Nanoemulsion vaccines
A technology of nanoemulsion and adjuvant, applied in pharmaceutical formulations, ester active ingredients, organic active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of ineffective and repeated immune broad-spectrum diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0360] Materials and methods: Nanoemulsion inactivated vaccinia virus
[0361] animal. Pathogen-free, 5- to 6-week-old female Balb / c mice were purchased from Charles River Laboratories. According to the American Association for Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care (American Association for Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care) standards, the inoculation group was housed separately, with 5 animals in one cage. All methods involving mice were performed in accordance with the University Committee on Use and Care of Animals (UCUCA) of the University of Michigan.
[0362] Virus. Two exemplary vaccinia viruses (VV), VV WR and VV WR-Luc . VV was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), USA WR (NIH TC-adapted). rVV WR-Luc Expression of firefly luciferase via the p7.5 early / late promoter has been described (see, eg, Luker et al., Virology. 2005, 341(2):284-300). VV WR-Luc It was not attenuated in vitro or in vivo because the virus was constructed using...
Embodiment 2
[0381] Nasal immunization with nanoemulsion-inactivated vaccinia virus resulted in the induction of specific systemic IgG responses.
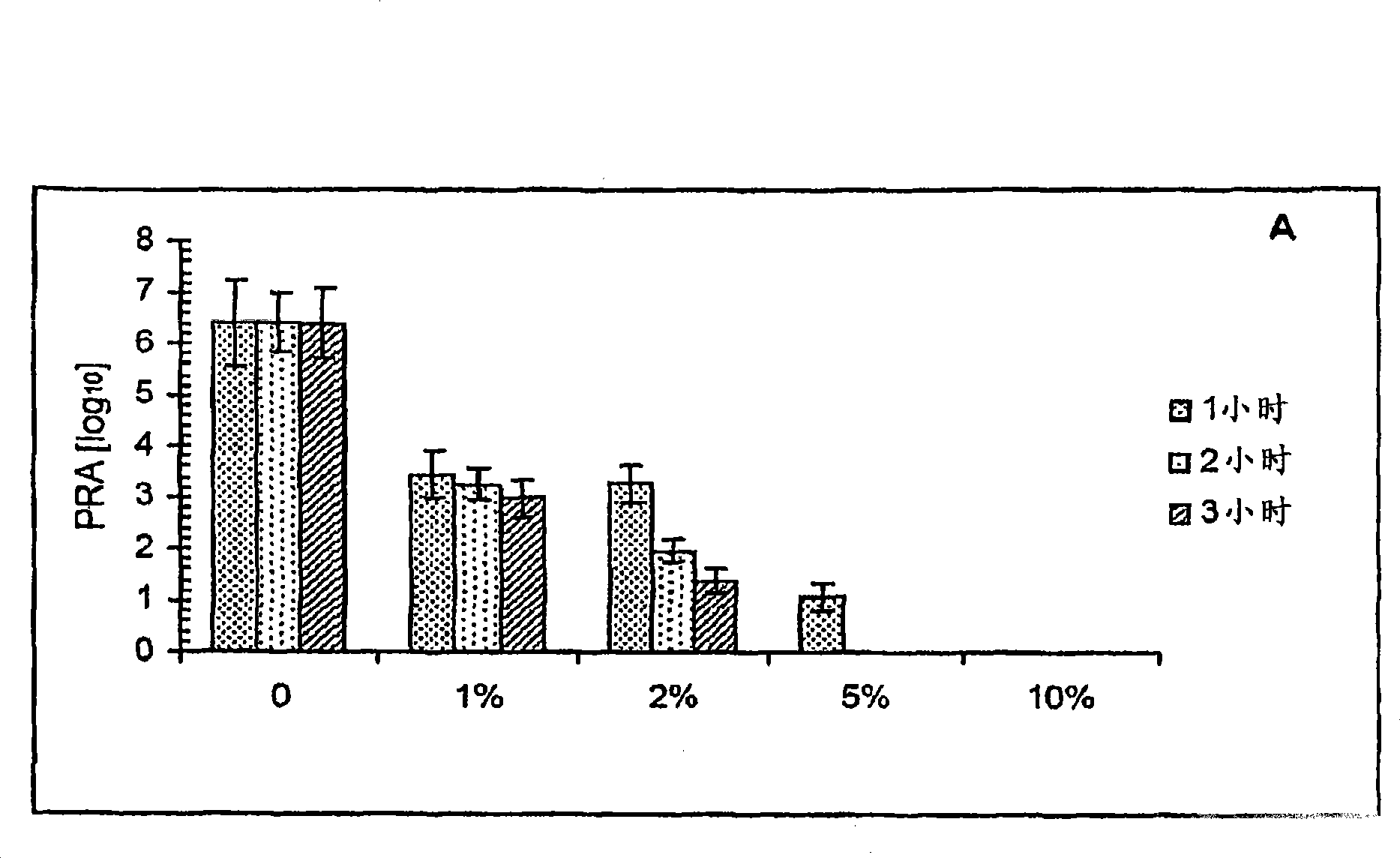
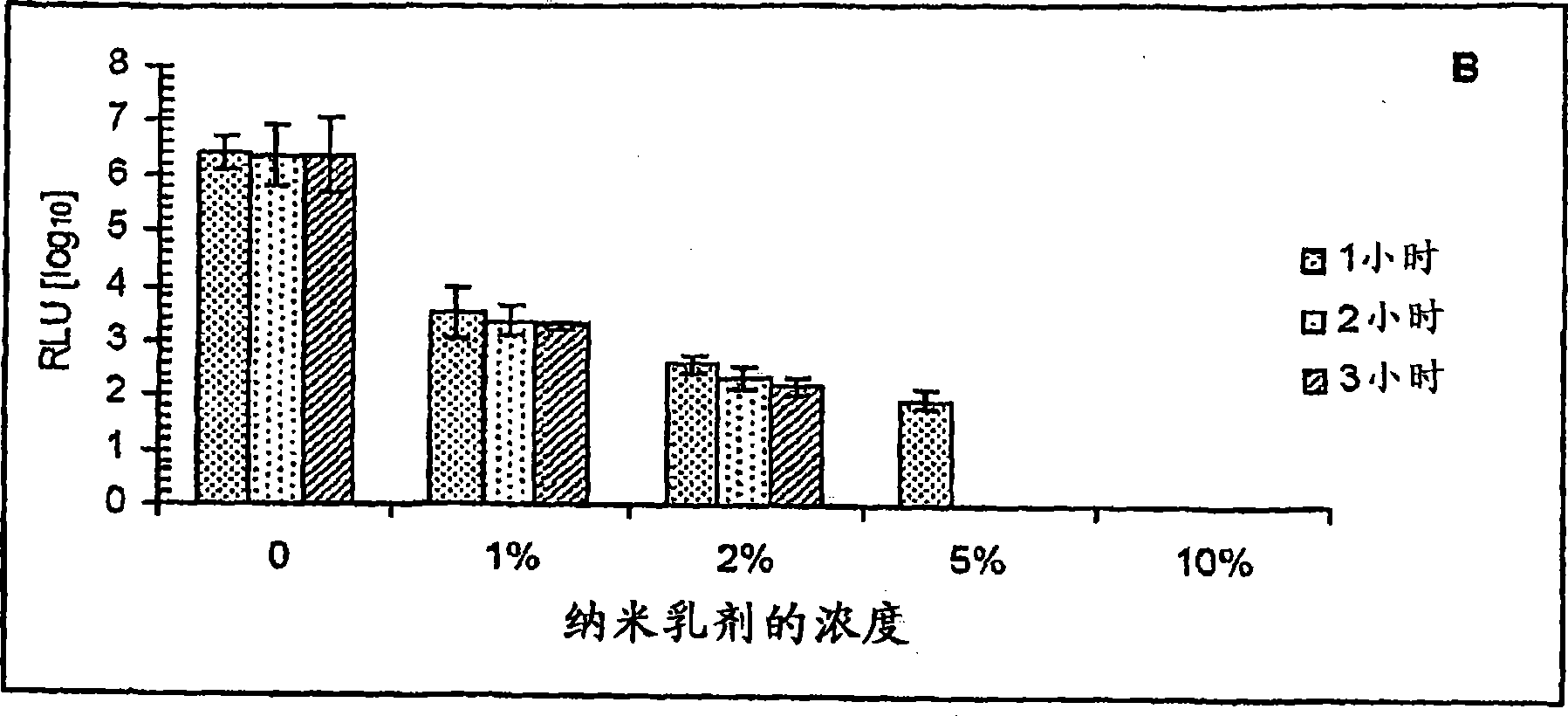
[0382] To estimate the virucidal activity of NE in vitro, a series of NE concentrations were compared with VV WR or VV WR-Luc Mix, and incubate at 37°C for 1 to 3 hours. The results of plaque reduction (PRA) and luciferase bioluminescence assays both showed NE concentration-dependent inactivation of both viruses. 10% NE can completely inactivate more than 10 6 pfu of vaccinia (see Figure 1A and B). Subsequent passage of culture supernatants from cells infected with VV (inactivated with 10% NE) showed no viable virus.
