Semiconductor light emitting element and method for fabricating the same
A light-emitting element and semiconductor technology, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, semiconductor lasers, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reducing production efficiency and reducing the number of semiconductor light-emitting elements, so as to improve production efficiency, prevent leakage current, and suppress the deterioration of electrical characteristics Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
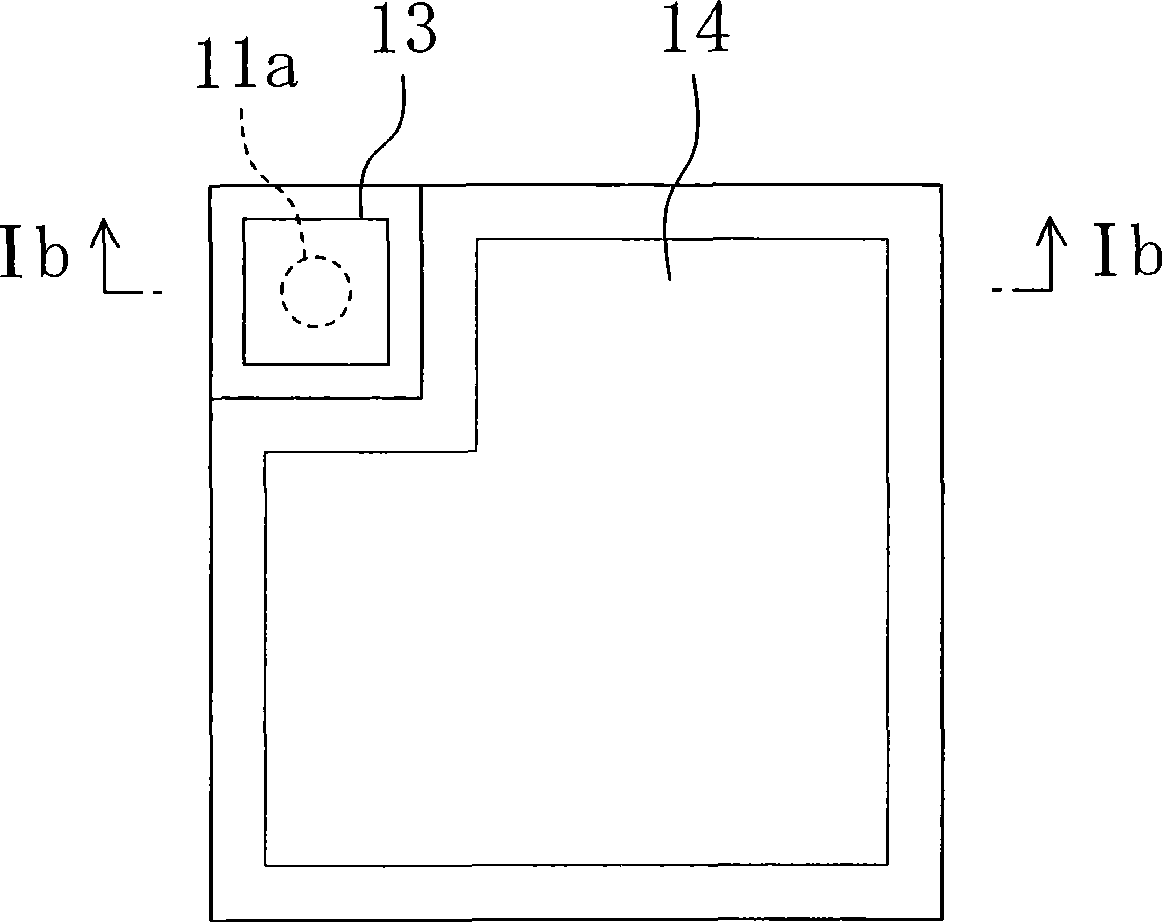
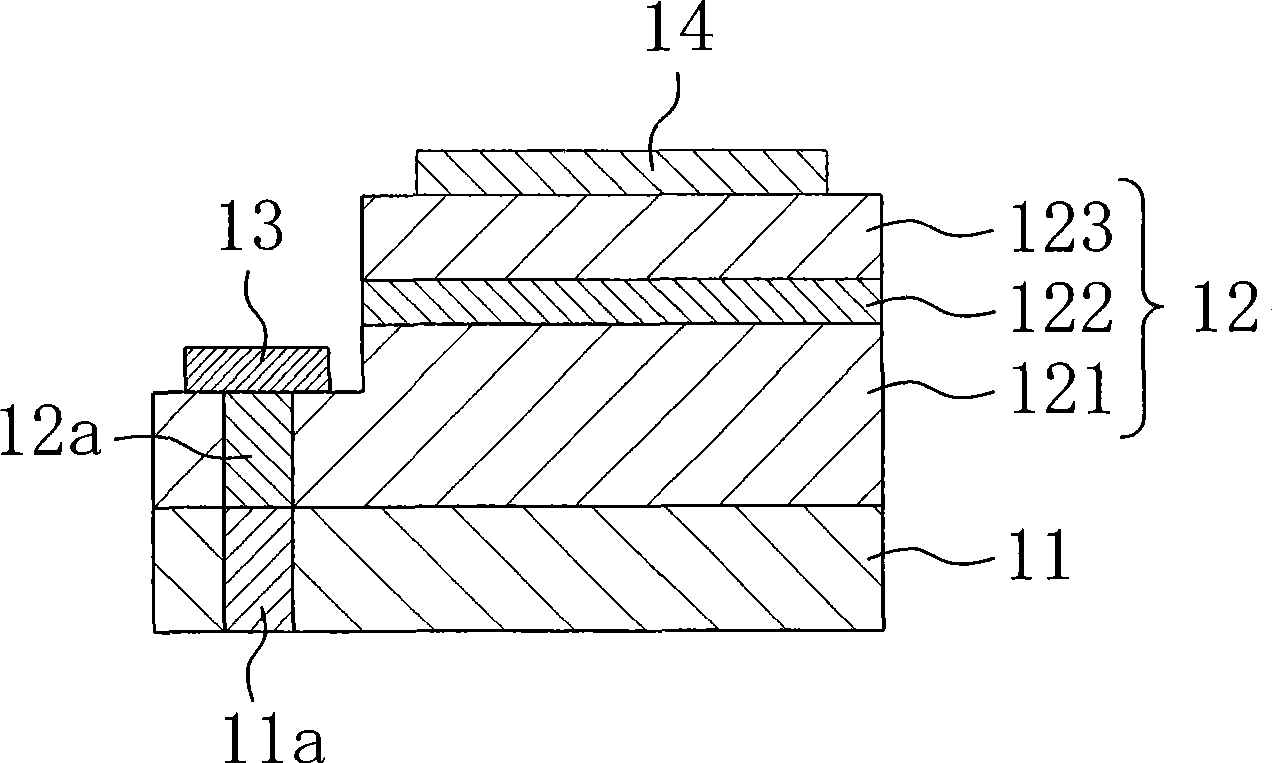
A first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Fig. 1 (a) and Fig. 1 (b) show the semiconductor light-emitting element related to the first embodiment of the present invention, Fig. 1 (a) shows the planar structure, Fig. 1 (b) is Ib of Fig. 1 (a) - Ib line profile composition.
[0018] The semiconductor light emitting element of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 is formed on a substrate 11 having a defect concentration region (core) 11a in which crystal defects are concentrated compared with other regions. In this embodiment, the substrate 11 is a single crystal substrate formed of a nitride-based semiconductor such as gallium nitride (GaN), and has a cubic shape with a side length of 1000 μm and a thickness of 300 μm. The core 11a penetrates the substrate 11 from the thickness direction, and is formed at the corner of the substrate in the present embodiment.
