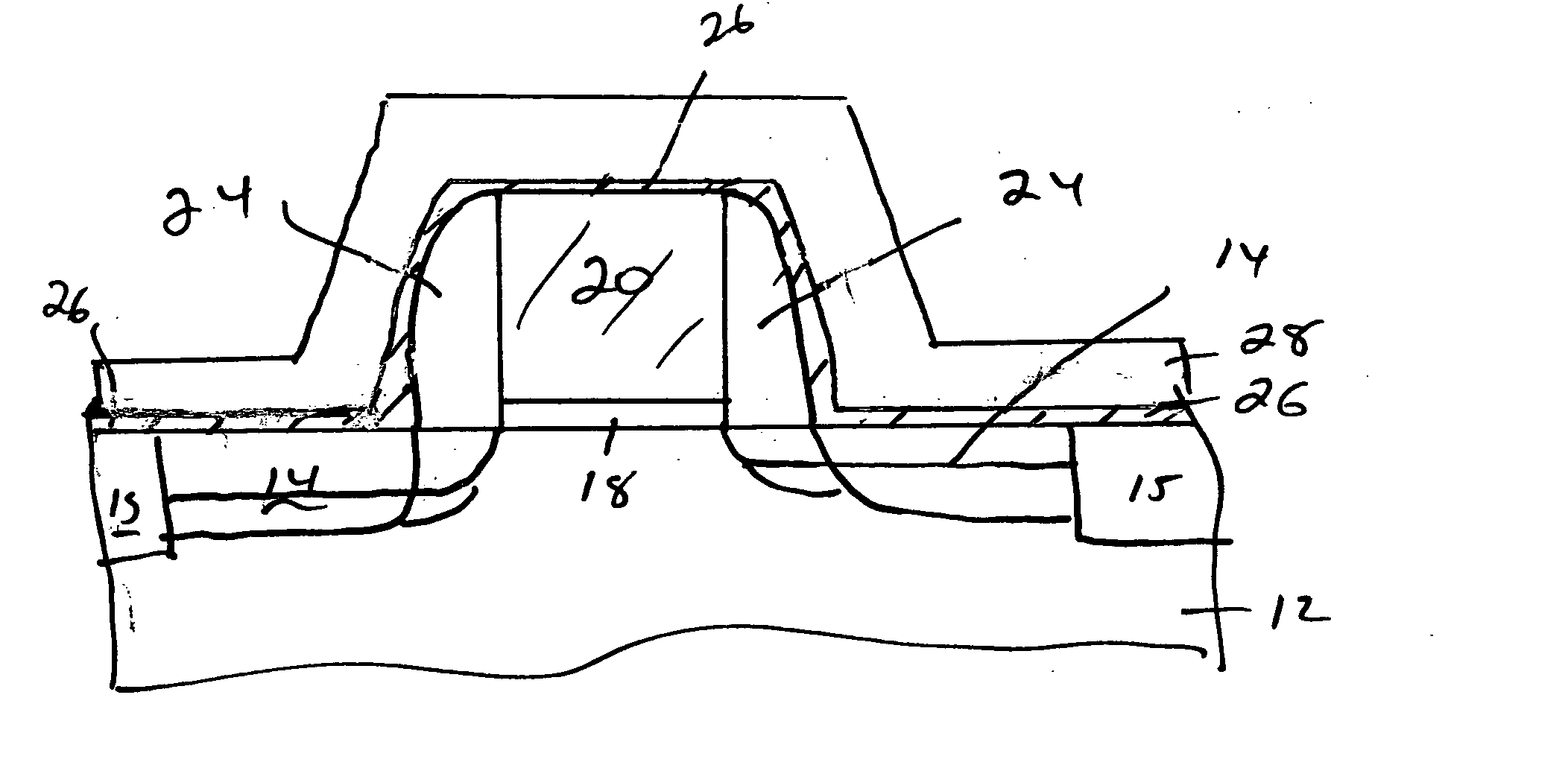
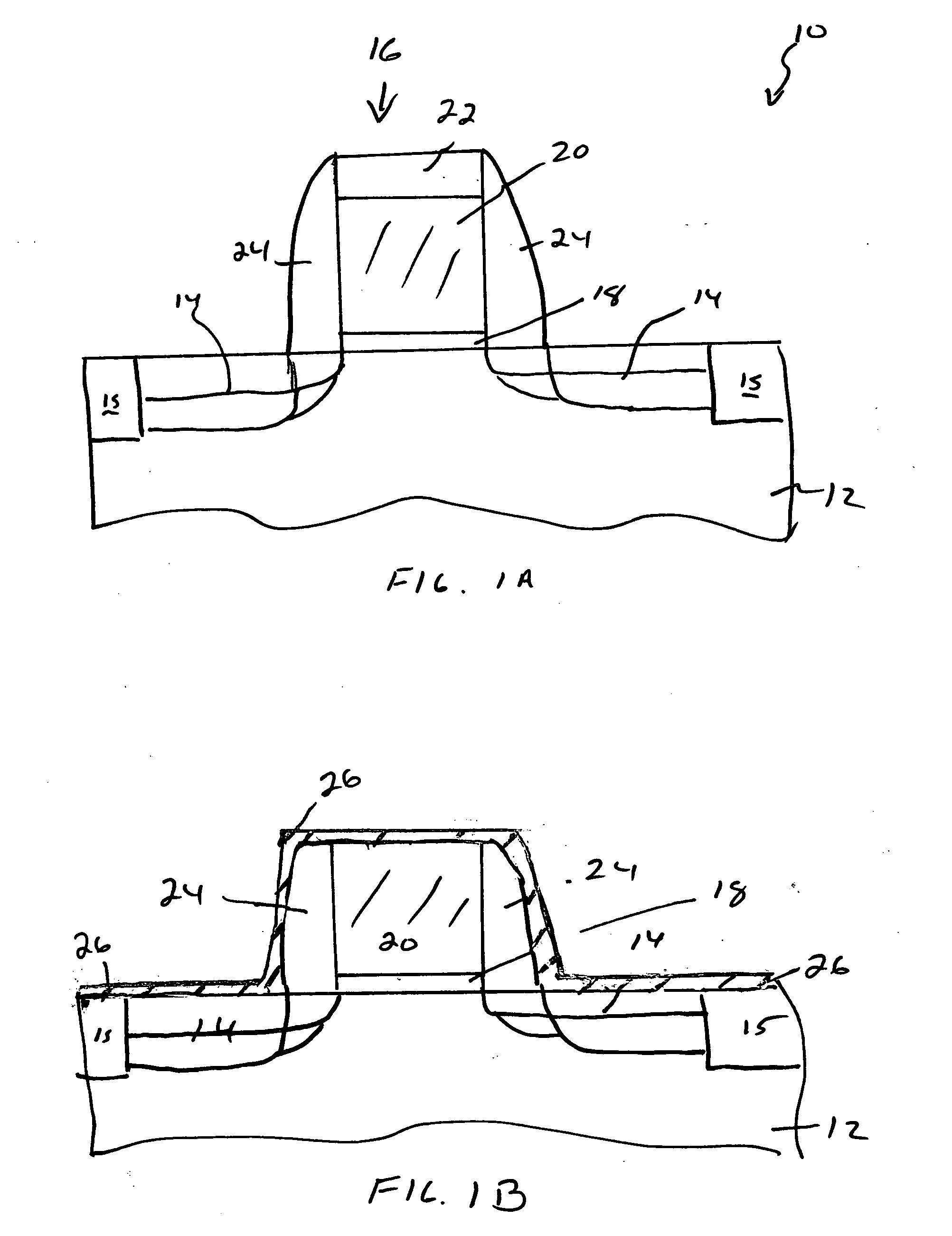
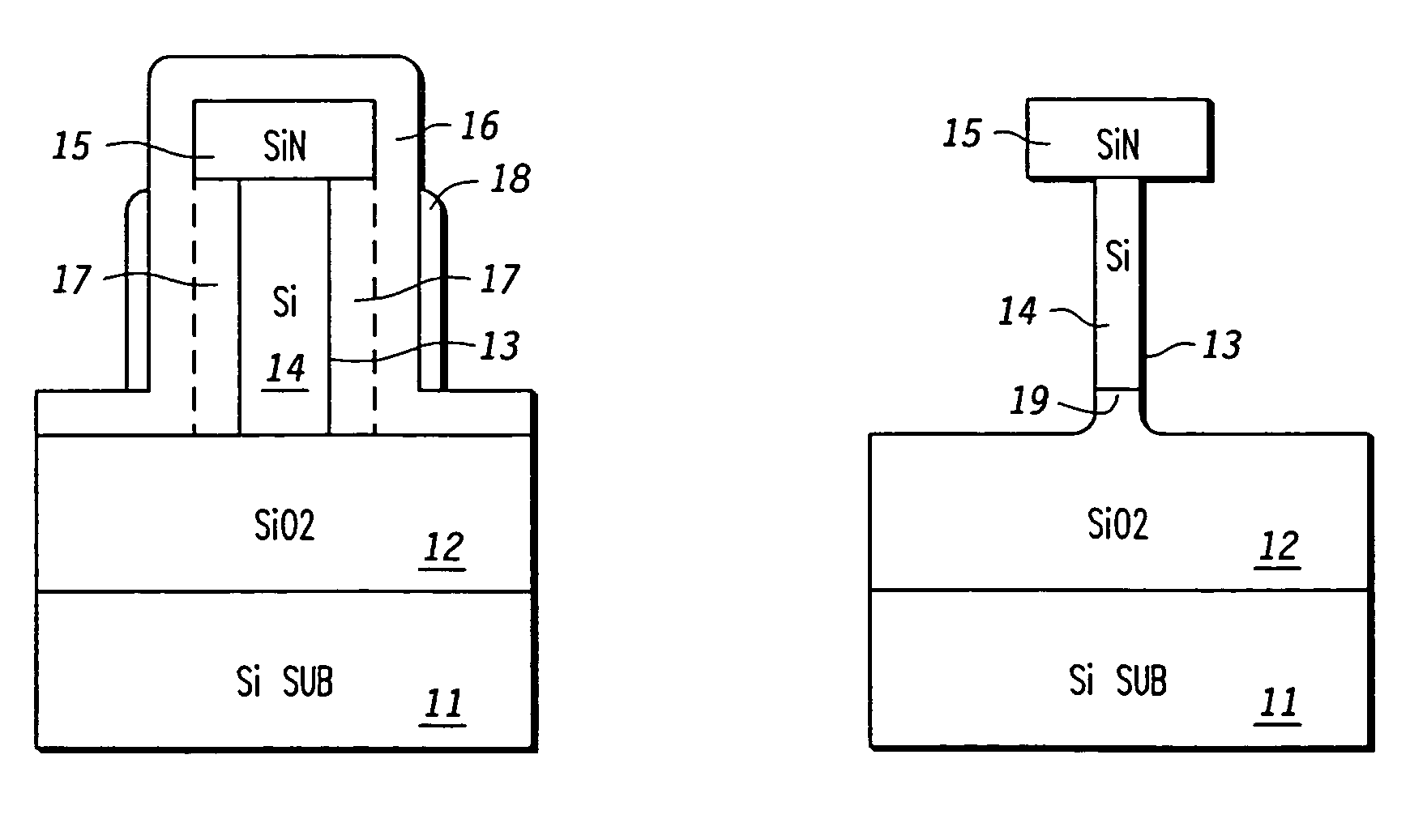
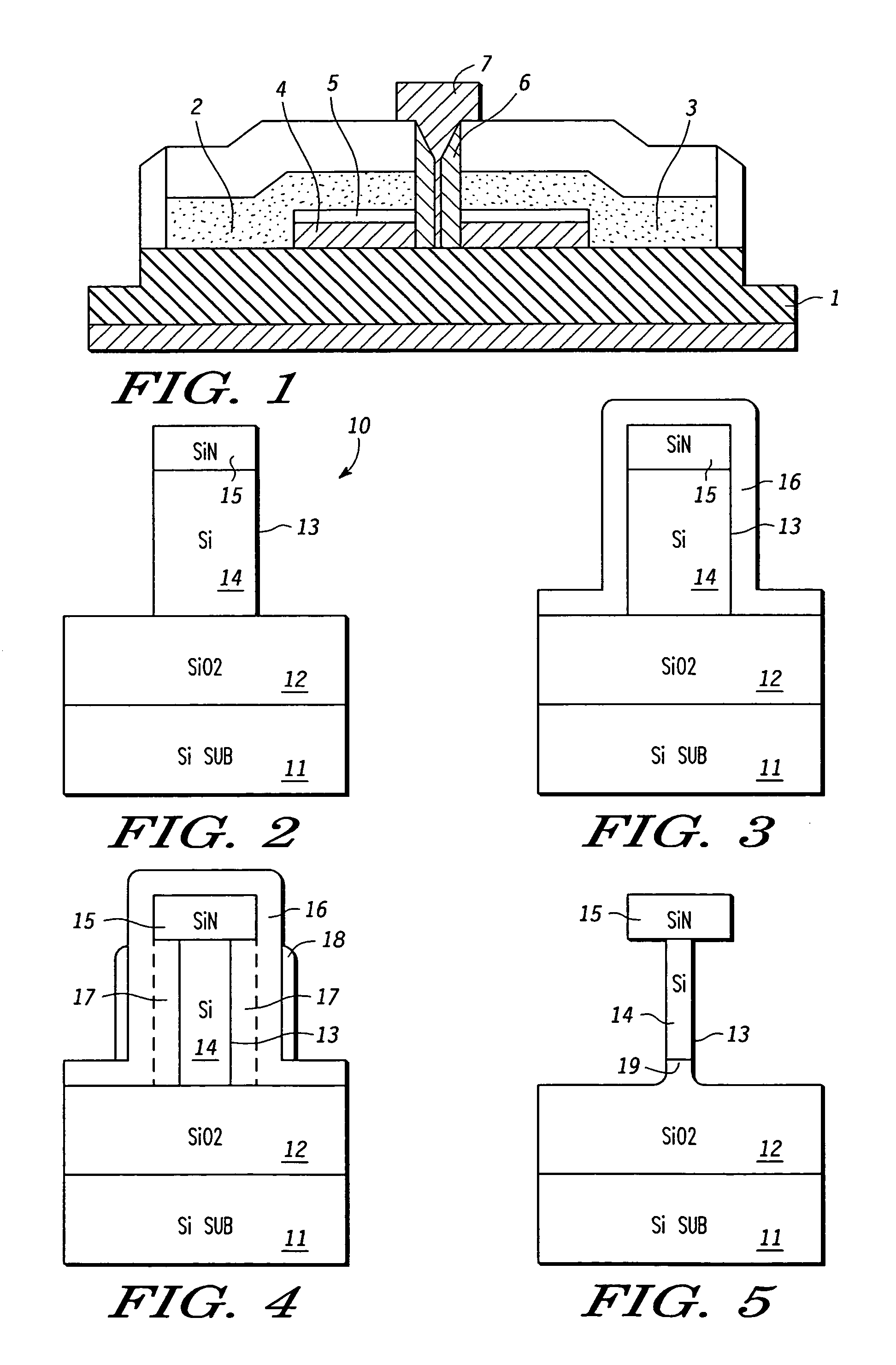
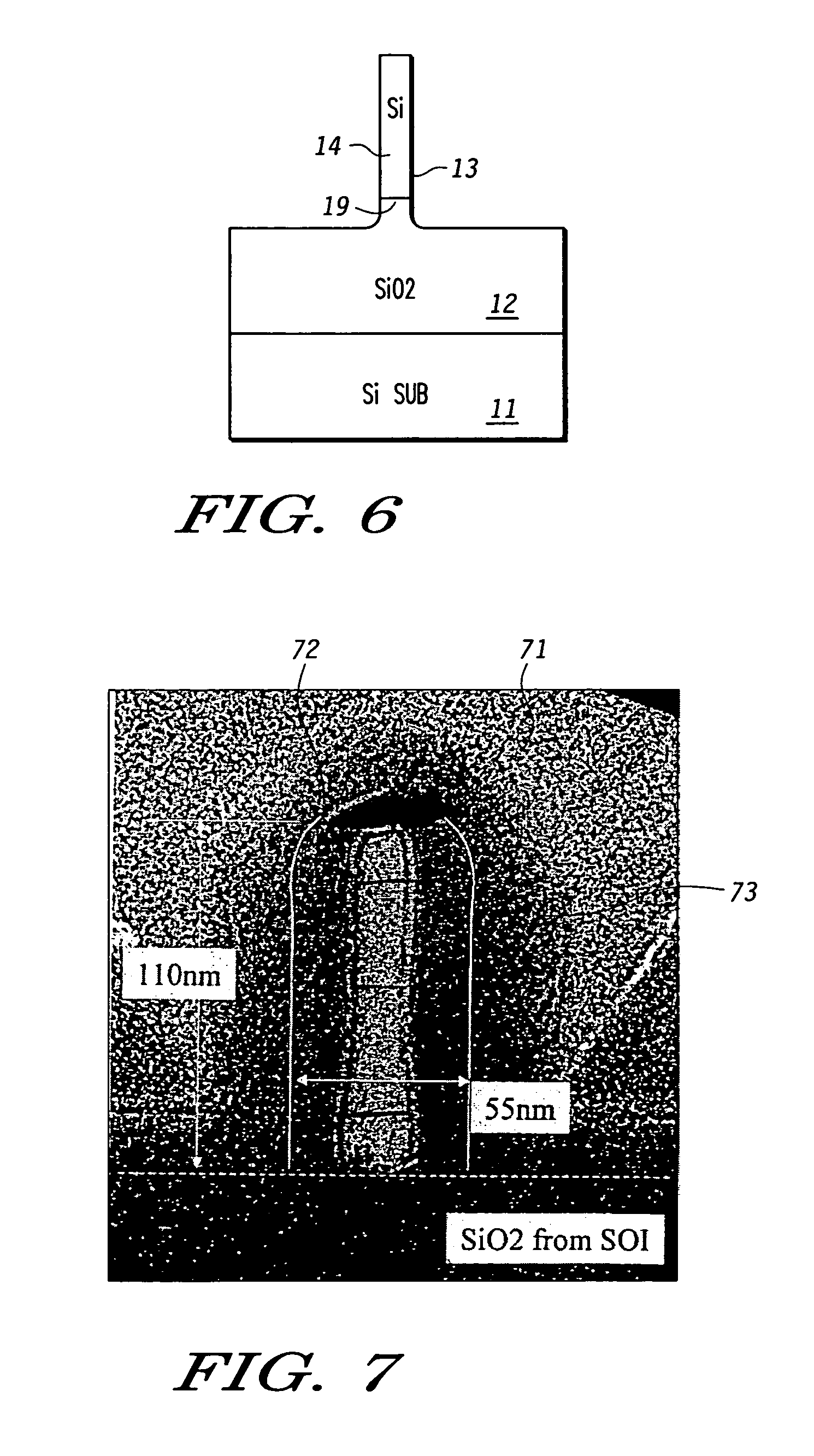
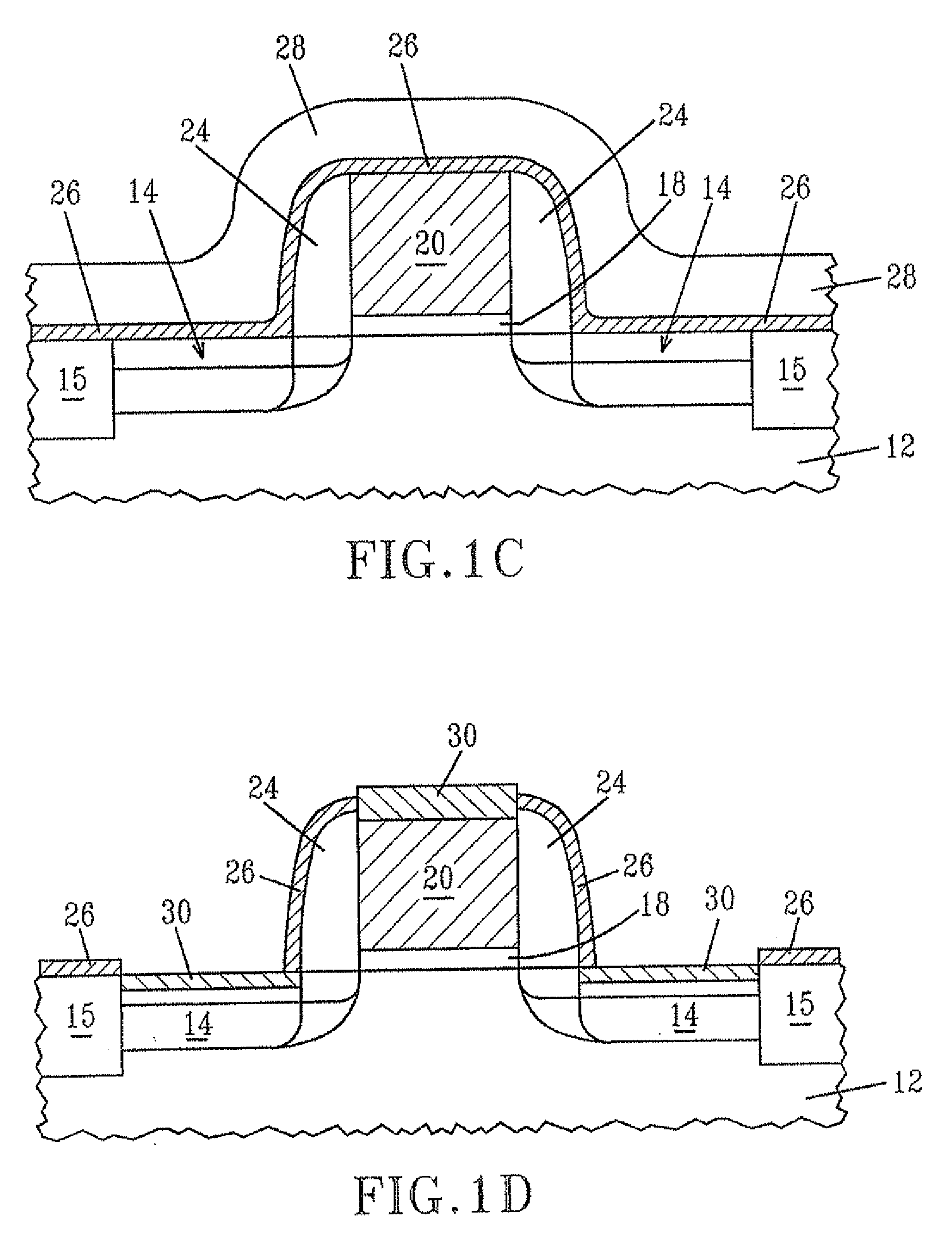
Method of fabricating three dimensional gate structure using oxygen diffusion
ActiveUS6960509B1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureSilica coating
The present invention provides a method of fabricating a silicon fin useful in preparing FinFET type semiconductor structures. The method is particularly useful for creating fins with a width and smoothness appropriate for sub-50 nm type gates. The method begins with a silicon fin prepared by lithographic means from an SOI type structure such that the fin is larger in dimension, particularly width, than is desired in the final fin. If desired the silicon fin can include a nitride cap. A conformal diffusion layer, such as of silicon dioxide, is then deposited onto the fin and silicon dioxide substrate. A PECVD deposition using TEOS gas is one method to deposit the diffusion layer. The coated fin is then heated and exposed to oxygen. The oxygen diffuses through the diffusion layer and converts a portion of the silicon material to silicon dioxide. This oxidation continues until a desired amount of silicon material is converted to SiO2 such that the remaining silicon has the desired dimensions. The silicon fin is then exposed through wet etching steps that remove the silicon dioxide coating.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Method and process for forming a self-aligned silicide contact
