Method and arrangement for the contactless inspection of moving electrically conductive substances
A non-contact, material technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, volume/mass flow generated by electromagnetic effects, material analysis through electromagnetic means, etc., can solve the problems that the measurement sensitivity cannot be increased, the measurement sensitivity has decreased, and the flow velocity cannot be measured.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
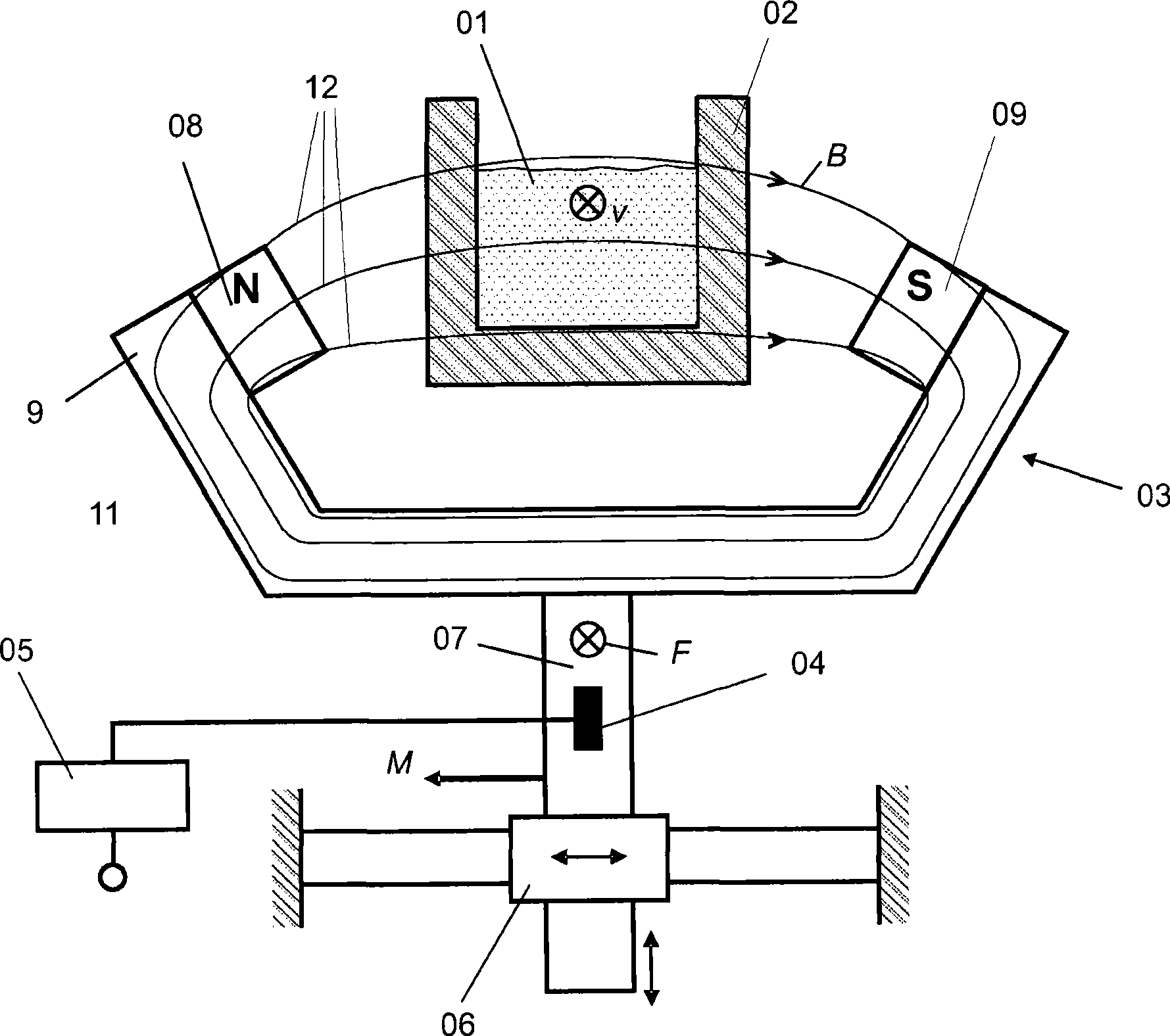
