Methods for the electrolytic production of erythrose or erythritol
A technology of erythritol and erythritol, which is applied in the direction of electrolytic organic production, electrolytic components, electrolytic process, etc., can solve the problems of foaming, by-product amount, expensive erythritol and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
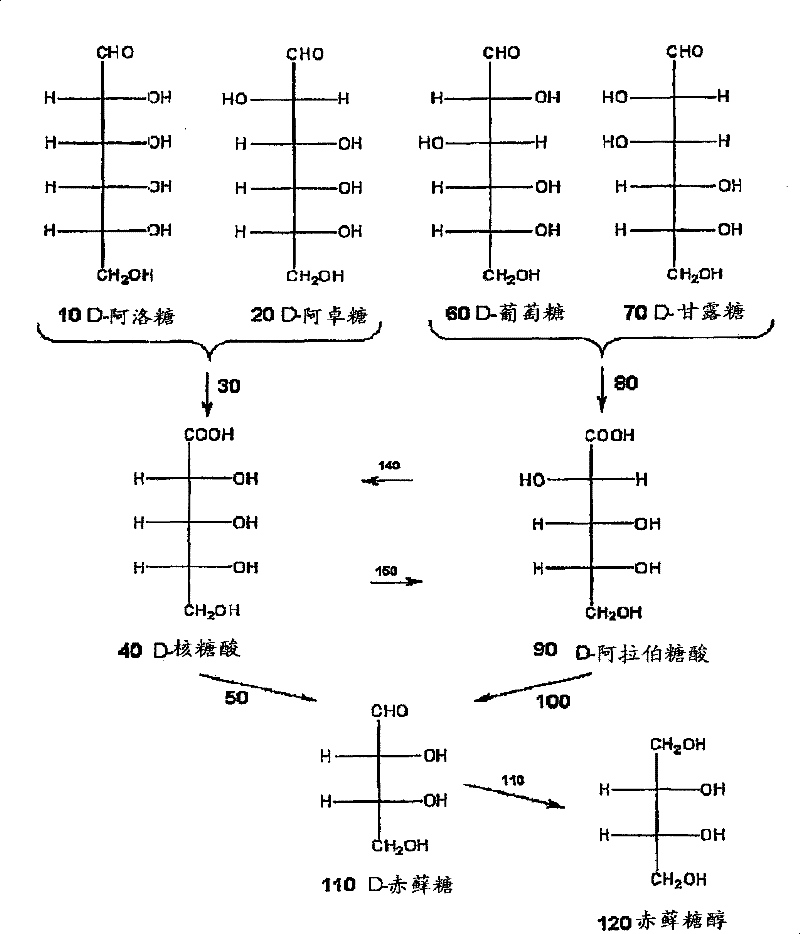
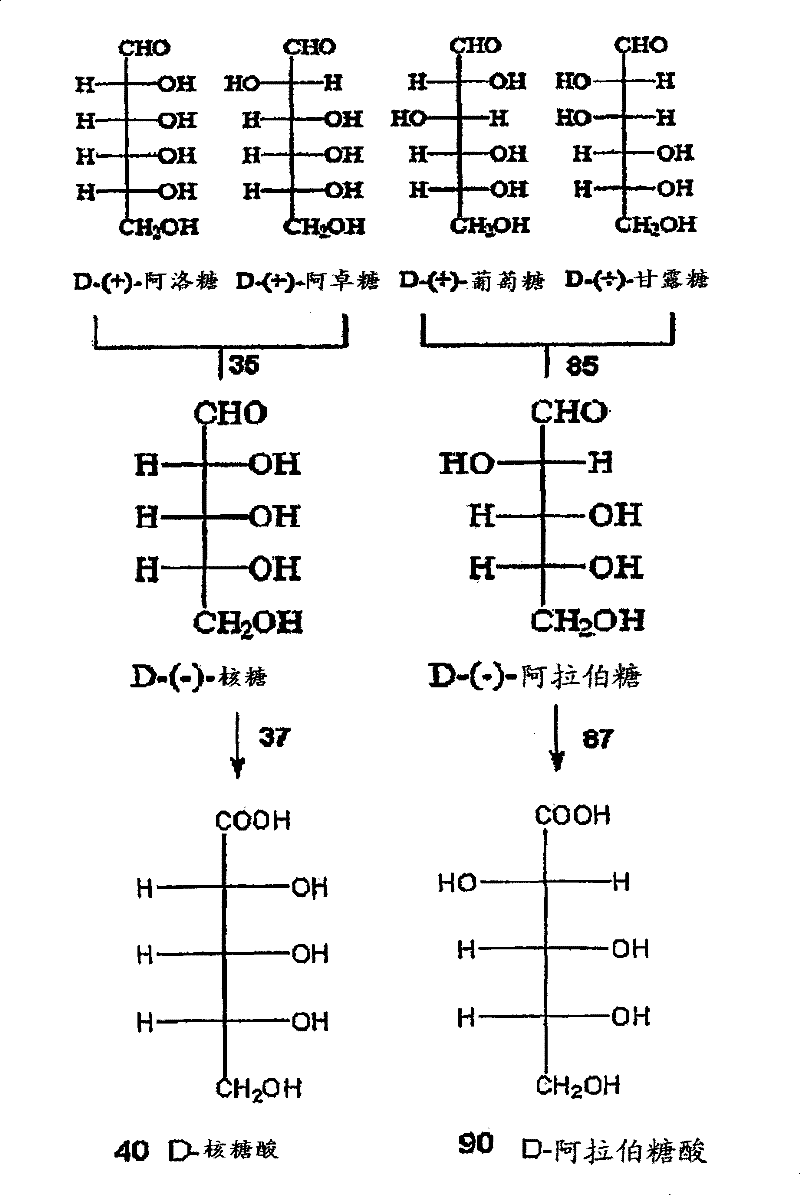
[0068] Example 1: Electrolytic decarboxylation of ribonic acid
[0069] Sodium ribonate (15 mmol) was dissolved in 20 mL water. Add cation exchange resin (Amberlite IRC747H+ type) to lower the pH from 6.8 to 3.5 (or neutralize about 50% of the raw material). The above solution was filtered to remove the cationic resin, the ribonate raw material was diluted to 30 mL, and 25 mL was transferred to a glass tank for electrolysis. The initial ribonate solution was analyzed by HPLC with respect to the standard, and the quantification was 9.54 mmol (0.38M). Stirring 25mL of raw material containing 9.54 mmol ribonate in a glass tank, while applying 0.5A (100mA / cm 2 ) Constant current. The cell voltage was about 6.5 volts on average, and the pH of the substrate increased from 3.5 to 7.6 after a charge of 2F / mol passed through. Take samples at 603, 1206 and 1809 coulombs. The sample containing the erythrose product was reduced to erythritol using excess sodium borohydride, and the eryth...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2: Electrolytic decarboxylation of arabinonic acid