InactiveUS20080274611A1Short lifeGood removal effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideSemiconductor structure
The present invention provides a method for forming a self-aligned Ni alloy silicide contact. The method of the present invention begins by first depositing a conductive Ni alloy with Pt and optionally at least one of the following metals Pd, Rh, Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, W or Re over an entire semiconductor structure which includes at least one gate stack region. An oxygen diffusion barrier comprising, for example, Ti, TiN or W is deposited over the structure to prevent oxidation of the metals. An annealing step is then employed to cause formation of a NiSi, PtSi contact in regions in which the metals are in contact with silicon. The metal that is in direct contact with insulating material such as SiO2 and Si3N4 is not converted into a metal alloy silicide contact during the annealing step A selective etching step is then performed to remove unreacted metal from the sidewalls of the spacers and trench isolation regions.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Unsymmetrical lithia battery
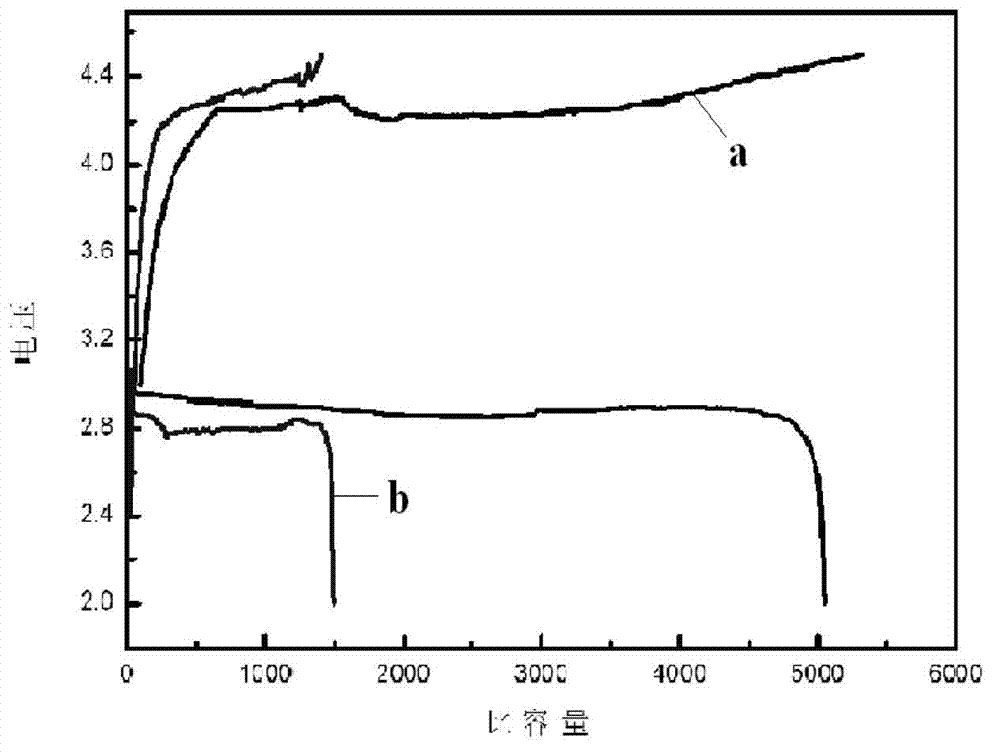
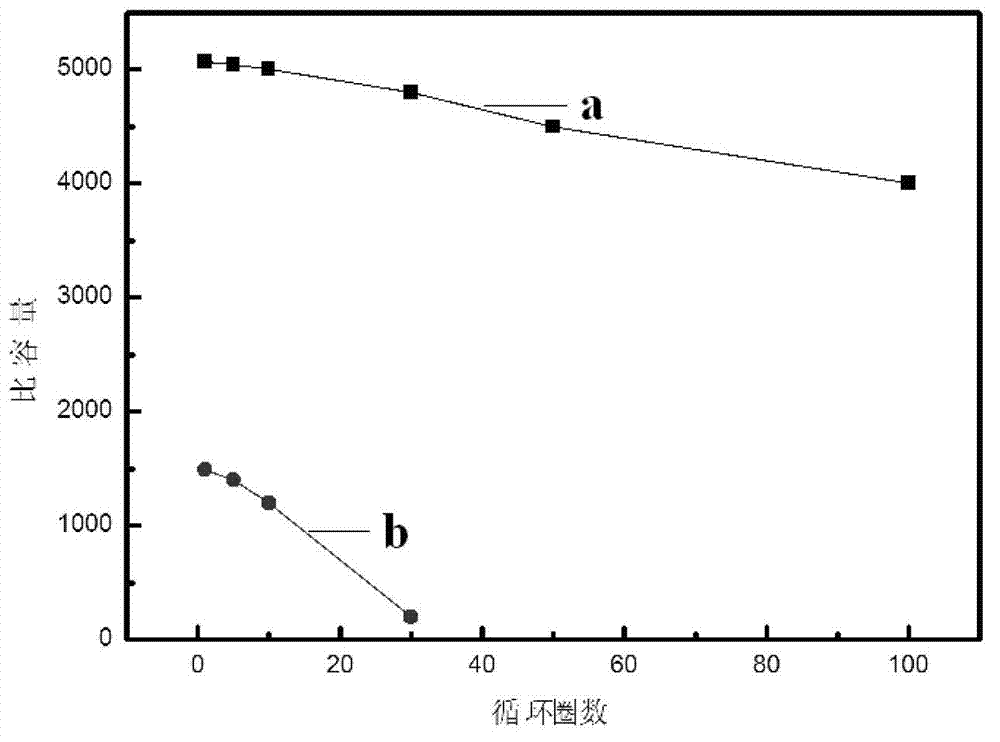
ActiveCN103035979AIncrease capacitySolving Safety Concerns of Piercing Battery SeparatorsFuel and secondary cellsCell electrodesPorous carbonPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses an unsymmetrical lithia battery. The battery takes lithium peroxide as a positive pole active