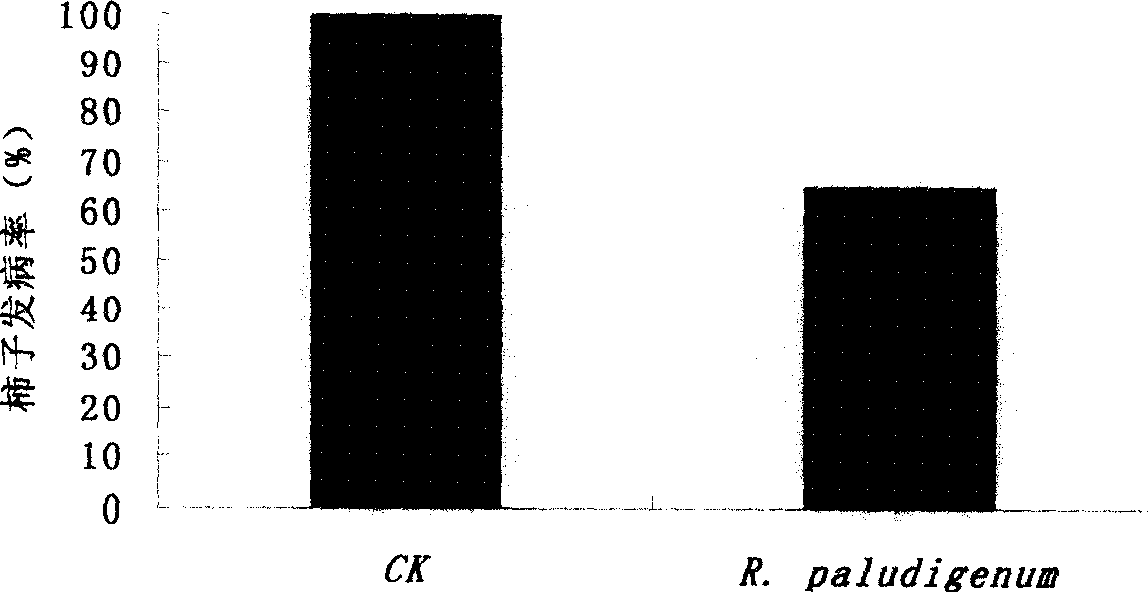Sea yeast for diseases biological control of postharvest fruits and vegetables, and preparation and use thereof
A technology for postharvest diseases and marine yeast, which is applied in the fields of chemicals for biological control, botanical equipment and methods, biocides, etc., can solve the problems of unstable effect and high production cost, and achieve low cost and market prospects. Broad, economical and social benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] 1) Take dozens of seawater samples from the coastal waters of Zhoushan, Qingdao sea area, China, dilute them in different multiples, draw 0.1mL from the seawater samples of each dilution concentration and evenly spread them on the NYDA medium plate with a NaCl concentration of 2%. Place it upside down in an incubator and culture at a constant temperature of 28°C for 3 days. Use an inoculation loop to pick out a single colony with different culture characteristics for purification by streaking on a plate. After microscopic examination confirms that it is yeast, transfer it to the slant of NYDA medium for culture and storage.
[0033] 2) Inoculate the yeast preserved on the slant into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 70mL of sterilized NYDB medium, cultivate at a constant temperature of 28°C at 150 rpm for 18 hours, and centrifuge at 2000 rpm for 10 minutes to collect the bacteria. And wash the yeast cells twice with sterile water, count with a hemocytometer and adjust ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] 1) Take seawater samples from the coastal waters of Zhoushan and Qingdao sea areas in China, dilute them, draw 0.2mL of diluted seawater samples and spread them evenly on the plate of NYDA medium containing 2% NaCl, place them upside down in the incubator, and cultivate at a constant temperature of 26°C On the 4th day, use an inoculation loop to pick out a single colony with different cultural characteristics for purification by streaking on a plate. After microscopic examination confirms that it is yeast, it is inserted into the slant of NYDA medium for culture and storage;
[0038] 2) Inoculate the yeast preserved on the slant into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 35mL of sterilized NYDB medium, culture at a constant temperature of 26°C at 200 rpm for 30 hours, and centrifuge the fermentation broth at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes to collect bacteria body, and washed the yeast cells twice with sterile water, counted with a hemocytometer and adjusted to a concentration of 1...