[0073] Dissolve potassium arabinoate (15 mmol) in 20 mL of water. The arabinolate was acidified to about 50% neutralization by adding a cation exchange resin (Amberlite IRC747H+ type) and reducing the pH from 8.4 to 3.5. The arabinonic acid salt was filtered to remove the resin, diluted to 30 mL, and transferred to a glass tank for electrolysis. The initial arabinonic acid salt was quantified by HPLC-RI relative to the arabinonic acid salt standard, and it was found to contain 9.2 mmol (0.37M). There is a loss of 3.3 millimoles of arabinonate in the cation exchange resin.
[0074] Stirring 25mL of raw material containing 9.2 millimoles of arabinonic acid salt in a glass tank, while applying 0.5A (100mA / cm 2 ) Constant current. The cell voltage is about 5.5 volts on average, and the pH of the substrate increases from 3.5 to 7.7 after each mole of raw material passes through the 2F charge. Take samples at 603, 12...
Embodiment 2-5
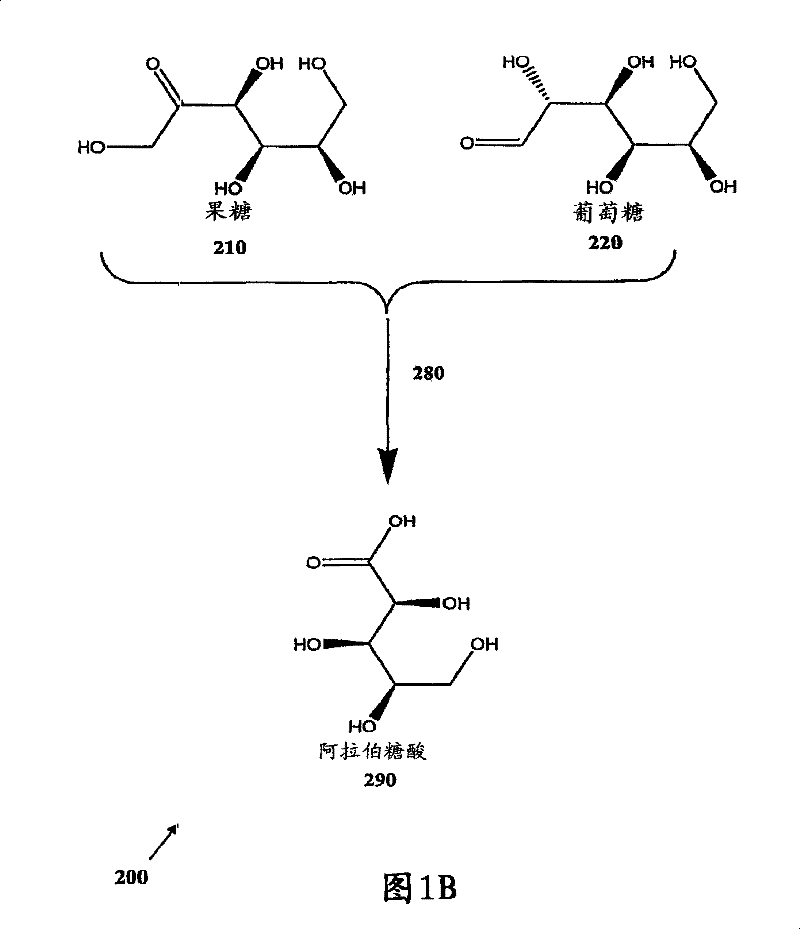
[0081] Theoretical Example 2-5: Oxidative decarboxylation and hydrogenation of glucose to arabitol
[0082] Elseviers et al. filed on July 23, 1997 and was granted U.S. Patent No. 5,831,078 on November 3, 1998, providing the reaction of oxidative decarboxylation of glucose raw material into arabinolate and conversion of arabinonate to arabitol Other suitable examples of are provided below as theoretical examples 2-5.
[0083] Theoretical Example 2: Oxidative decarboxylation using oxygen at a pressure of 2 bar
[0084] Under stirring at 1000 rpm, the raw material of glucose solution (1.5kg-10% w / w solution) was heated to 45°C in a two-liter autoclave. The reactor containing the glucose solution was purged with oxygen at a pressure of 1 bar twice for 0.5 minutes. After purging, the oxygen pressure in the reactor was adjusted to 2 bar. A quantitative feed burette was used to quantitatively add potassium hydroxide solution (242g-50% w / w solution) to the glucose solution at a quantitat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com