material, lithium peroxide and a catalyst which are uniformly mixed are loaded on a porous carbon material so as to form a positive pole, the material capable of realizing deintercalation of lithium ions is taken a negative pole, and the weight content of lithium peroxide is 1-50% in a composite material. According to the invention, the discharging product lithium peroxide of the traditional lithia battery is directly used as the positive pole active material, the pole material of the traditional lithium ion battery, which is capable of realizing deintercalation of lithium ions, is taken as the negative pole, the damage of negative pole lithium dendrites of a lithia battery to the battery is solved, and meanwhile, the controllable distribution of the discharging product is realized, an unblocked oxygen diffusion channel is guaranteed, and the charge-discharge capacity and cycle performance of the lithia battery are effectively improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
High-temperature stable gate structure with metallic electrode
The present invention provides a method for depositing a dielectric stack comprising forming a dielectric layer atop a substrate, the dielectric layer comprising at least oxygen and silicon atoms; forming a layer of metal atoms atop the dielectric layer within a non-oxidizing atmosphere, wherein the layer of metal atoms has a thickness of less than about 15 Å; forming an oxygen diffusion barrier atop the layer of metal atoms, wherein the non-oxidizing atmosphere is maintained; forming a gate conductor atop the oxygen diffusion barrier; and annealing the layer of metal atoms and the dielectric layer, wherein the layer of metal atoms reacts with the dielectric layer to provide a continuous metal oxide layer having a dielectric constant ranging from about 25 to about 30 and a thickness less than about 15 Å.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
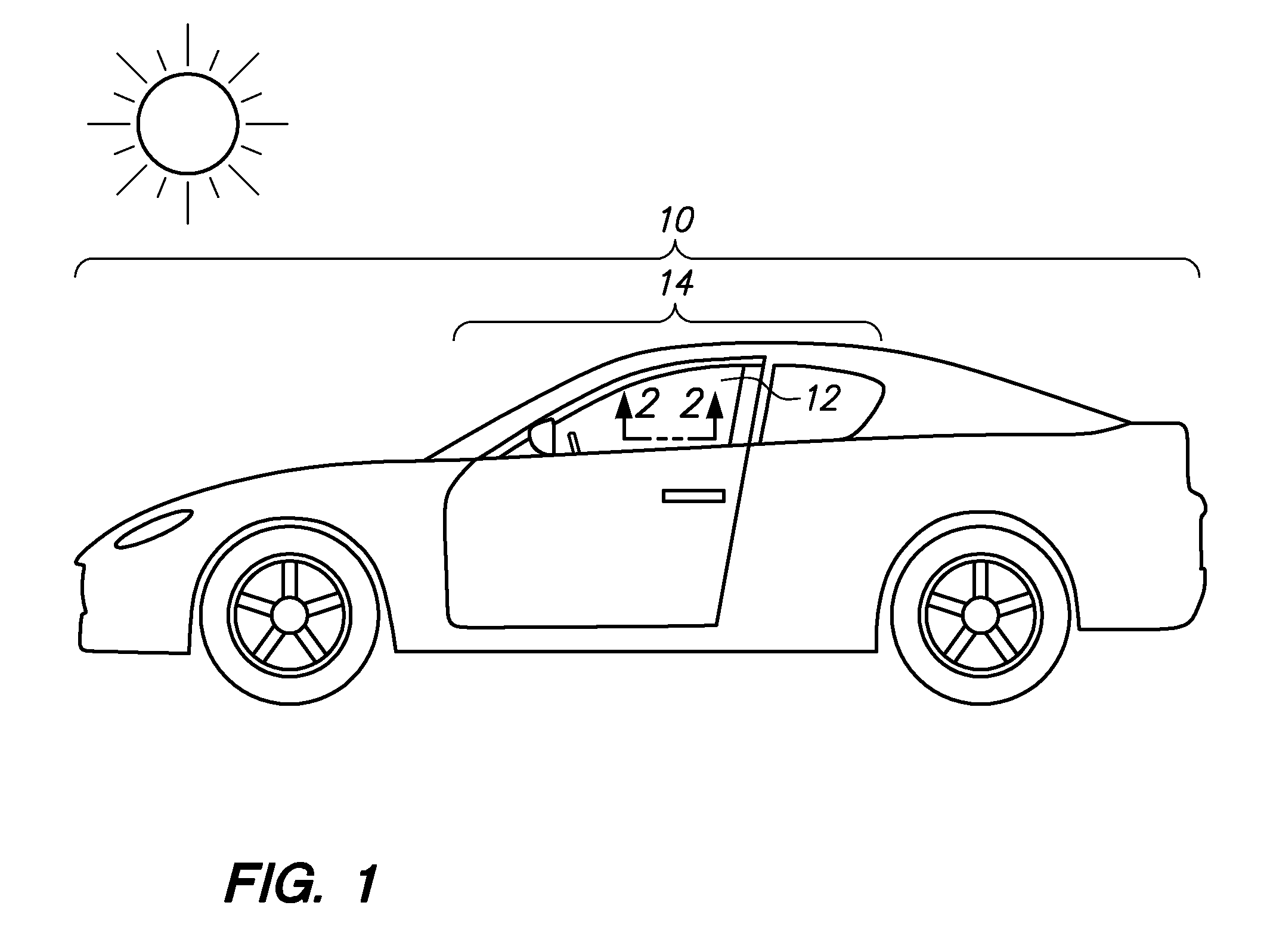
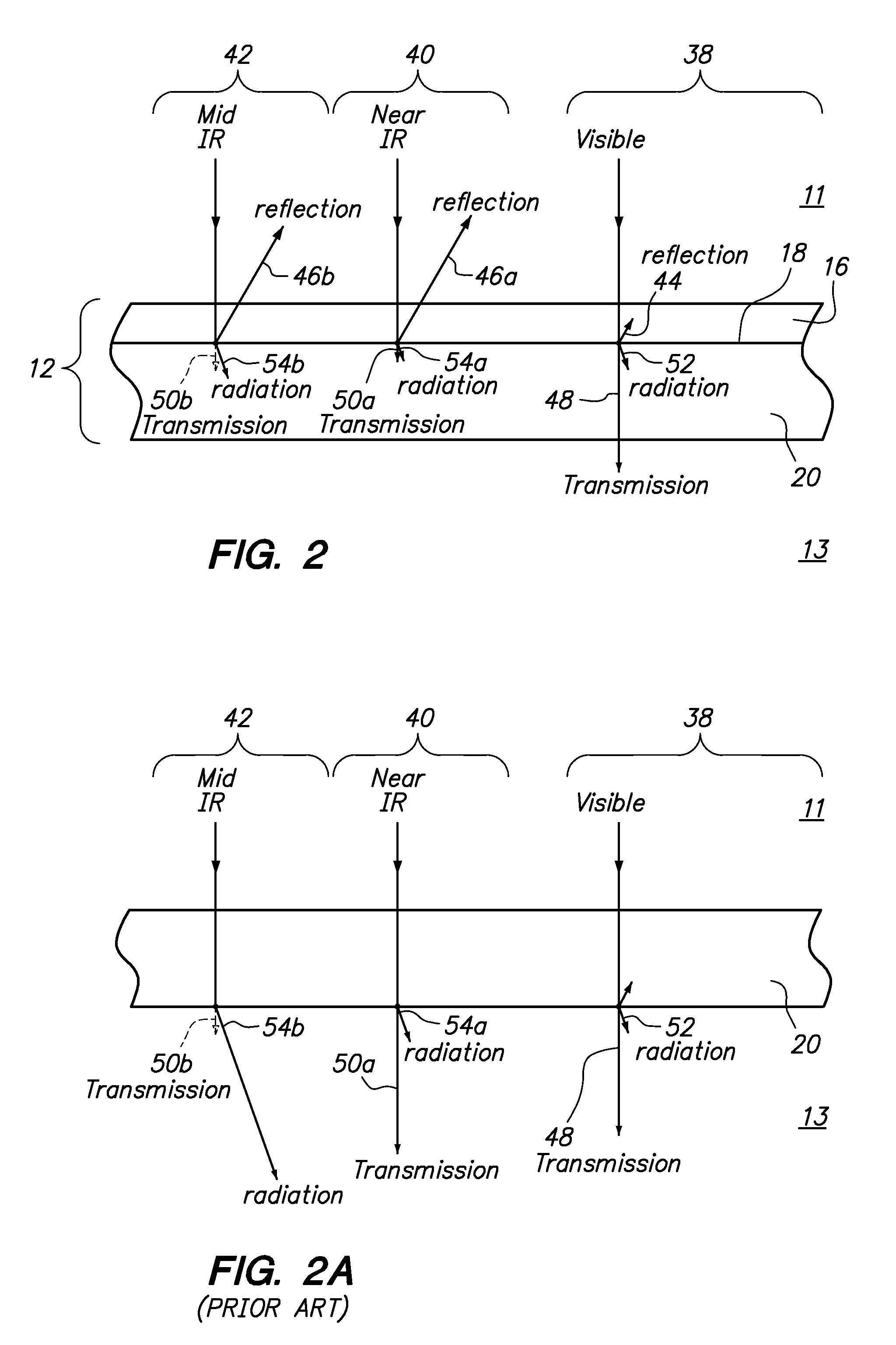
Vehicles Having a High Efficiency Solar Control System
InactiveUS20110007388A1Improve efficiencyHigh light transmittanceWindowsMirrorsControl systemBlack body
An automobile or vehicle having a high efficiency solar control system is provided. The automobile may have a window defined by a sheet of glass and a film mounted to its exterior side. The film may reflect solar radiation in the near and mid infrared ranges yet allow high transmission of light in the visible range such that the occupants of the automobile may view his / her surroundings through the window. The film may have a layer of silver which reflects the solar radiation in the near and mid infrared ranges. Since the silver is susceptible to oxidation and turns the silver into a black body which absorbs the near and mid infrared radiation, the film may be designed to slow the rate of oxidation of the silver layer to an acceptable level. The silver layer may be sandwiched between the glass which does not allow oxygen to diffuse there through and reach the layer of silver and a stack of sacrificial layers having a certain thickness which slows down the rate of oxygen diffusion to an acceptable level.