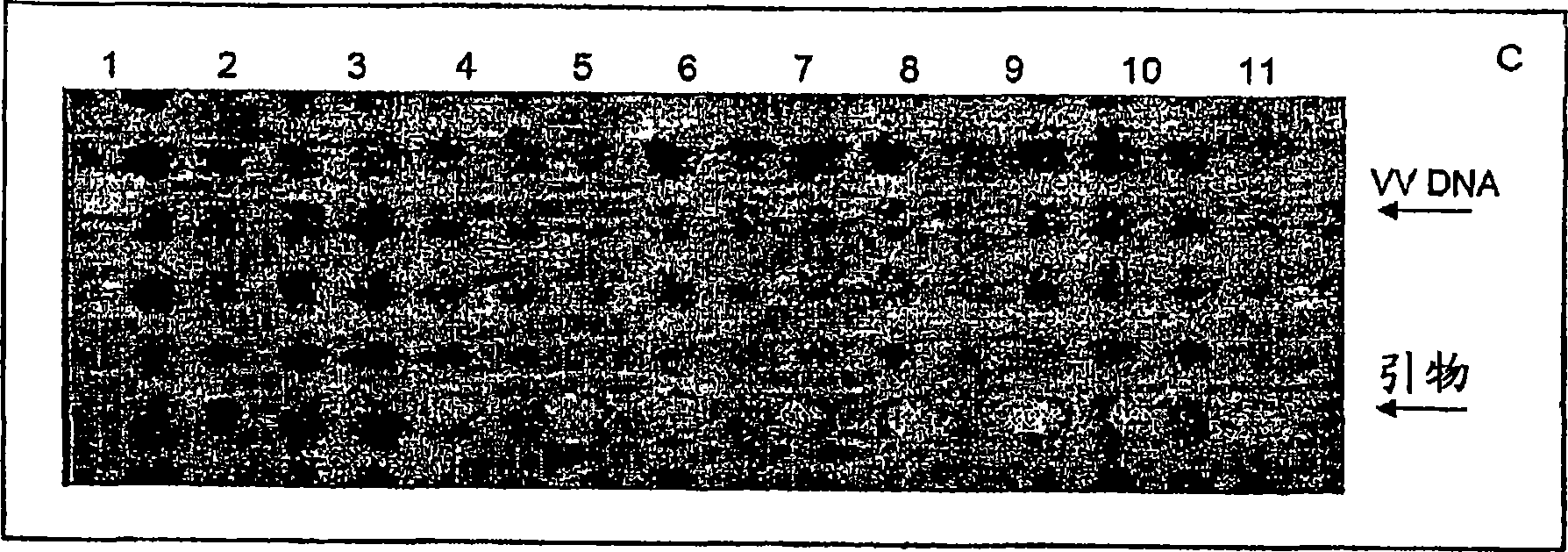
[0383] Intranasal administration of inactivated VV WR Later, complete inactivation of virus in NE formulations was further demonstrated in vivo by PCR amplification using DNA isolated from post-administration mouse lungs. In any treated mice (see Figure 1C No viral DNA was detected in ), whereas the control PCR (incorpo...
Embodiment 3
[0387] Subjects administered nanoemulsion-killed vaccinia virus have mucosal immunity against vaccinia virus
[0388] Mucosal immunity was determined by VV-specific secretory IgA antibodies in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL). In from using 10 3 / NE or 10 5 Anti-VV IgA was detected in the BAL of / NE immunized animals. Animals vaccinated with formulations containing formalin-killed virus (whether diluted in saline or diluted in NE) did not produce a measurable mucosal response despite the presence of serum anti-VV IgG (see Figure 2B ). Accordingly, the invention provides that a composition comprising NE-killed VV produces mucosal immunity in a subject (e.g., as evidenced by the presence of VV-specific secretory IgA antibodies in the subject's BAL), However, compositions that do not contain NE-killed VV (eg, formalin-killed VV) cannot generate mucosal immunity against VV.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com