Conjugate comprising pharmaceutical active compound covalently bound to mucoadhesive polymer and transmucosal delivery method of pharmaceutical active compound using the same
A mucoadhesive, covalently linked technology, applied in the field of conjugates comprising pharmacologically active compounds covalently linked to mucoadhesive polymers and transmucosal administration of pharmacologically active compounds using the conjugates, capable of solving drug Unsatisfactory treatment effect and other problems, to achieve the effect of high degradability in vivo
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
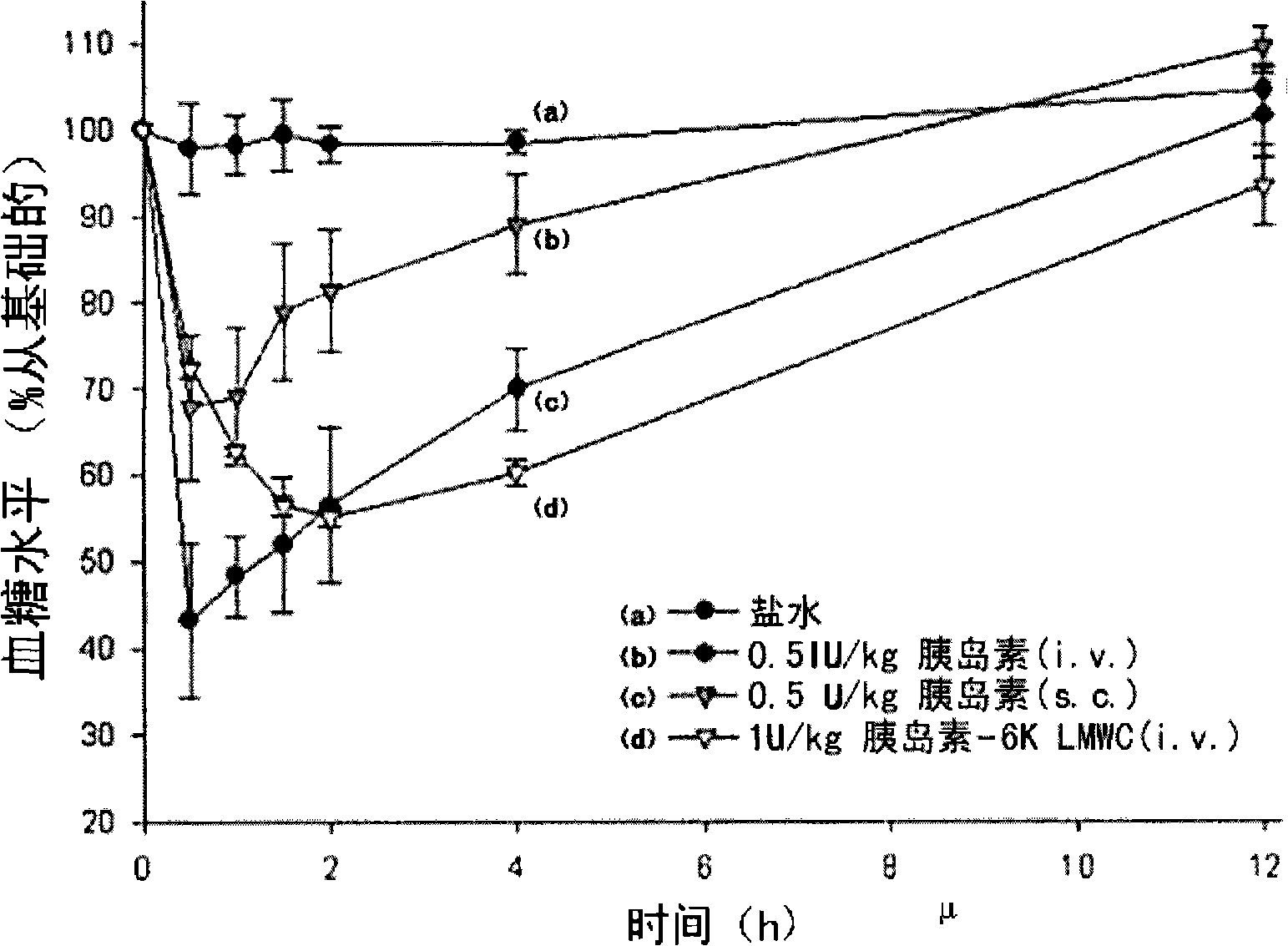
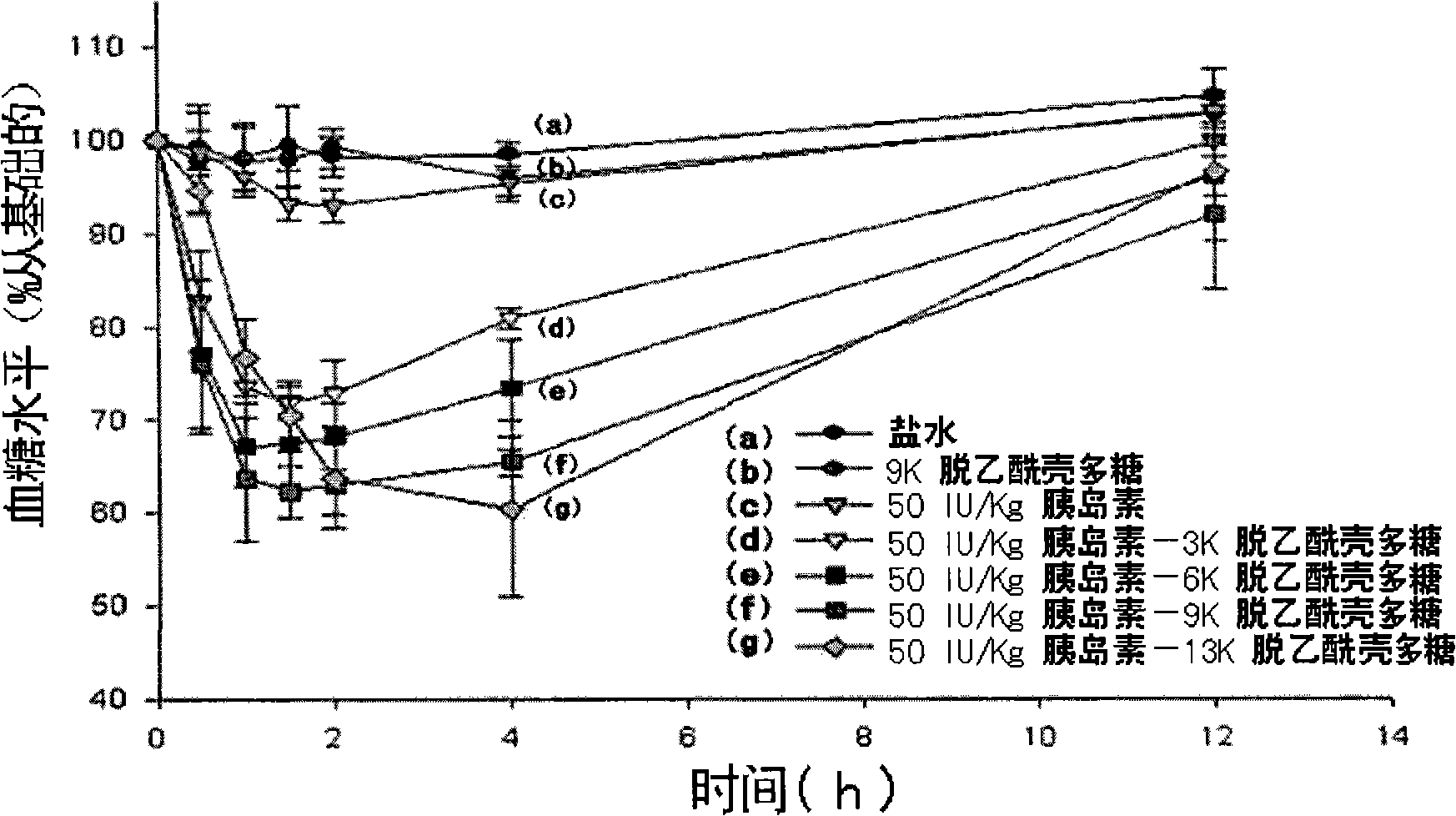
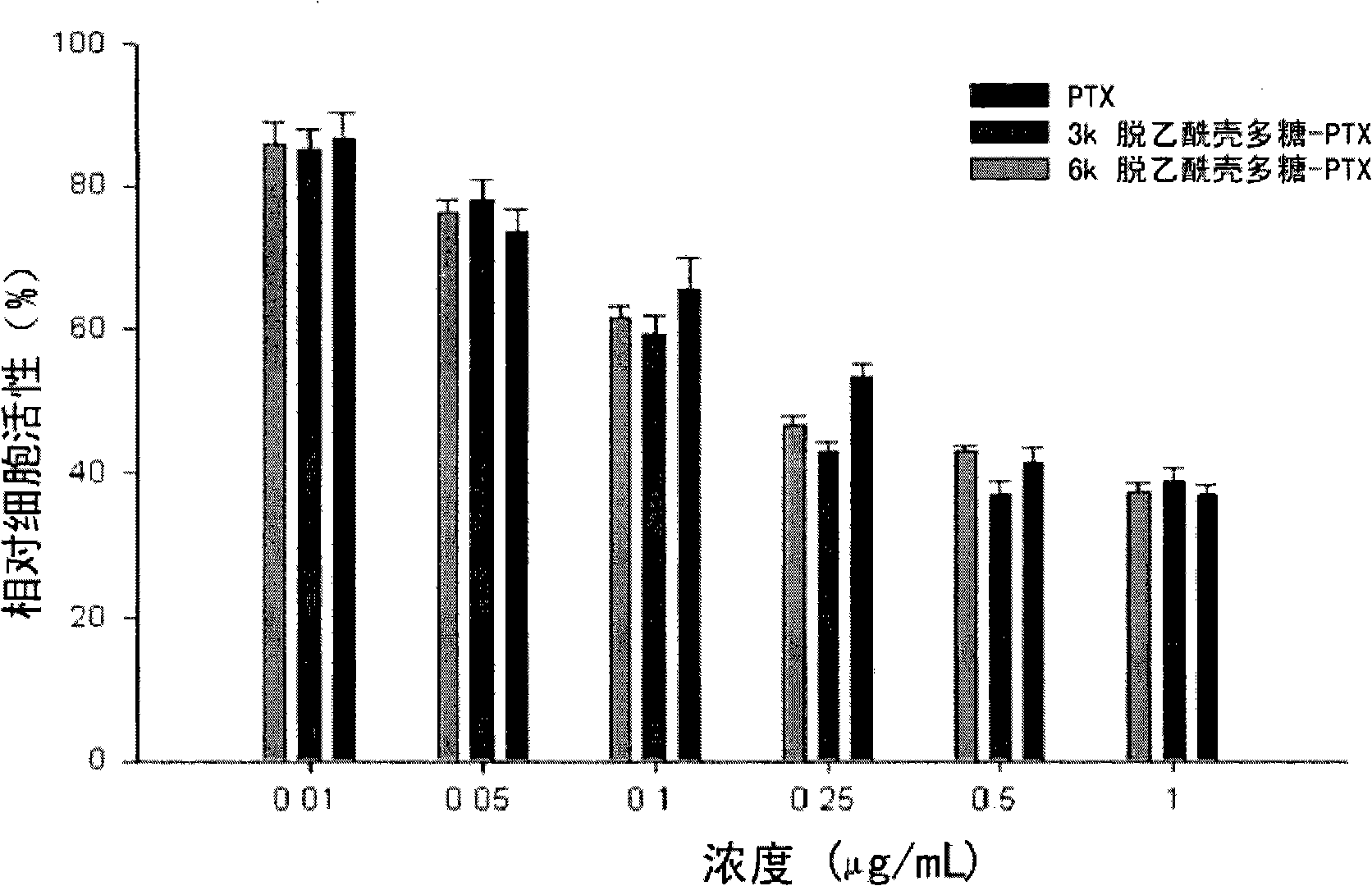
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1: Preparation of Insulin Intermediates with Insulin Linked to a Linker
[0084] 0.1g (17.22×10 -6 mol) insulin (Serologicals company) was dissolved in 10mL hydrochloric acid solution, and 0.008g (25.83×10 -6 mol) N-succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate (SPDP, Pierce) was dissolved in 0.2×10 -3 mL of DMF (Sigma), which was then added to the insulin solution. In order to obtain the regioselective combination of SPDP and the 29th amino acid lysine (B29) on the B chain of the insulin molecule, the above mixed solution was adjusted to a pH range of 9-10 with NaOH water and stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes . The resulting stirred solution was subjected to reverse-phase HPLC (Shimadzu) separation and freeze-dried (lyophilization) to prepare an insulin intermediate (see Equation 1).
Embodiment 2
[0085] Example 2: Chitosan intermediate with chitosan attached to linker product preparation
[0086] Each 0.1 g (16.67×10 -6 mol, monomer mole number = 0.67×10 -3 mol) was dissolved in 2mL phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and 0.016g (50.01×10 -6 mol) of SPDP dissolved in 0.2×10 -3 mL of DMF, which was then added to the above chitosan solution, followed by stirring at room temperature for 2 h. Acetone was added to the resulting stirred solution to precipitate particulate matter. The resulting granules were dissolved in distilled water and freeze-dried to prepare a chitosan intermediate (see Reaction Scheme 1).
[0087] [Reaction 1]
[0088]
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3: Construction of insulin-chitosan conjugates
[0090] In order to reduce the above-mentioned chitosan intermediate product, 0.008g (1.24×10 -6 mol) chitosan intermediate and 0.3mL of DTT (24.9×10 -6 mol) (Pierce) was dissolved in 0.3 mL of PBS and stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. 0.005g (0.83 × 10 -6 mol) insulin intermediate was dissolved in citrate buffer solution (500 μg), the reduced chitosan intermediate solution (100 μg) was added thereto, and the resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12-24 hours. The stirred mixture was separated by reverse-phase HPLC and freeze-dried to prepare an insulin-chitosan conjugate (see Equation 2).
[0091] [Reaction 2]
[0092]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com