Owner:WILSON STEPHEN S +2
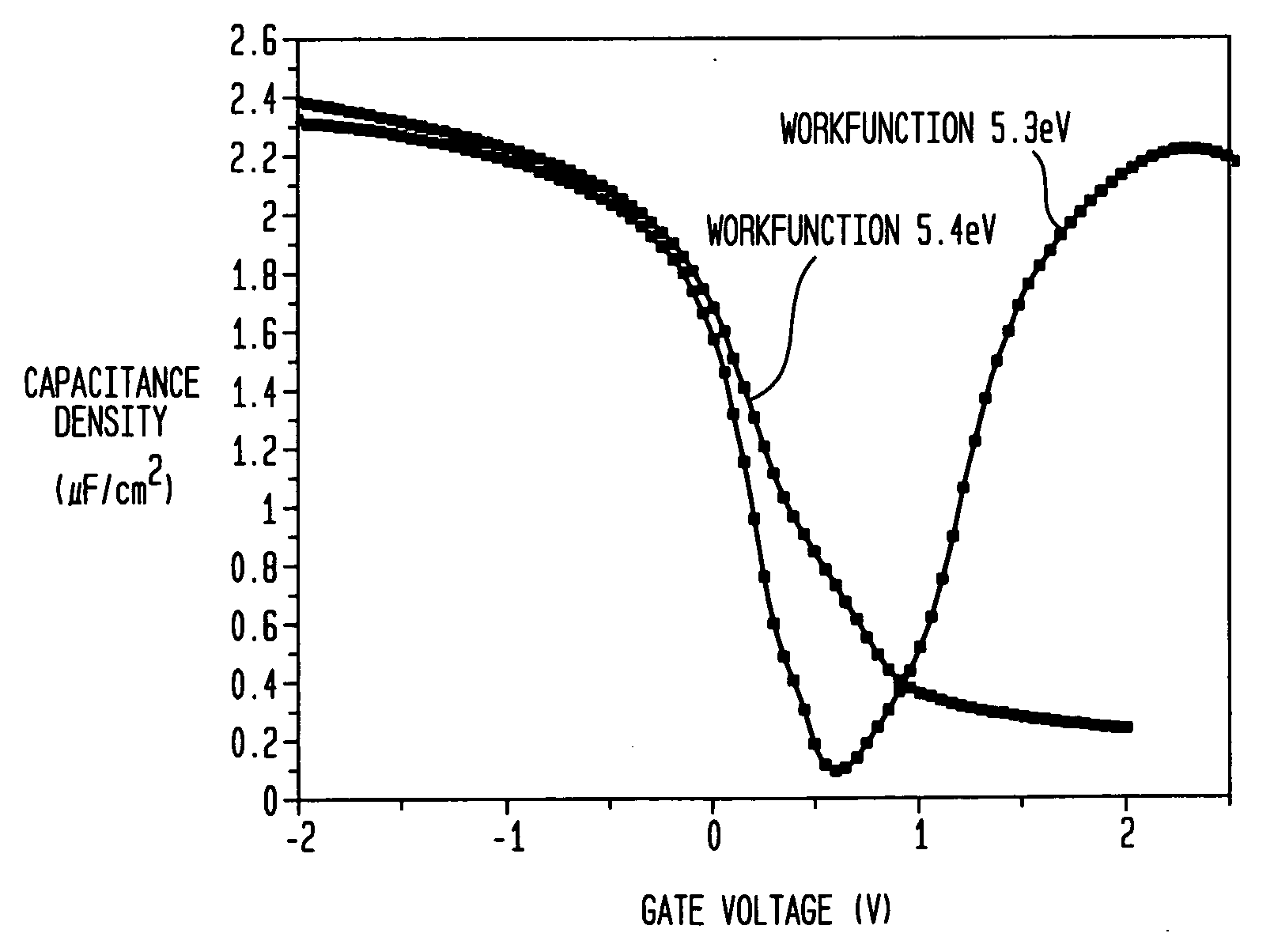
Metal oxynitride as a pFET material
ActiveUS20070138578A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricEquivalent oxide thickness
A compound metal comprising MOxNy which is a p-type metal having a workfunction of about 4.75 to about 5.3, preferably about 5, eV that is thermally stable on a gate stack comprising a high k dielectric and an interfacial layer is provided as well as a method of fabricating the MOxNy compound metal. Furthermore, the MOxNy metal compound of the present invention is a very efficient oxygen diffusion barrier at 1000° C. allowing very aggressive equivalent oxide thickness (EOT) and inversion layer thickness scaling below 14 Å in a p-metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) device. In the above formula, M is a metal selected from Group IVB, VB, VIB or VIIB of the Periodic Table of Elements, x is from about 5 to about 40 atomic % and y is from about 5 to about 40 atomic %.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
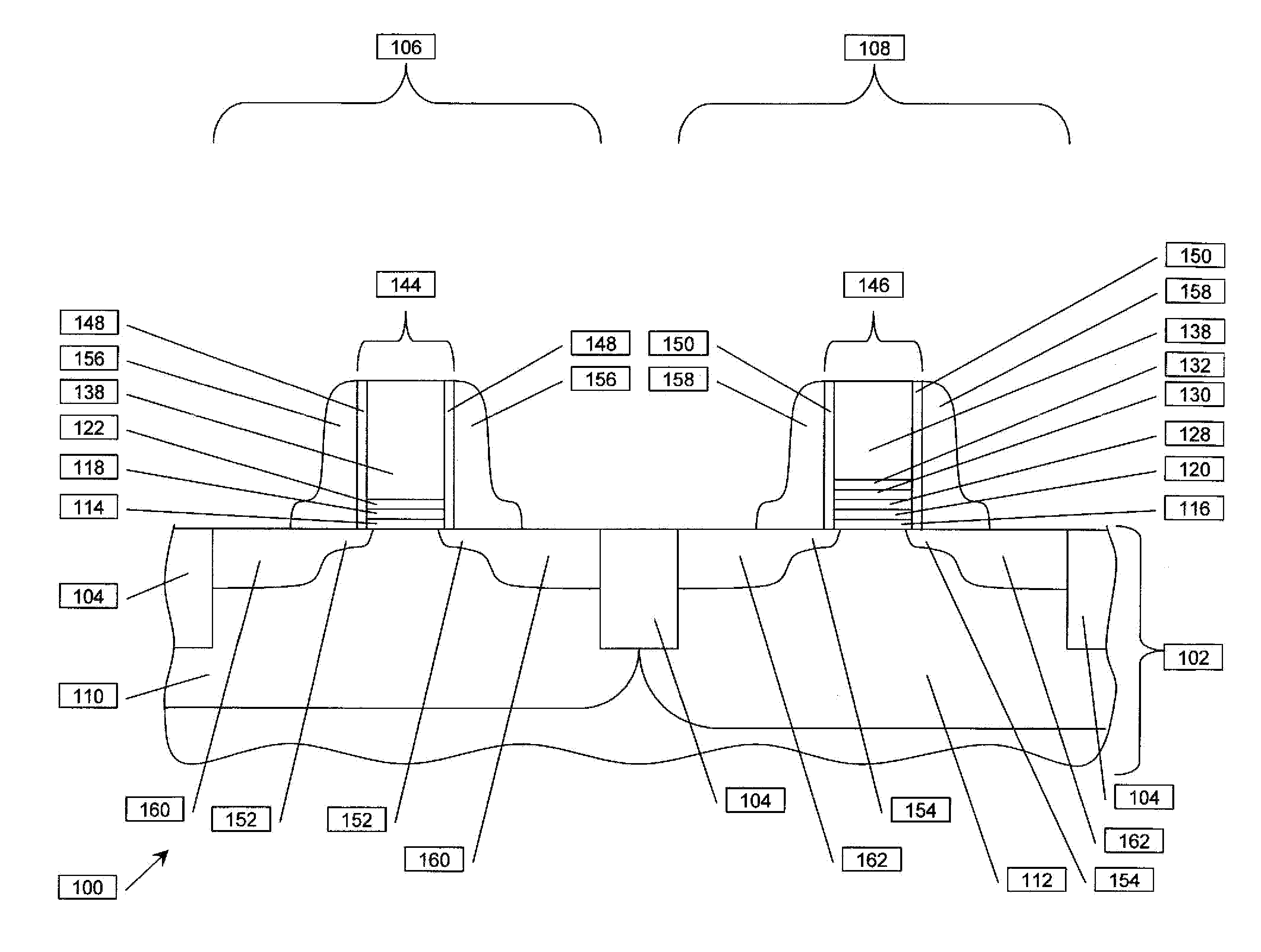
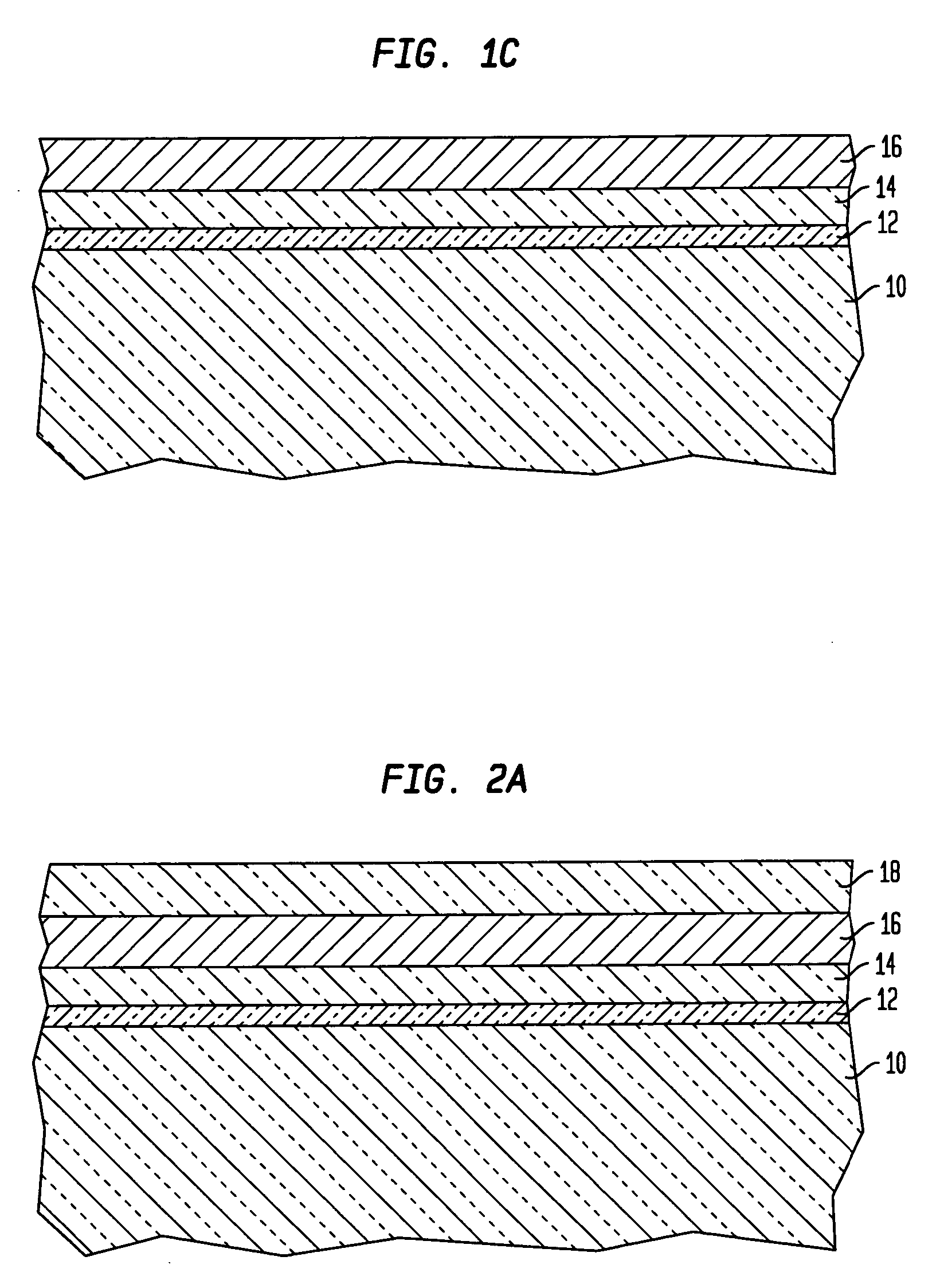
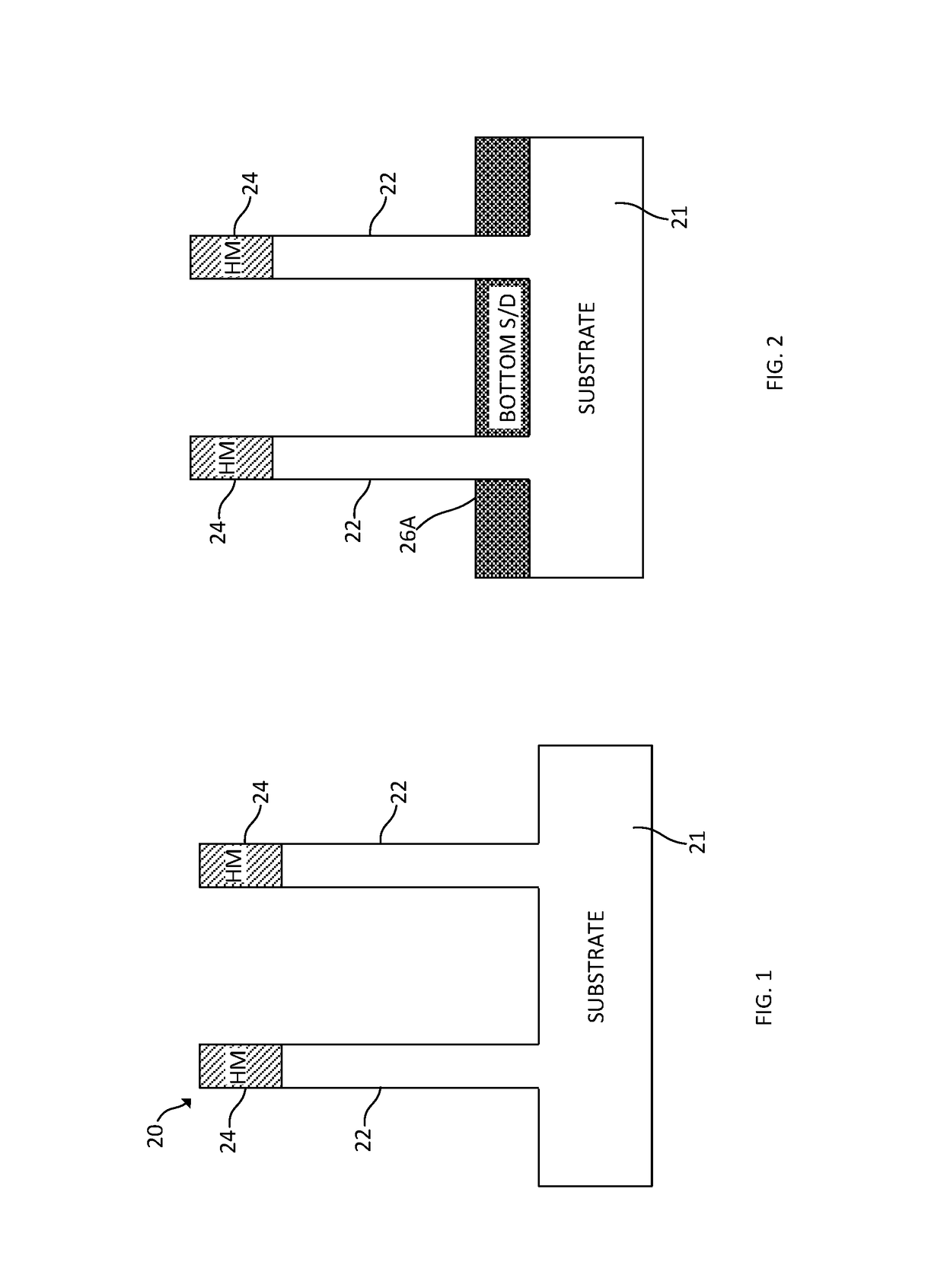
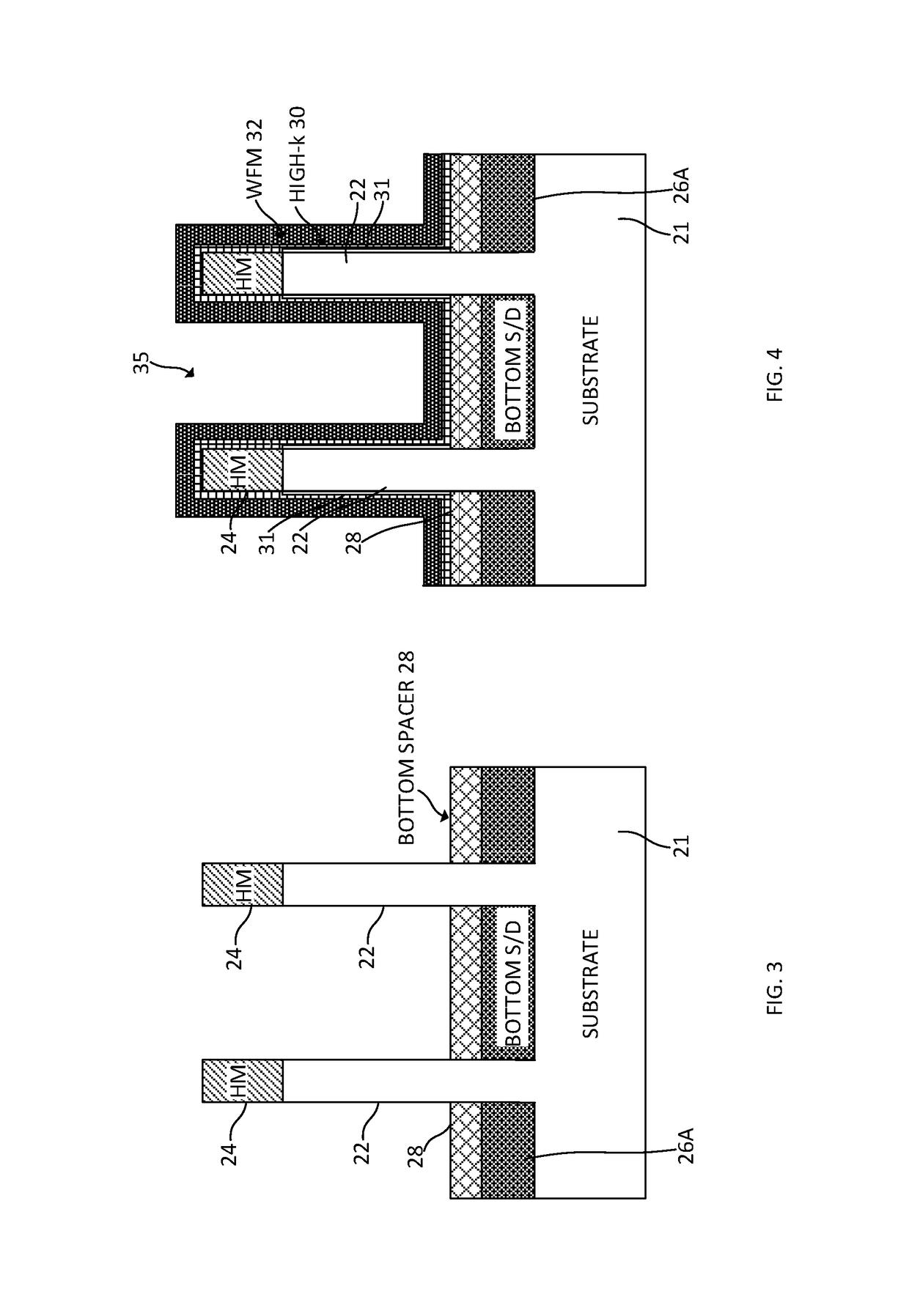
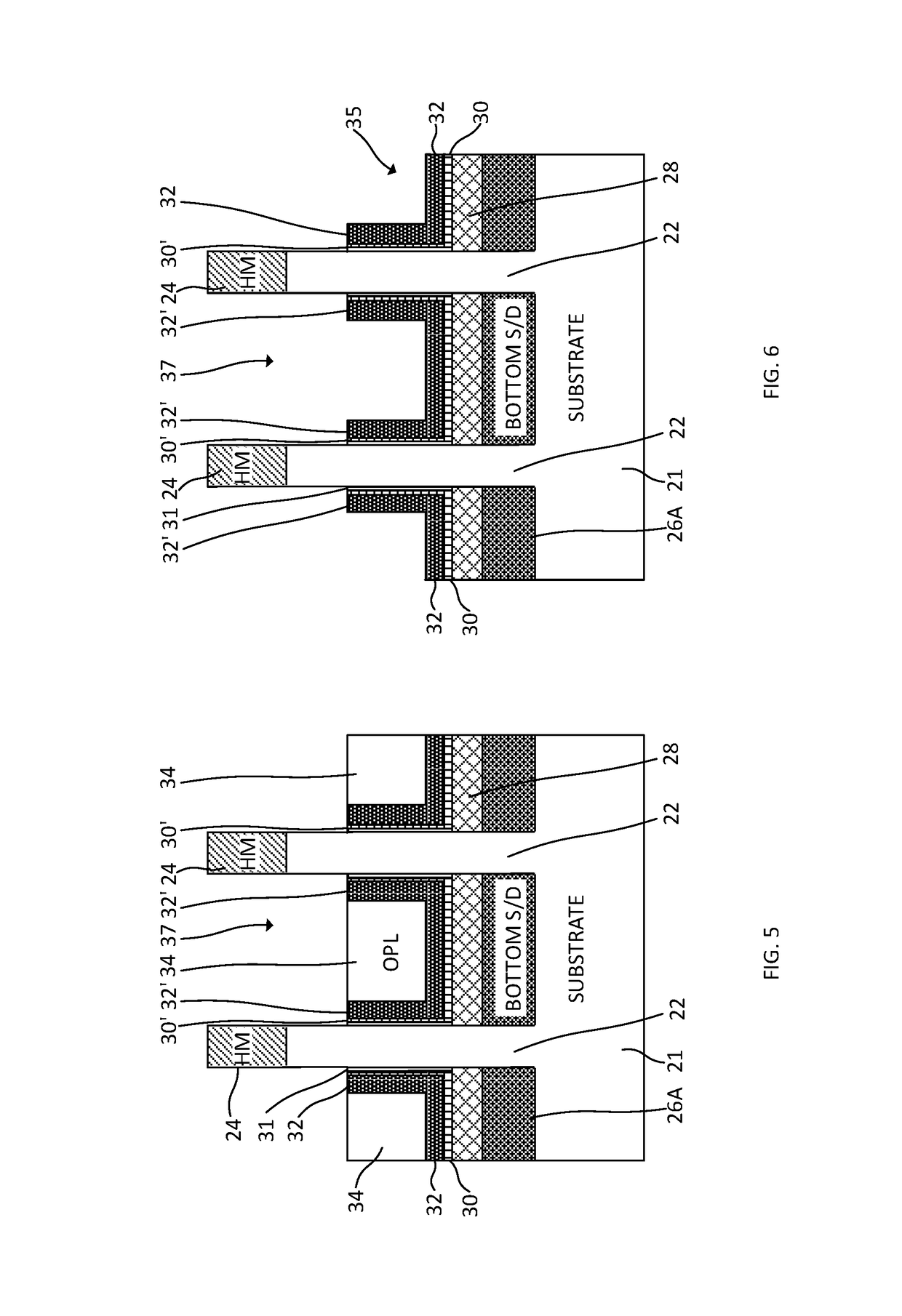
Vertical transport field-effect transistor including dual layer top spacer
ActiveUS10229986B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate stackEngineering
A vertical transport field-effect transistor includes a top source / drain region separated from an underlying gate stack by a multi-layer top spacer that includes an oxygen barrier layer beneath a top dielectric layer. Techniques for fabricating the transistor include depositing the oxygen barrier layer over the gate stack prior to depositing the top dielectric layer. The oxygen barrier layer blocks oxygen diffusion during deposition of the top dielectric layer, thereby avoiding damage to underlying interfacial and gate dielectric layers.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for forming CoWRe alloys by electroless deposition
