Differential calibration
A technology of calibrator and difference value, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as speed limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
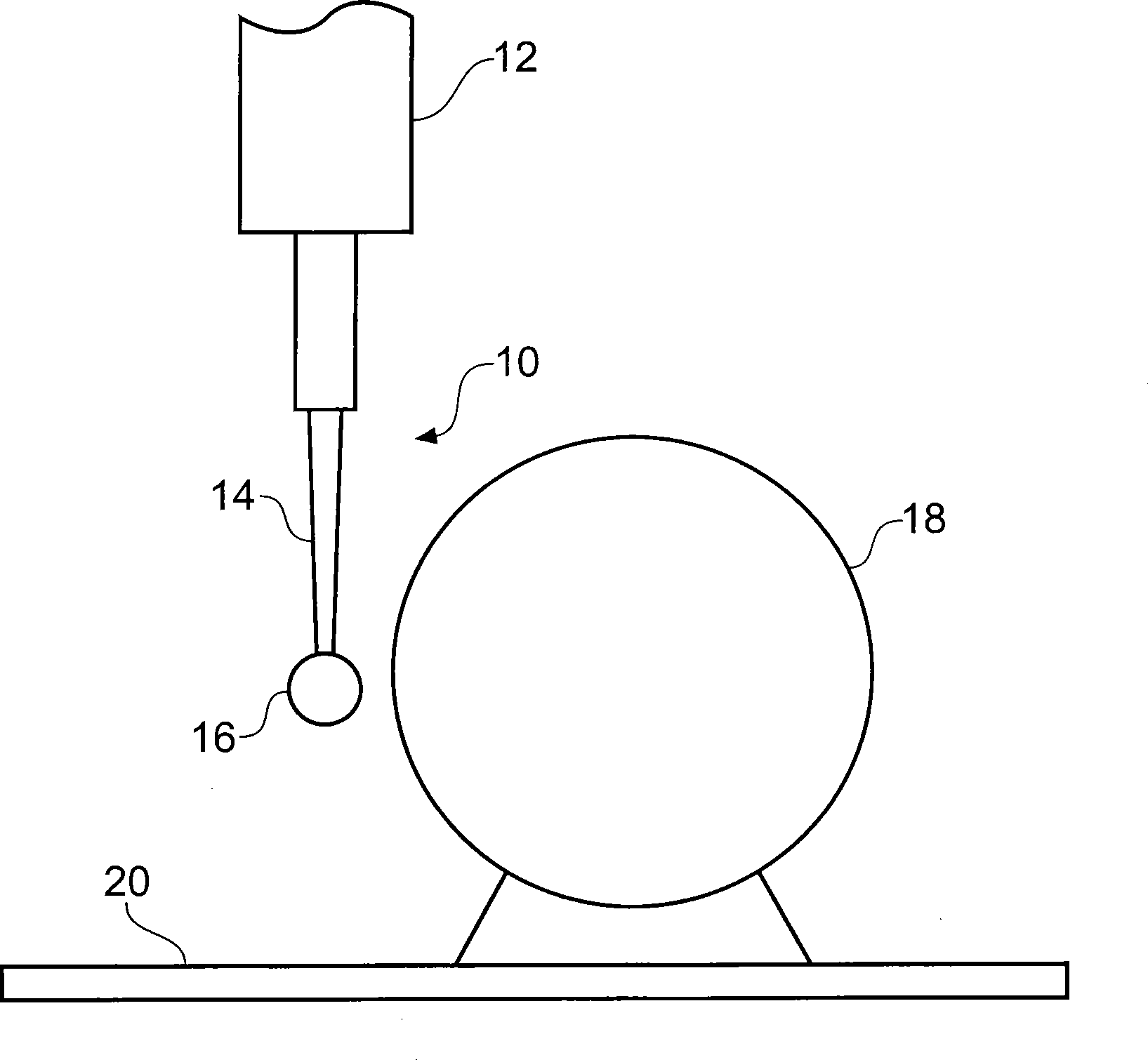
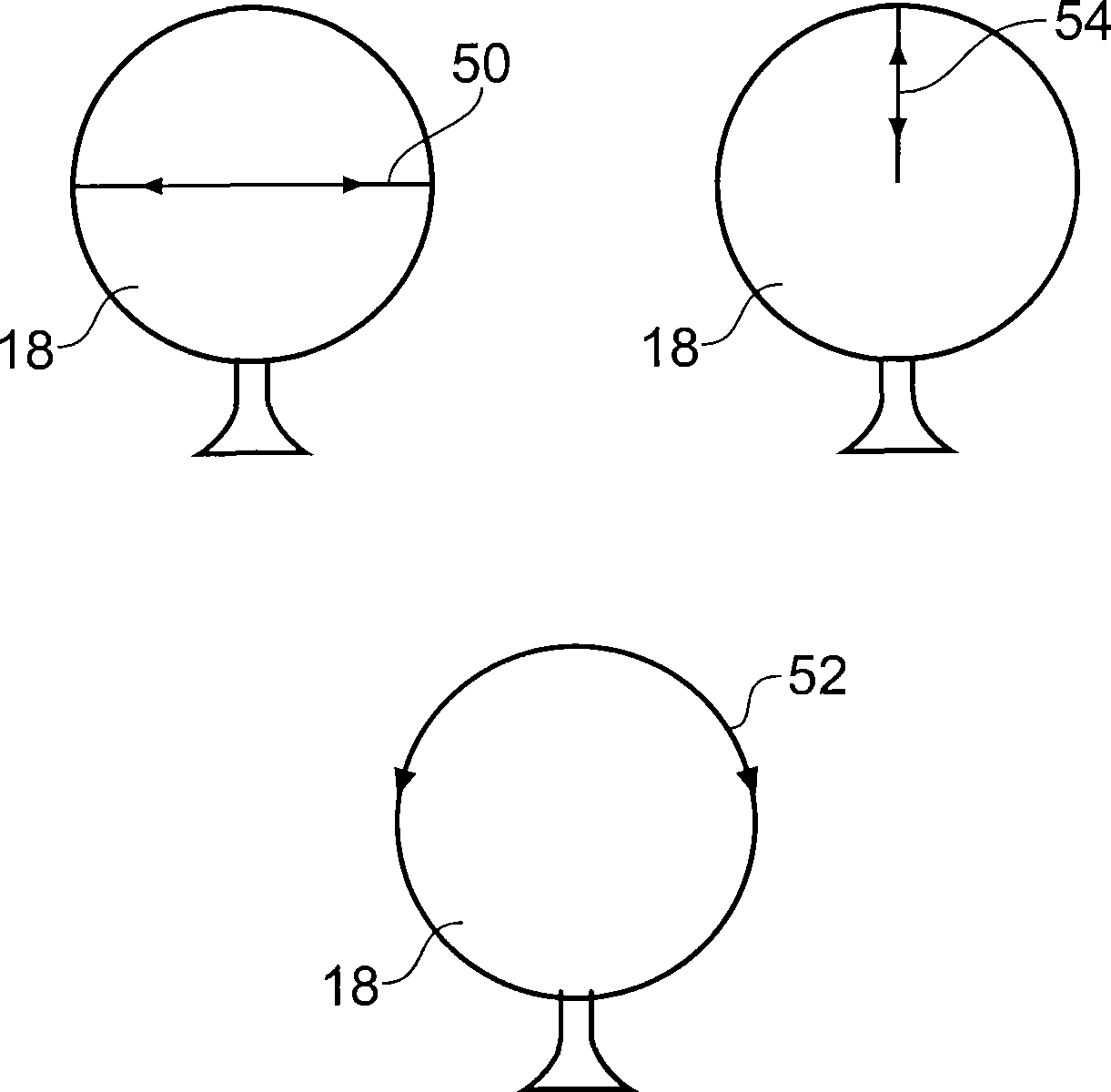
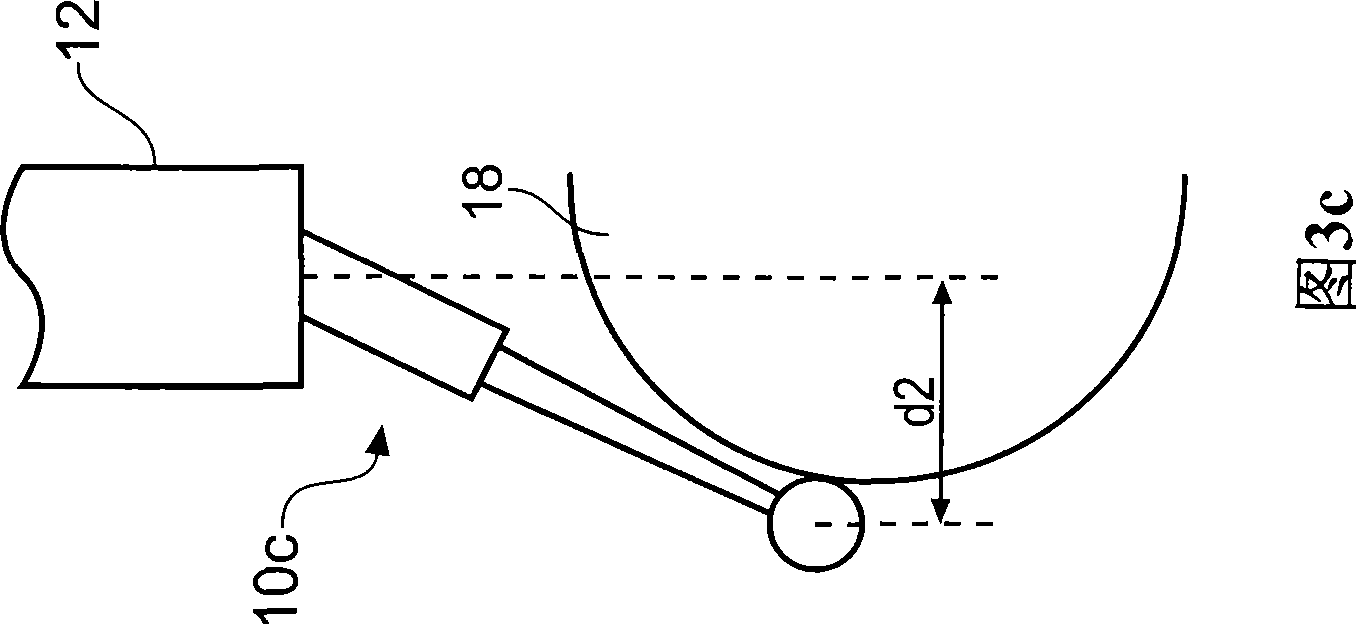
[0037] figure 1 A probe 10 is shown, linked at one end to the machine tool by a hollow shaft 12 , with a stylus 14 having a workpiece contact tip 16 located at the distal end of the probe 10 . The machine tool comprises a bed 20 on which a workpiece or in this case a calibration sphere 18 is located.
[0038] Probe 10 is an analog or scanning probe that produces probe deflection data related to any deflection of the stylus in its three orthogonal (Cartesian) scan axes. Here the raw probe deflection output is referred to as a, b, c coordinate values. The machine tool also includes a position encoder or similar for measuring the position of the hollow shaft in machine coordinate (X, Y, Z) geometry, ie providing so-called machine data.
[0039] In order to provide a measurement of the position of the stylus tip, measurements made in the probe (a, b, c) coordinate system must be converted to the machine (X, Y, Z) coordinate system. To provide this transformation, it is known t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com