[0019] On the substrate 11, a semiconductor layer 12 is formed. T...
no. 2 approach
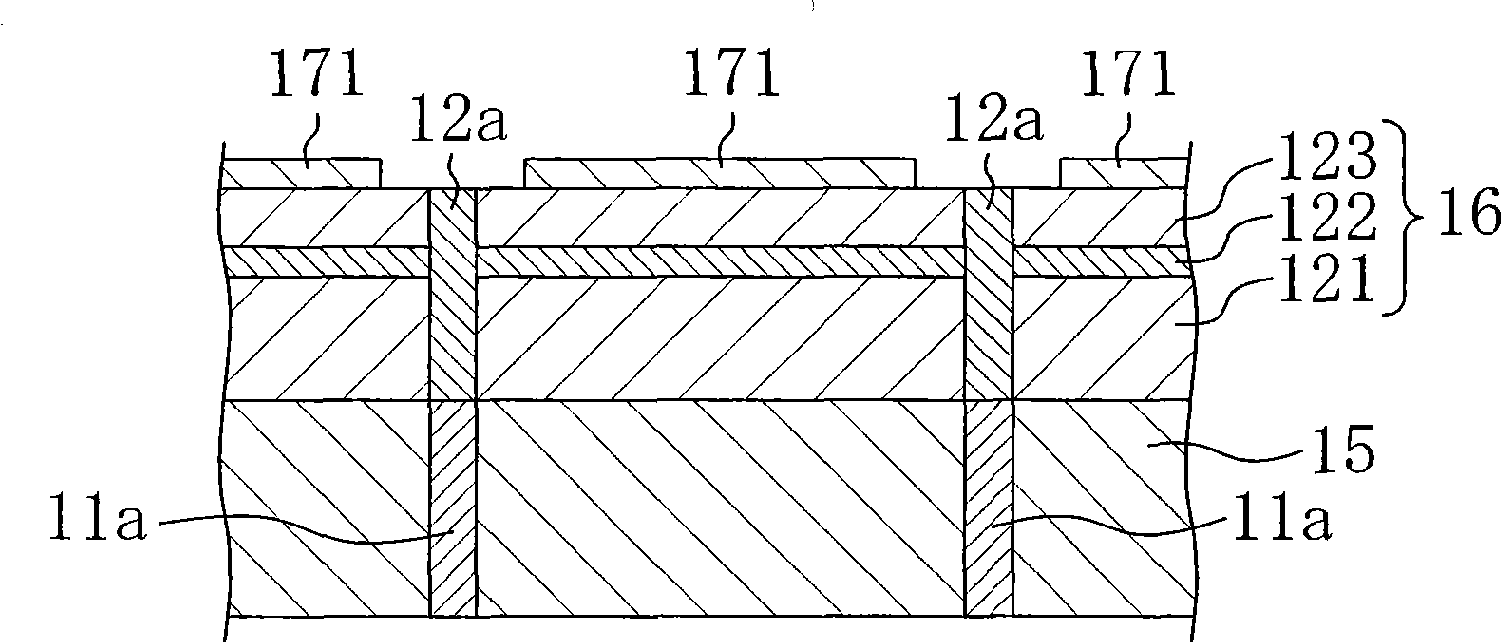
Hereinafter, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Fig. 6 (a) and Fig. 6 (b) show the semiconductor light-emitting device related to the second embodiment of the present invention, Fig. 6 (a) shows the planar structure, Fig. 6 (b) is VIb of Fig. 6 (a) - Sectional view of line VIb. In FIG. 6, elements having the same configuration as those in FIG. 1 are denoted by the same reference numerals and descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0041] As shown in FIG. 6 , in the semiconductor light emitting element of the present embodiment, the core 11 a is formed almost at the center of the substrate 11 . Thus, the n-side electrode 13 is provided at the center of the semiconductor layer 12 . Thus, the current from p-side electrode 14 flows from the entire p-side electrode 14 to n-side electrode 13 at the center of semiconductor layer 12 through p-type layer 123 , light emitting layer 122 , and n-type layer 121 . Therefore, the curr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com