Parallel space topology analyzing method based on discrete grid
A technology of spatial topology and analysis methods, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as errors in the topological relationship of spatial objects, incomplete types of spatial topology analysis operations, and storage of results without spatial data division. , to achieve the effect of reducing data communication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
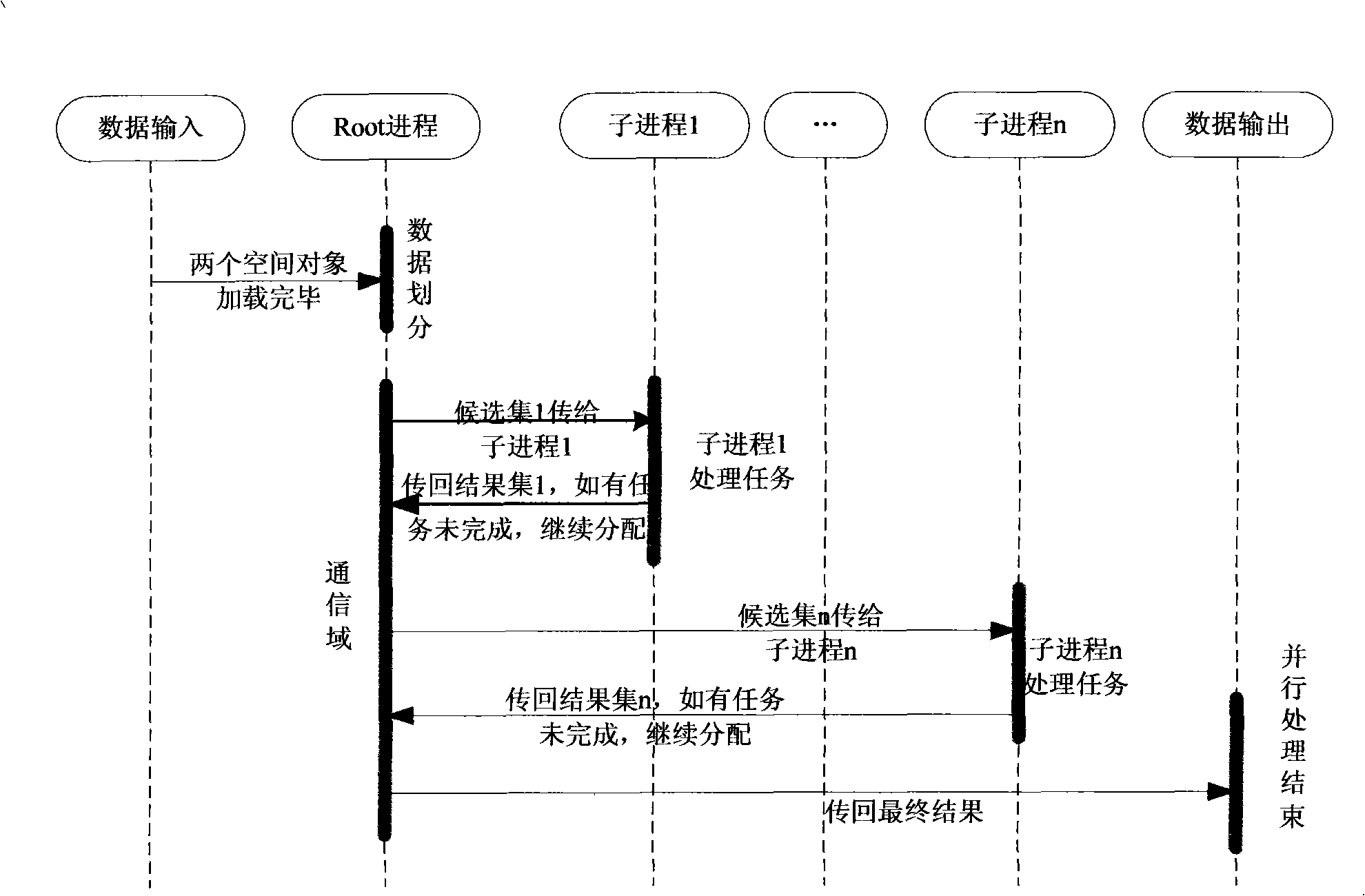
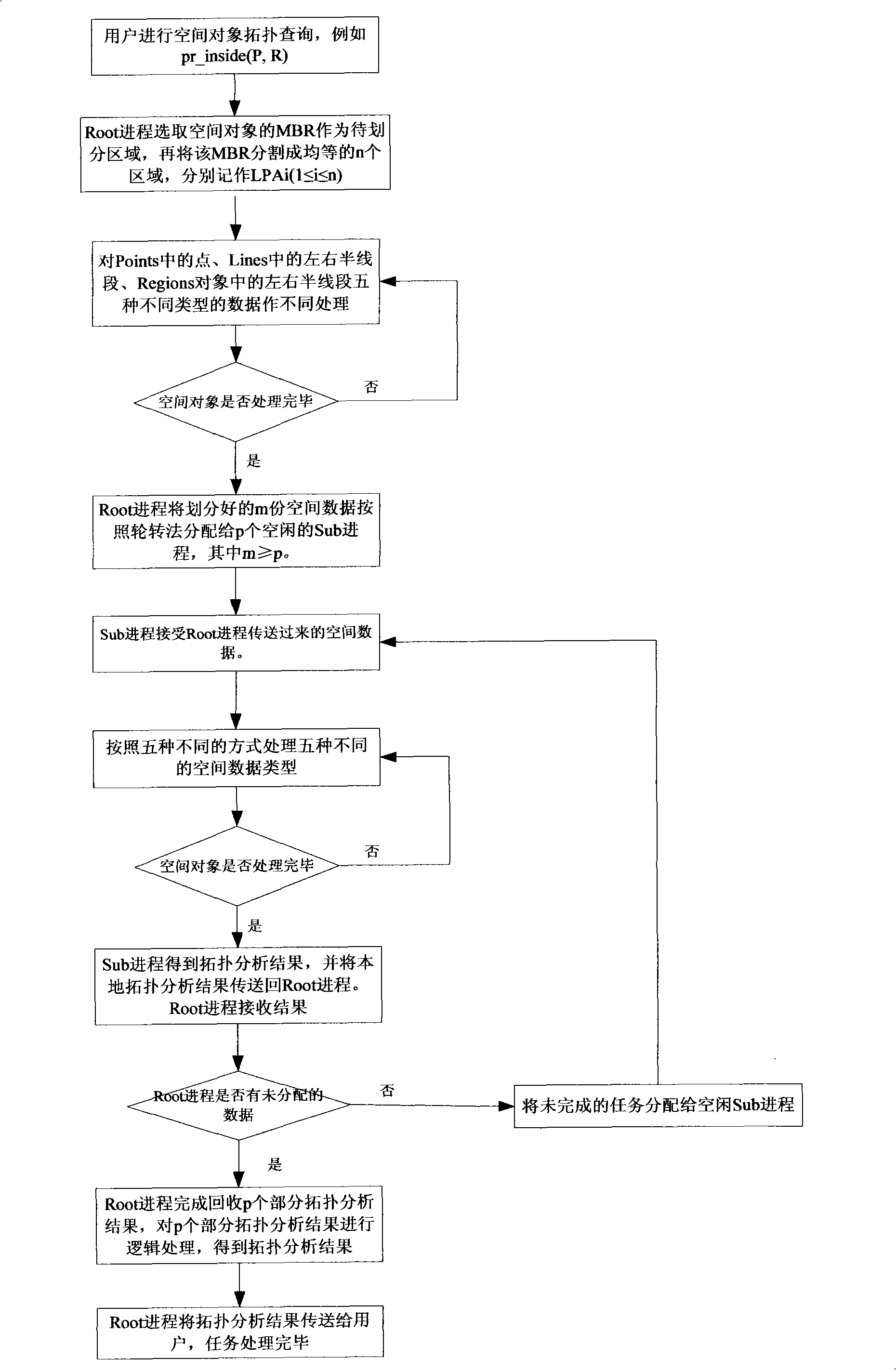
[0116] Its specific implementation method is:
[0117] (1) The user conducts spatial object topology query: pr_inside(P, R).
[0118] (2) The Root process selects the joint MBR of P and R as the area to be divided.