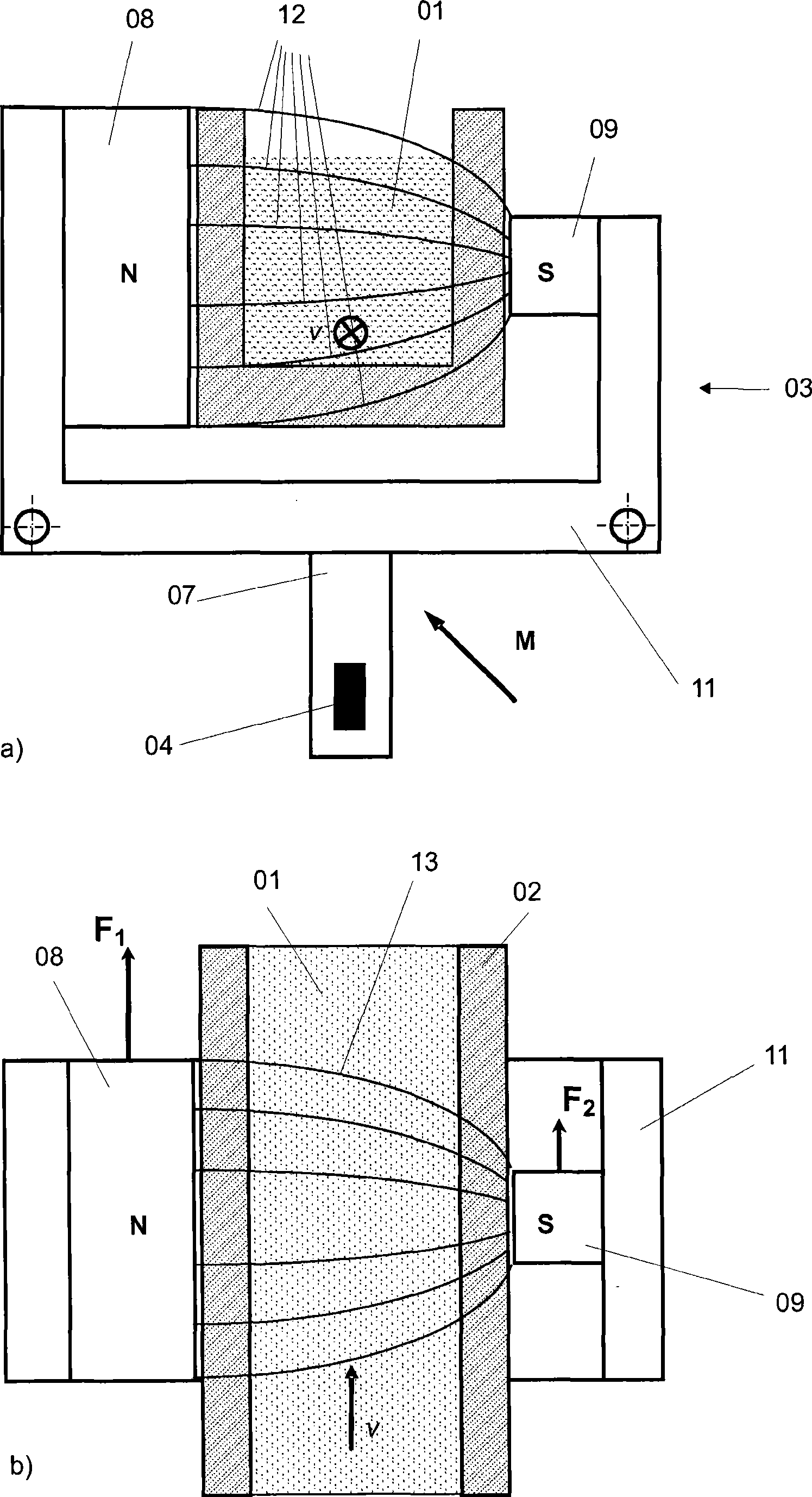
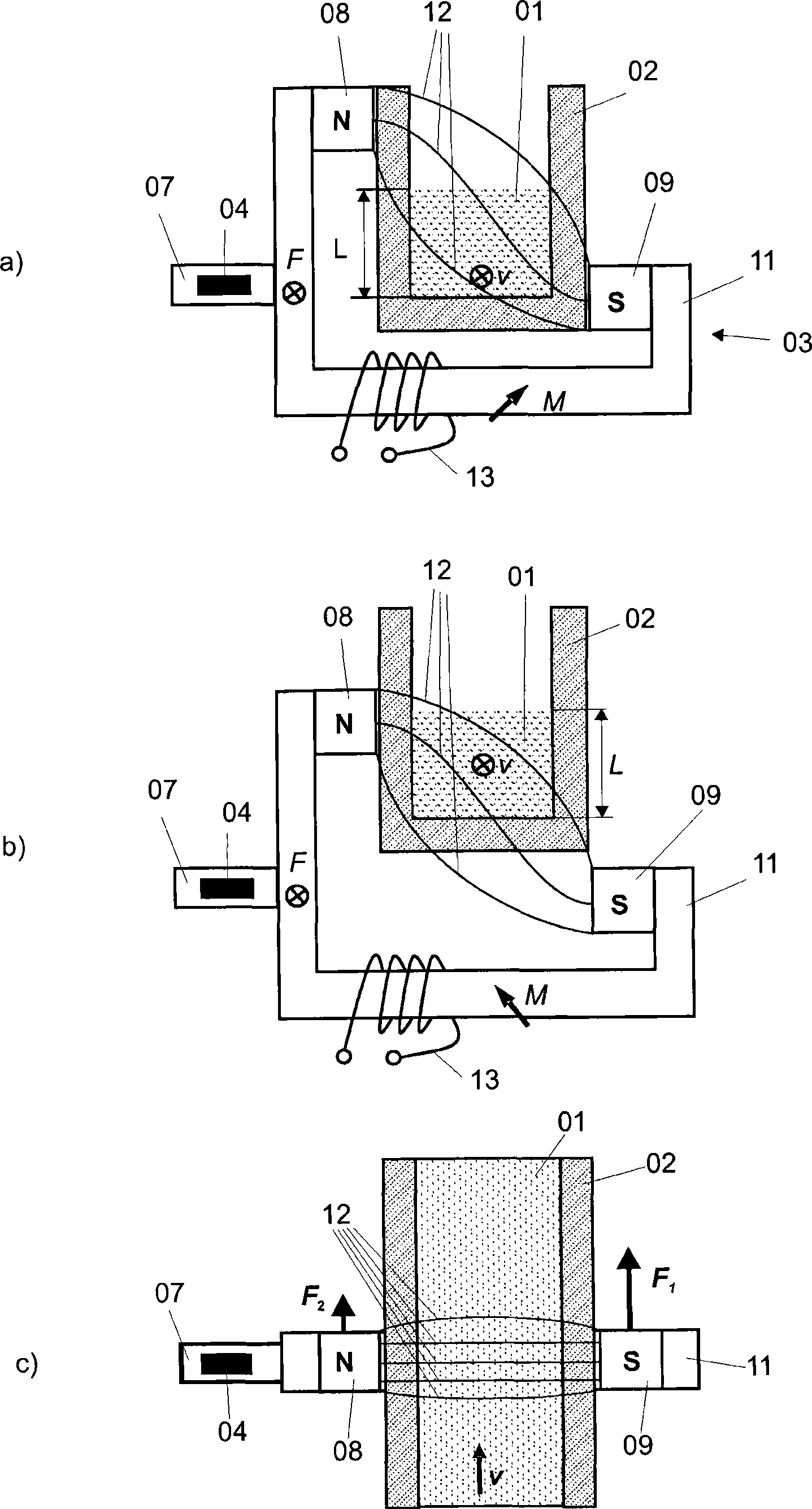
[0043] figure 1 A preferred embodiment of a Lorentz-force flowmeter according to the invention is shown for the contactless detection of a substance 01 flowing in a channel 02 (hereinafter also referred to as a flow channel). The flow direction of the substance 01 is represented by a vector v. The Lorentz force flowmeter comprises a magnetic system 03 , a measurement system 04 , an analysis unit 05 and an actuation system 06 . The magnetic system 03 , the evaluation unit 05 , the actuation system 06 are arranged in a common seat 07 .
[0044] The magnetic system 03 comprises at least two opposing permanent magnets 08 and 09 arranged outside the flow guide channel 02 and a yoke 11 made of a magnetically conductive material. It serves to generate the main field B, which is represented by its field lines 12 .
[0045] Integrated in the holder 07 is a measuring system 04 , preferably comprising a plurality of extended measuring strips, which measures a state parameter of the su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com