Adiabatic waveguide transitions
A waveguide and optical waveguide technology, applied in the coupling of optical waveguides, optical guides, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of effective manufacturing difficulties, channel waveguide discontinuity, etc., and achieve the effect of low insertion loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
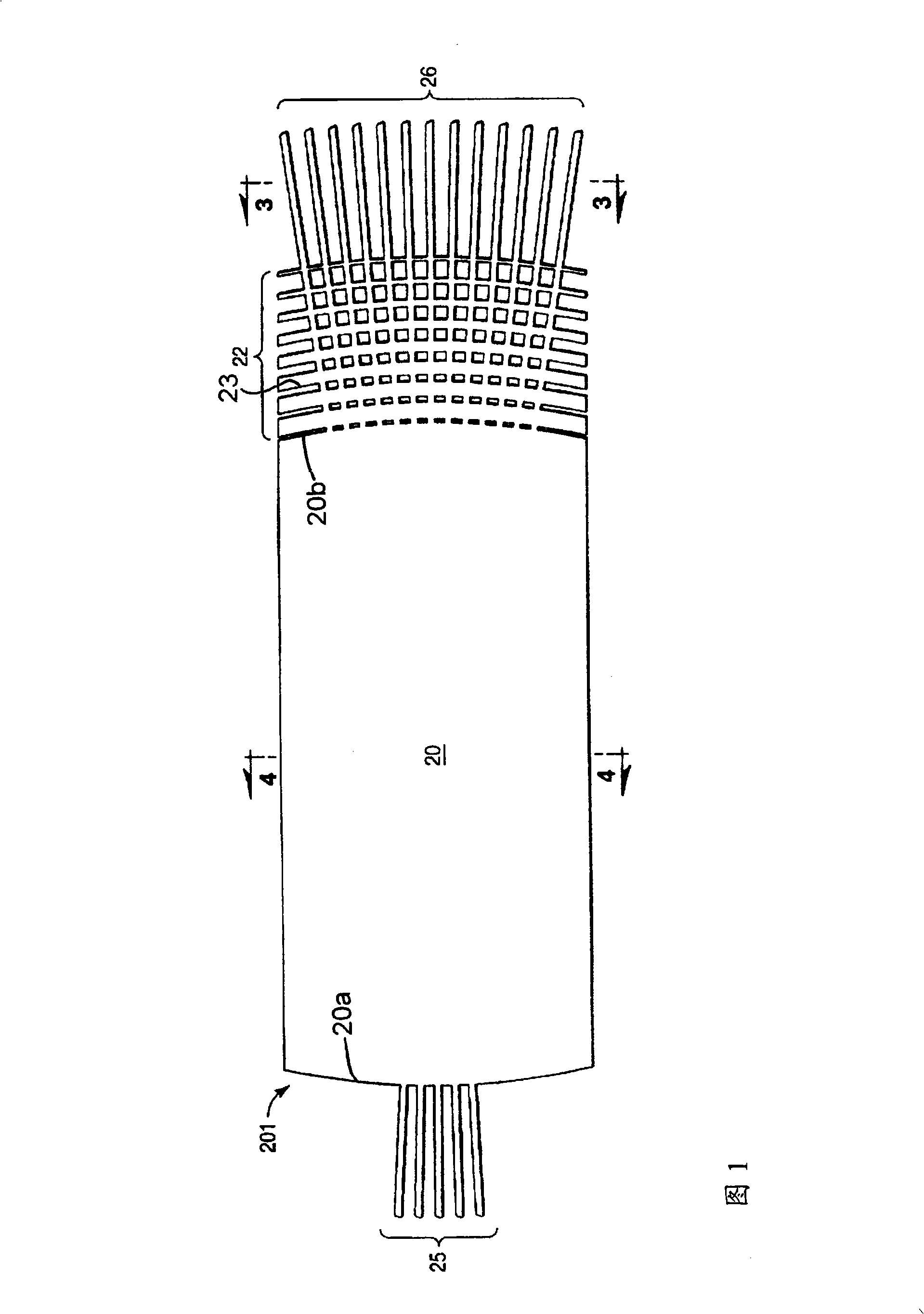
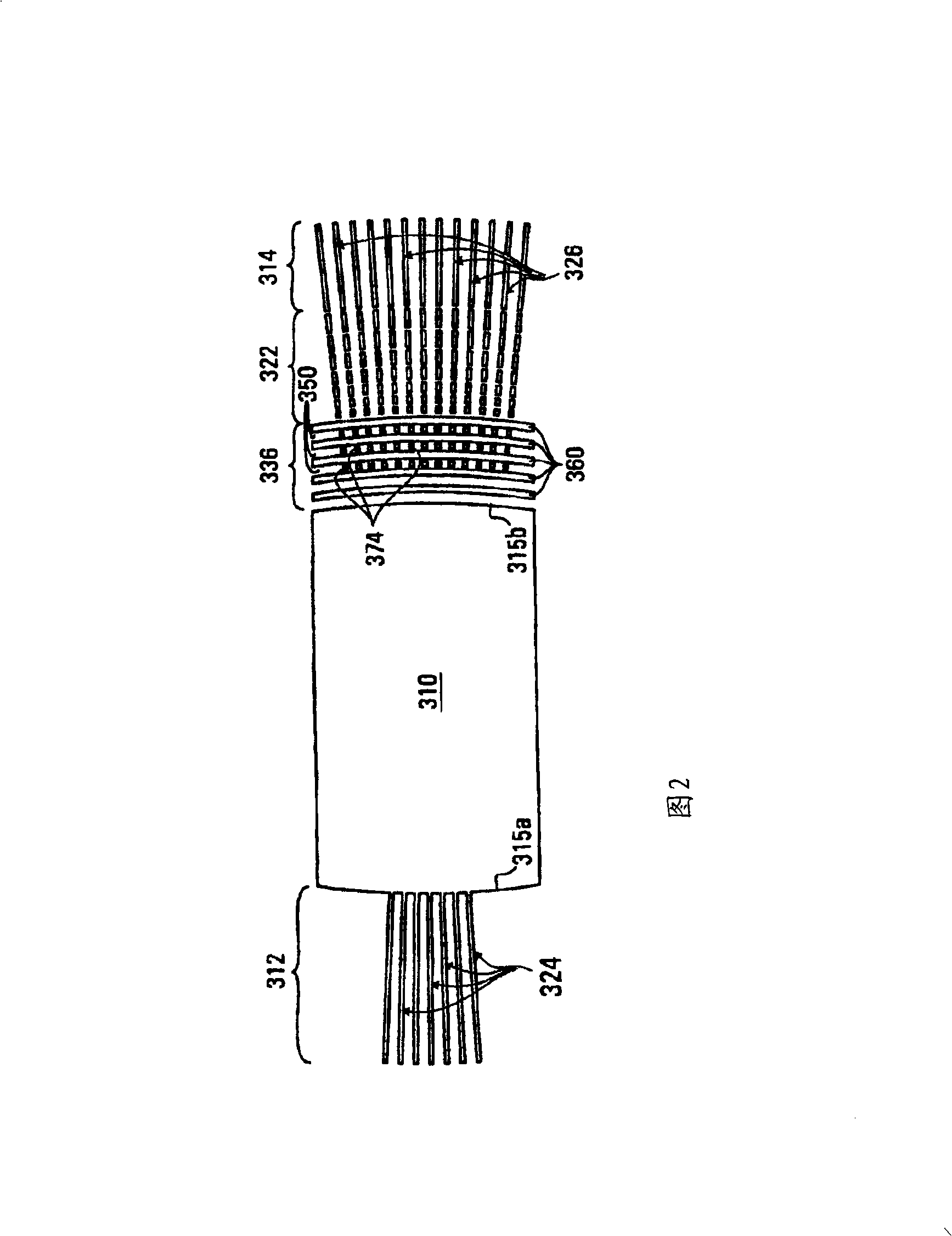
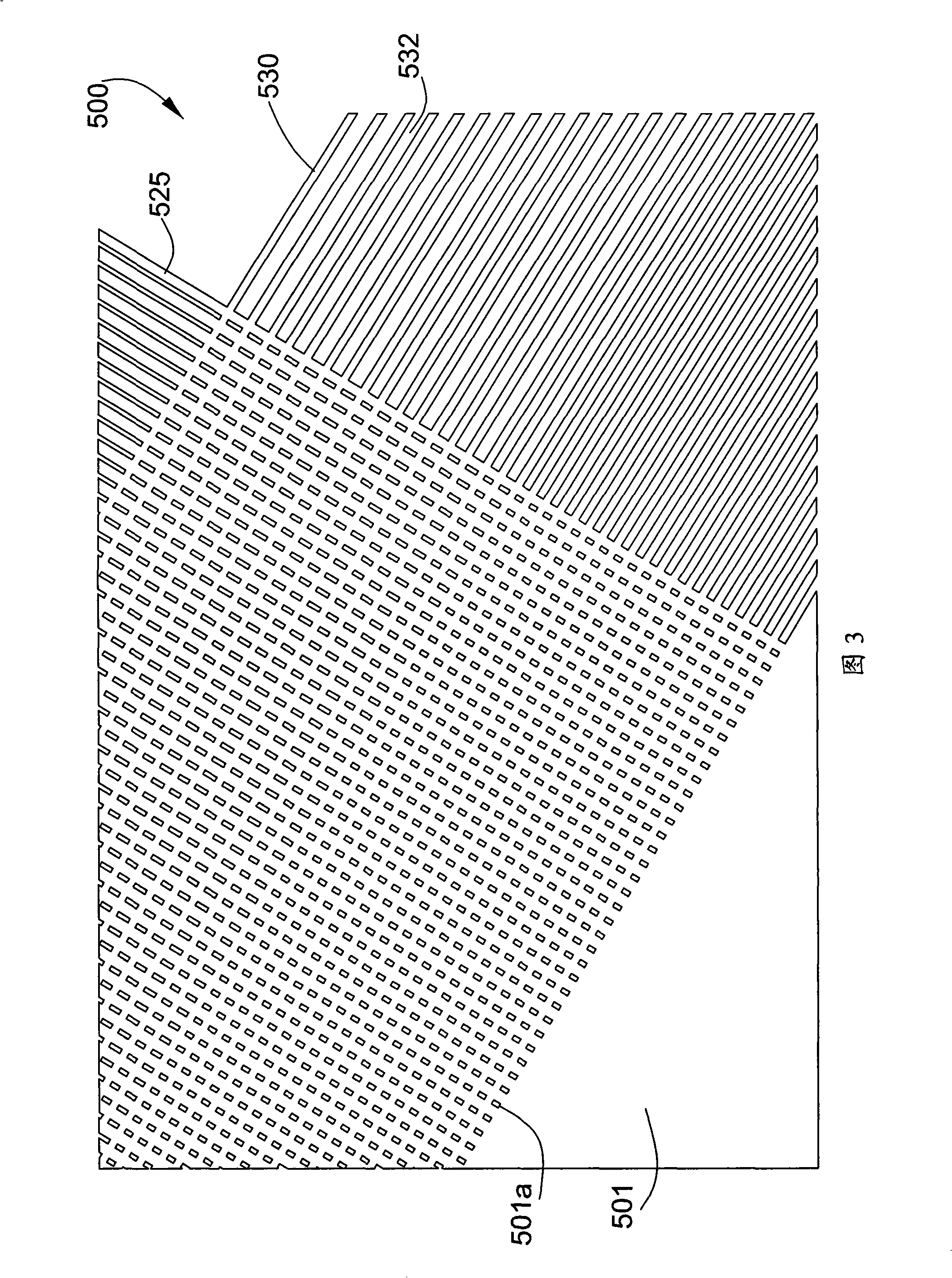
[0047] [32] Referring to FIG. 1, there is shown a prior art star coupler 201 disclosed in US 5,745,618 having a transition region 22 comprising a plurality of silicon material vias 23, typically parallel to each other and transverse to the output waveguide 26 to greatly reduce insertion loss. A star coupler splits the optical power entering any one of its output ports. The star coupler 201 comprises a free space region containing an optical slab waveguide 20 with two curved, preferably circular, boundaries 20a, 20b. Power transmission between the input waveguide array 25 and the output waveguide array 26 is achieved by radiation from the flat panel 20 . These arrays of waveguides 25, 26 are directed radially towards the virtual focus and are configured to set their respective focal lengths at a predetermined distance from the panel 20 such that phase errors due to mutual coupling between adjacent waveguides are minimized. . Each waveguide array is coupled to plate 20 along ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com