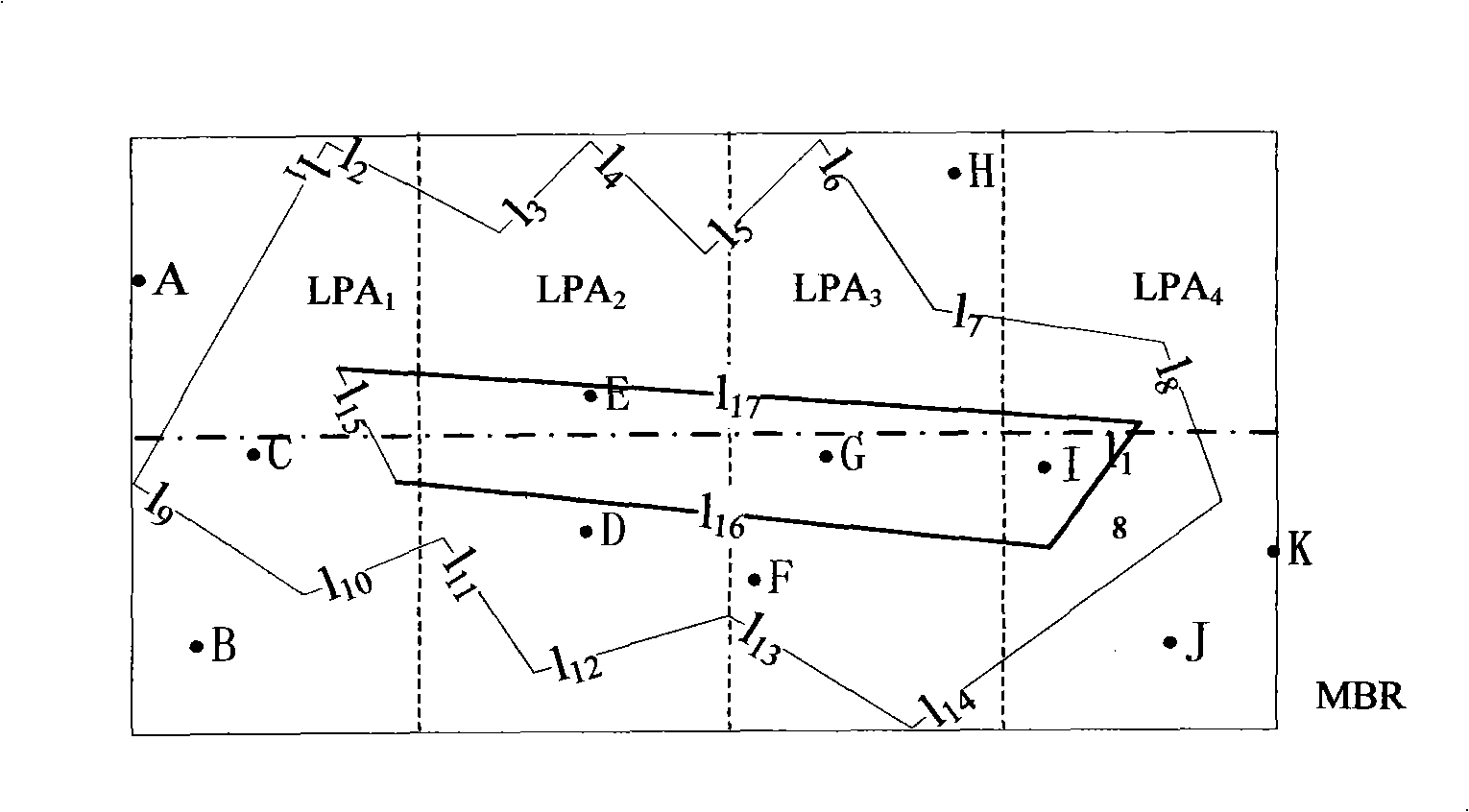
[0119] (3) The Root process divides the MBR selected in (2) into four equal areas, which are respectively denoted as LPA i (1≤i≤4).
[0120] (4) Root process according to LPA i Divide the spatial object into 4 spatial data, and treat several different types of data differently:
[0121] ① Point p in P: Let p∈LPA i , then p→Sub process i.
[0122] ②The left half line segment l in R l : set l l The left endpoint of is pl, the right endpoint is pr, and pl∈LPA i , pr ∈ LPA j , 1≤i≤j≤m, then l l →Sub process i...Sub process j. where pl is l l leading point.
[0123] ③Right half line segment l in R r : set l r The dominant point is pr, if pr∈LPA j , then l r → Sub process j.
[0124] (5) The Root process allocates the 4 pieces of spatial data divided i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com