Embodiment 3
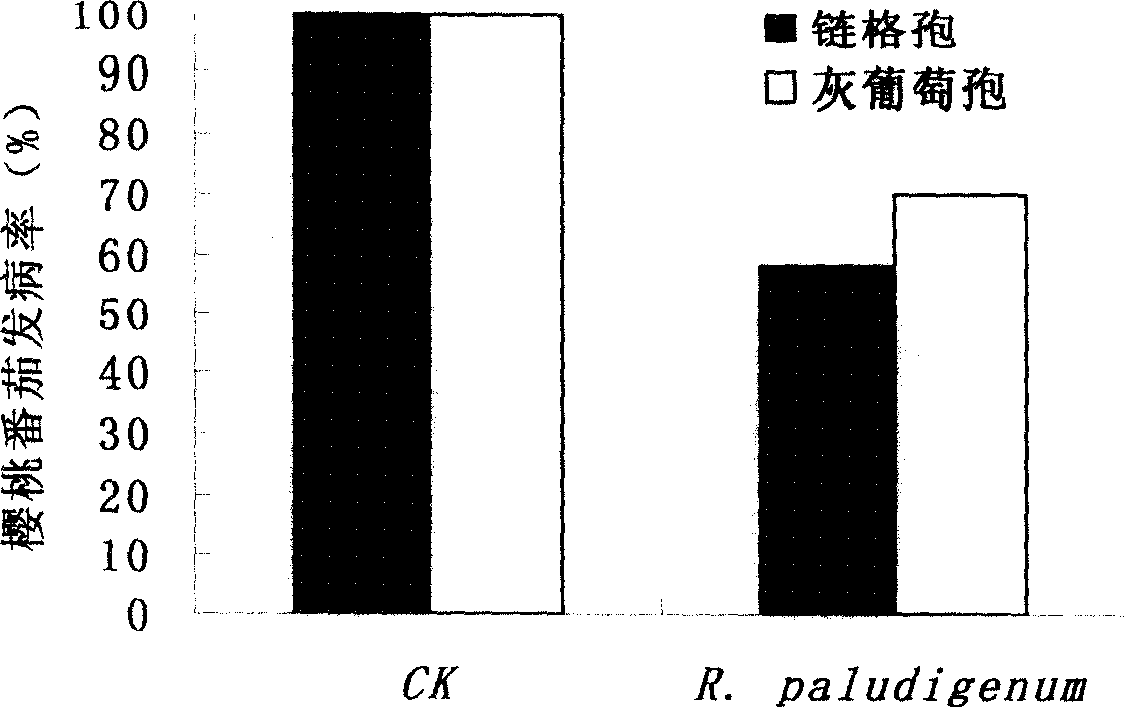
[0047] Control effect of marine yeast strain R.paludigenum Fell & Tallman of the present invention on postharvest Alternaria and Botrytis cinerea diseases of cherry tomato fruit at room temperature
[0048] 1) Configuration of yeast cell suspension
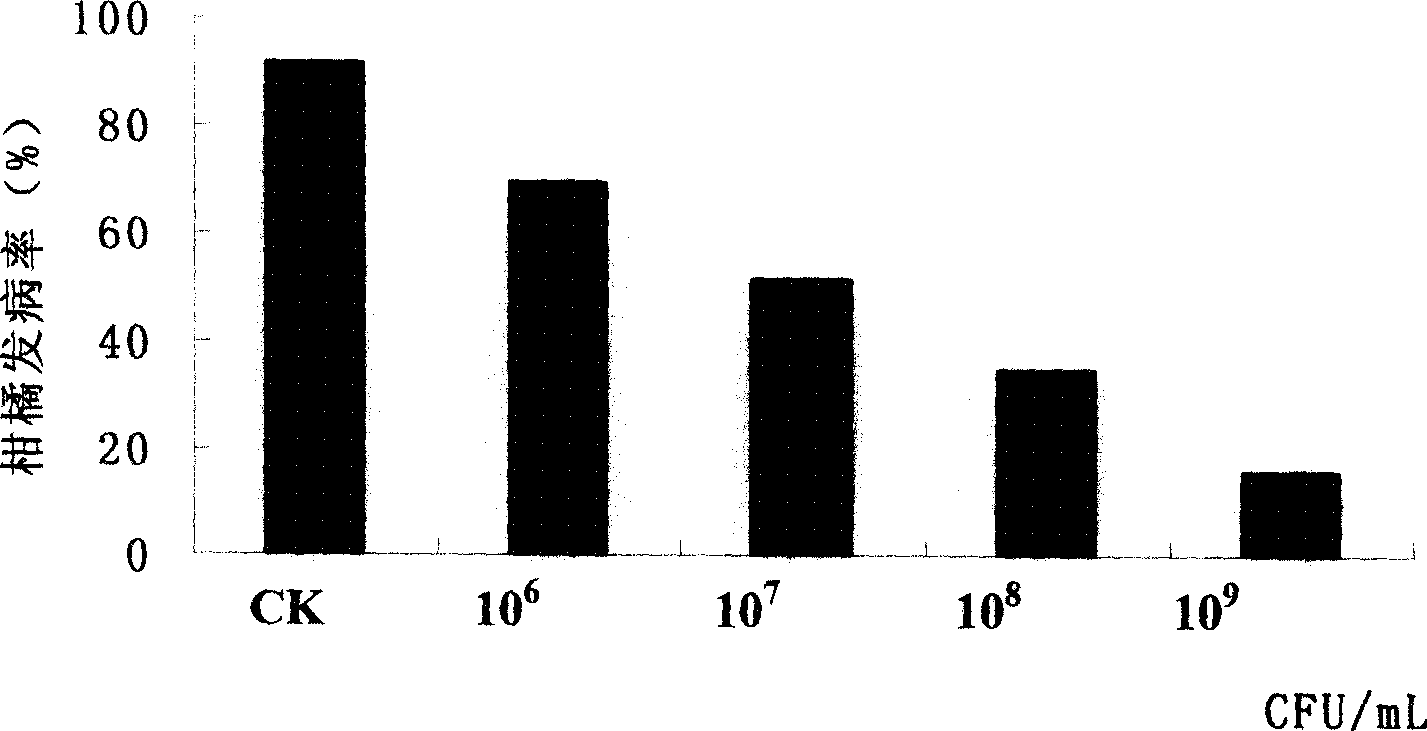
[0049] Inoculate the preserved medium bacteria into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 35ml of sterilized medium after activation, culture at 150 rpm at 26°C for about 30 hours, and centrifuge at 2000 rpm for 10 minutes to collect the bacteria , and wash the yeast cells with sterile water, count with a hemocytometer, and adjust the concentration of the cell suspension to 10 8 CFU / mL of yeast cell suspension.
[0050] 2) In this embodiment, cherry tomatoes are used as test materials. The fruit comes from orchards in the suburbs of Hangzhou.
[0051] Pathogens: Alternaria alternata, Botrytis cinerea
[0052] Cherry tomato fruits were inoculated with yeast cell suspension after pricking. The inoculum size is 20 μl. After 2 hou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com