InactiveUS7205233B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingRheniumElectroless deposition
A method for fabricating a capping layer with enhanced barrier resistance to both copper and oxygen diffusion, comprises forming a capping layer on a conductive surface of an interconnect, wherein the capping layer comprises cobalt (Co), tungsten (W), rhenium (Re), and at least one of phosphorus (P) and boron (B). In an embodiment of the invention, forming the capping layer comprises exposing the conductive surface to an electroless capping solution comprising a cobalt source, a tungsten source, a rhenium source, and at least one of a phosphorus source and a boron source, and annealing the capping layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
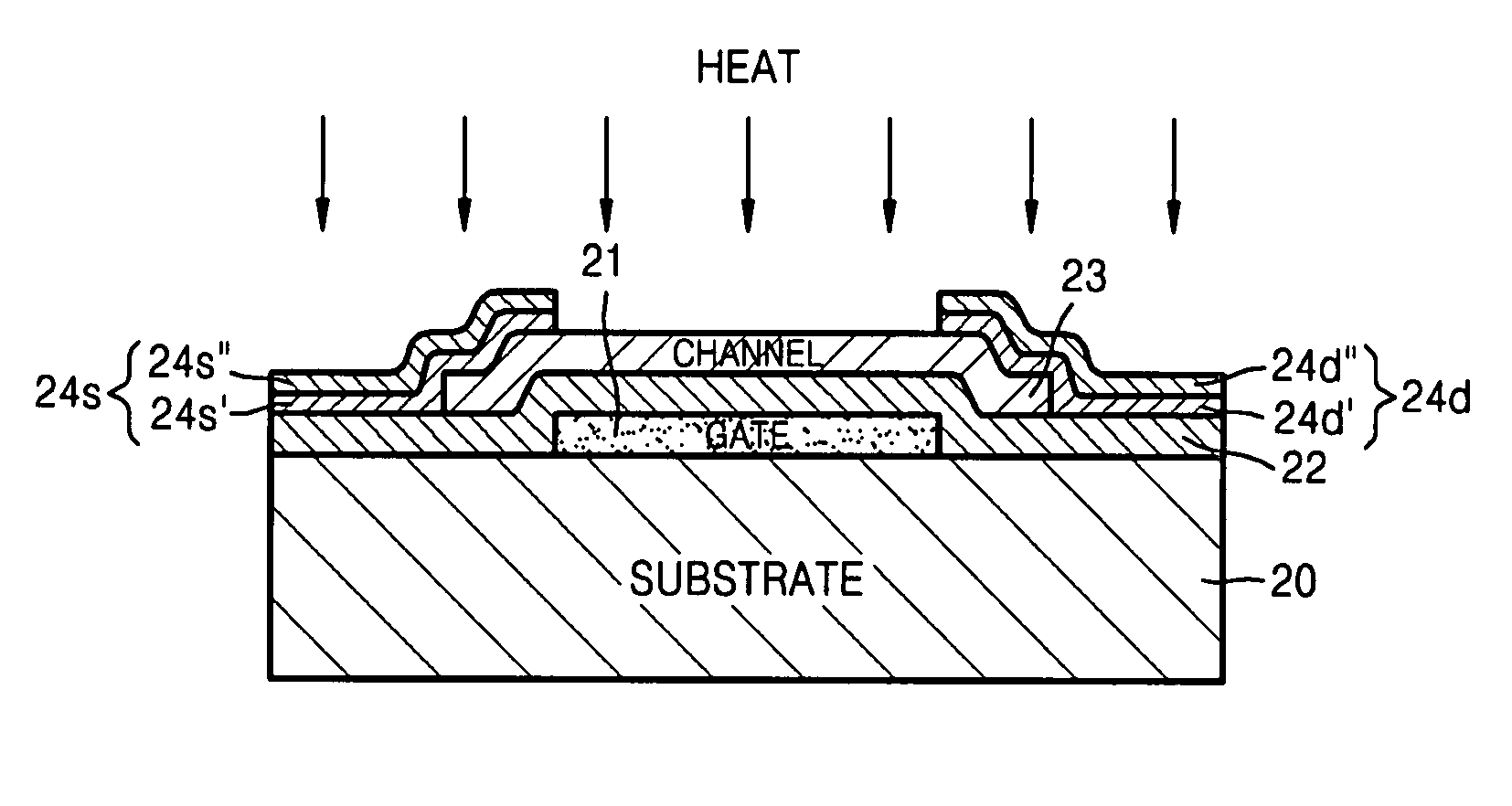
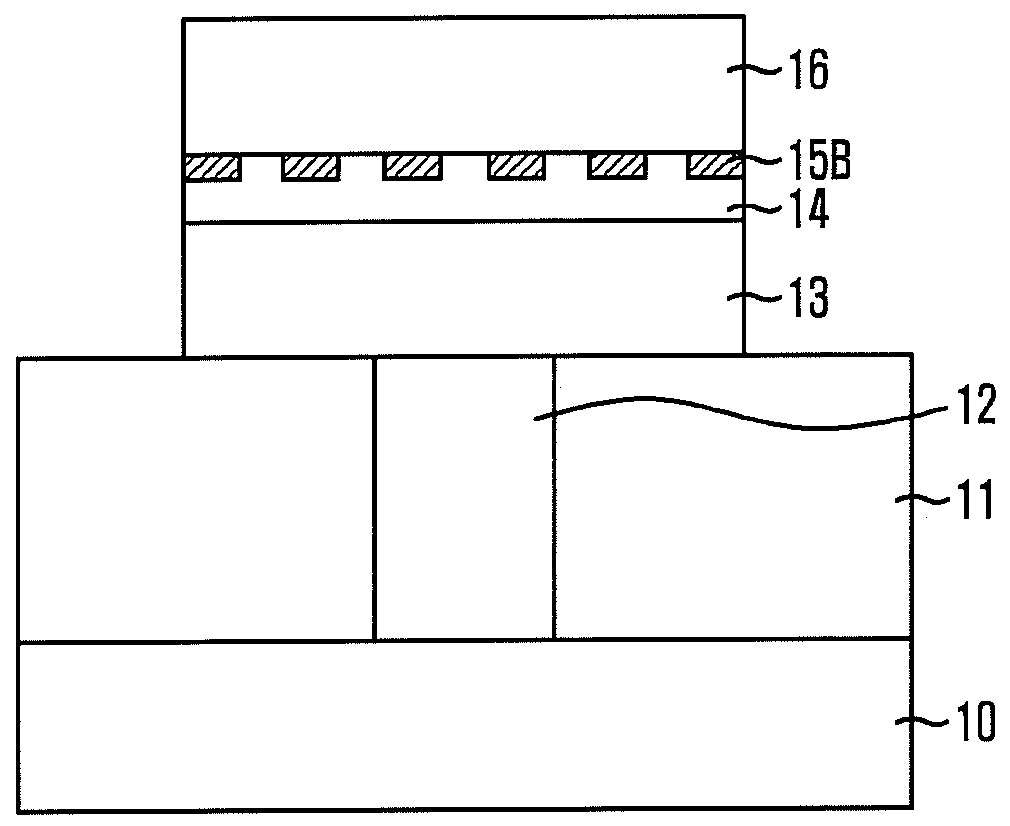
Method of manufacturing thin film device and thin film device manufactured using the same
InactiveUS20100255344A1Simple processMaintain good propertiesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsMetal electrodes
There is provided a method of manufacturing a thin film device and a thin film device manufactured using the same. The method includes forming a sacrificial layer using a first oxide having a perovskite structure on a preliminary substrate; forming an electrode layer using a second oxide having a perovskite structure on the sacrificial layer; forming a thin film laminate on the electrode layer; bonding a permanent substrate onto the thin film laminate; decomposing the sacrificial layer by irradiating a laser onto the preliminary substrate; and separating the preliminary substrate from the