Lens driving device
A lens driving device and lens technology, applied in the field of photography, can solve the problems of the driving rod 13 falling off, the poor response ability of the piezoelectric motor 12, and the poor response ability of the piezoelectric motor 12 vibration, etc., and achieve good bonding effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] In order to make the technical problems, technical solutions and beneficial effects to be solved by the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
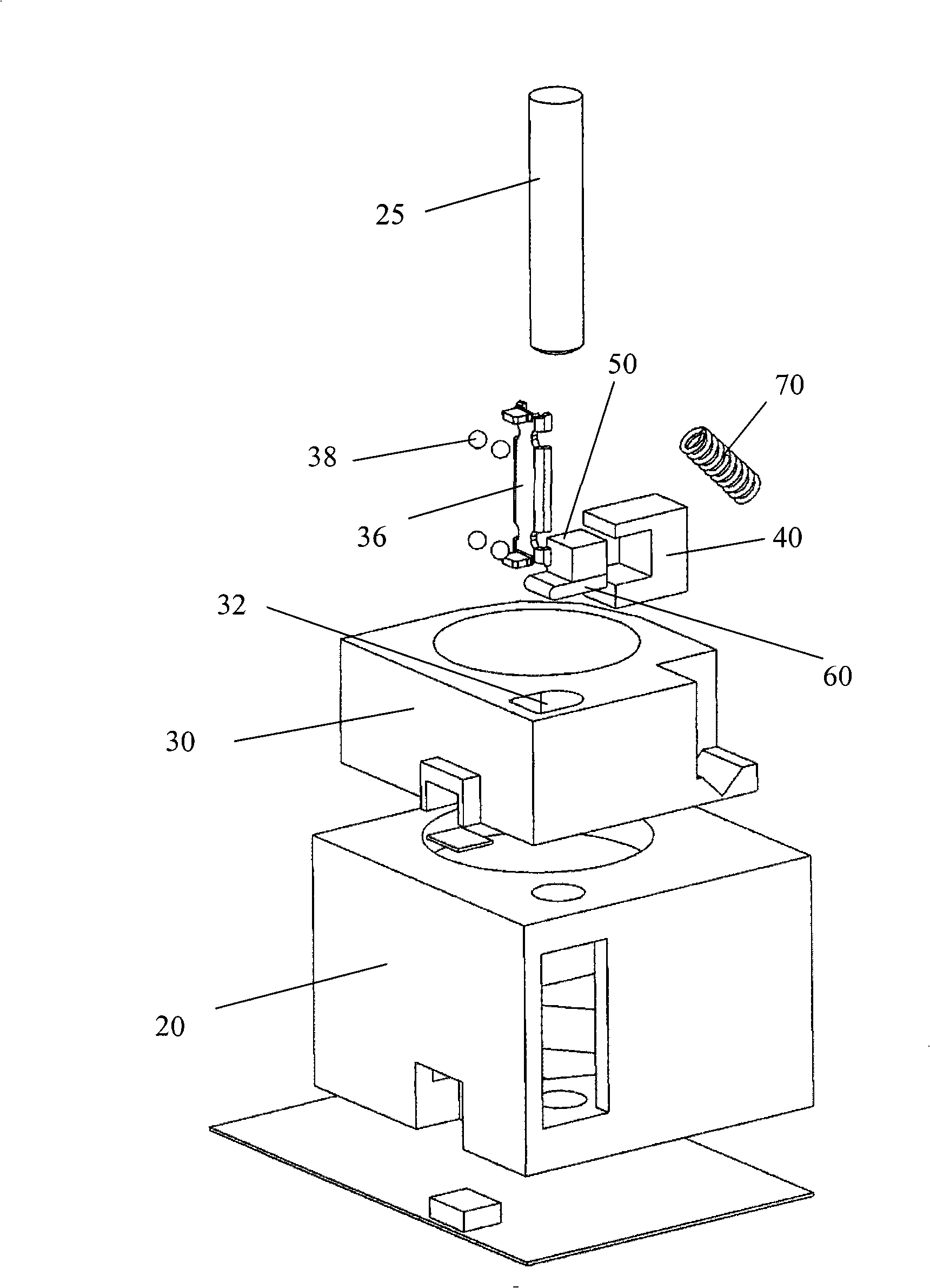
[0016] Such as image 3 and Figure 4 As shown, the lens driving device according to one embodiment of the present invention includes a base 20, a guide post 25 fixed on the base 20, a lens holder 30 slidably installed on the guide post 25, and a motor installed on the lens holder. A seat 40 , a piezoelectric motor 50 fixed at one end to the motor seat, a friction coupling head 60 fixed at the other end of the motor, and a preload assembly 70 .
[0017] The lens holder 30 has a through hole 32 and a receiving cavity 34 . A bead holder 36 is fixed in the through ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com