Fault-tolerance method in wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and sensor node technology, applied in the field of sensor networks, can solve problems such as unforeseen fault-tolerant processing technology and unclear optimal methods, and achieve the effects of reducing communication traffic, improving fault tolerance, and improving success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0018] A fault-tolerant method in a wireless sensor network, comprising the following steps:
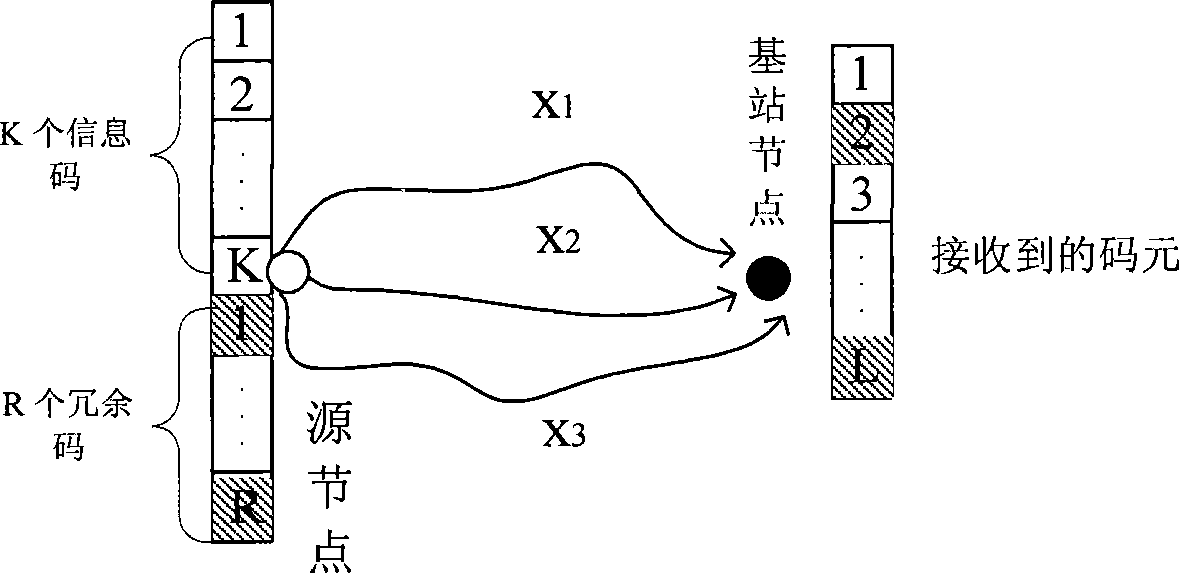
[0019] 1) After the sensor nodes in the wireless sensor network are deployed, define the sensor node used for sensing data in the wireless sensor network as the source node, and use the existing multi-path routing algorithm to establish a 2N network between the source node and the base station node node-disjoint transmission paths. In this embodiment, the node-disjoint transmission paths refer to sensor nodes that do not intersect any two transmission paths from the source node to the base station node. N is an integer greater than 0.
[0020] 2) At the source node, divide the original data sensed by the source node into K information codes, and then use (N′, K) RS erasure codes to perform RS erasure coding on the K information codes to obtain N′ s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com