electrode layer. During a laser lift-off process, degradation of properties caused by oxygen diffusion can be prevented. Since the electrode layer has thermal conductivity lower than an existing metal electrode, heat emission can be considerably reduced and the sacrificial layer can be easily decomposed by heat accumulation. Therefore, a thin film device having excellent properties can be manufactured.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
High temperature, low oxidation stabilization of pitch fibers
InactiveUS6123829AReduce riskStabilize fiberWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by chemical meansFibre chemical featuresHigh densityFiber structure
The present invention provides a process for thermosetting pitch fibers in reduced times, at low concentrations of oxygen and at higher temperatures than previously possible. Additionally, the present invention provides a pitch fiber which has an oxygen diffusion rate to the center of the fiber which is competitive with the rate of oxidation at the fiber's surface. Further, the present invention provides a high density pitch fiber batt which thermosets without loss of fiber structure.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Spectral Selective Solar Control Film Containing an Air Layer for Windows
InactiveUS20110010994A1Improve efficiencyHigh light transmittanceDoors/windowsBuilding locksThermal insulationBlack body
A building structure having a high efficiency solar control system is provided. The building structure may have a window defined by a sheet of glass and a film mounted to its exterior side. There may be a gap between the film and the glass wherein the film, film and gap, or gap provides thermal insulation. The film may reflect solar radiation in the near and mid infrared ranges yet allow high transmission of light in the visible range such that the occupants of the building structure may view his / her surroundings through the window. The film may have a layer of silver which reflects the solar radiation in the near and mid infrared ranges. Since the silver is susceptible to oxidation and turns the silver into a black body which absorbs the near and mid infrared radiation, the film may be designed to slow the rate of oxidation of the silver layer to an acceptable level. The silver layer may be sandwiched between the glass which does not allow oxygen to diffuse there through and reach the layer of silver and a stack of sacrificial layers having a certain thickness which slows down the rate of oxygen diffusion to an acceptable level.
Owner:WILSON STEPHEN S +2
Diffused cap layers for modifying high-k gate dielectrics and interface layers
ActiveUS20130052814A1Reduce eliminateReduce and eliminate layerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricDevice material
Method of forming a semiconductor device includes providing a substrate with defined NMOS and PMOS device regions and an interface layer on the NMOS and PMOS device regions, depositing a high-k film on the interface layer, depositing a first cap layer on the high-k film, and removing the first cap layer from the high-k film in the PMOS device region. The method further includes depositing a second cap layer on the first cap layer in the NMOS device region and on the high-k film in the PMOS device region, performing a heat-treating process to diffuse a first chemical element into the high-k film in the NMOS device region and to reduce or eliminate the interface layer by oxygen diffusion from the interface layer into the second cap layer, removing the first and second cap layers from the high-k film, and depositing a gate electrode film over the high-k film.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com