FastSLAM algorithm based on improved resampling method and particle selection
A resampling and particle technology, applied in the direction of position/direction control, measuring device, non-electric variable control, etc., can solve the problems of real-time destruction, poor consistency, and insufficient robustness of data association problems, so as to improve consistency and improve The effect of precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
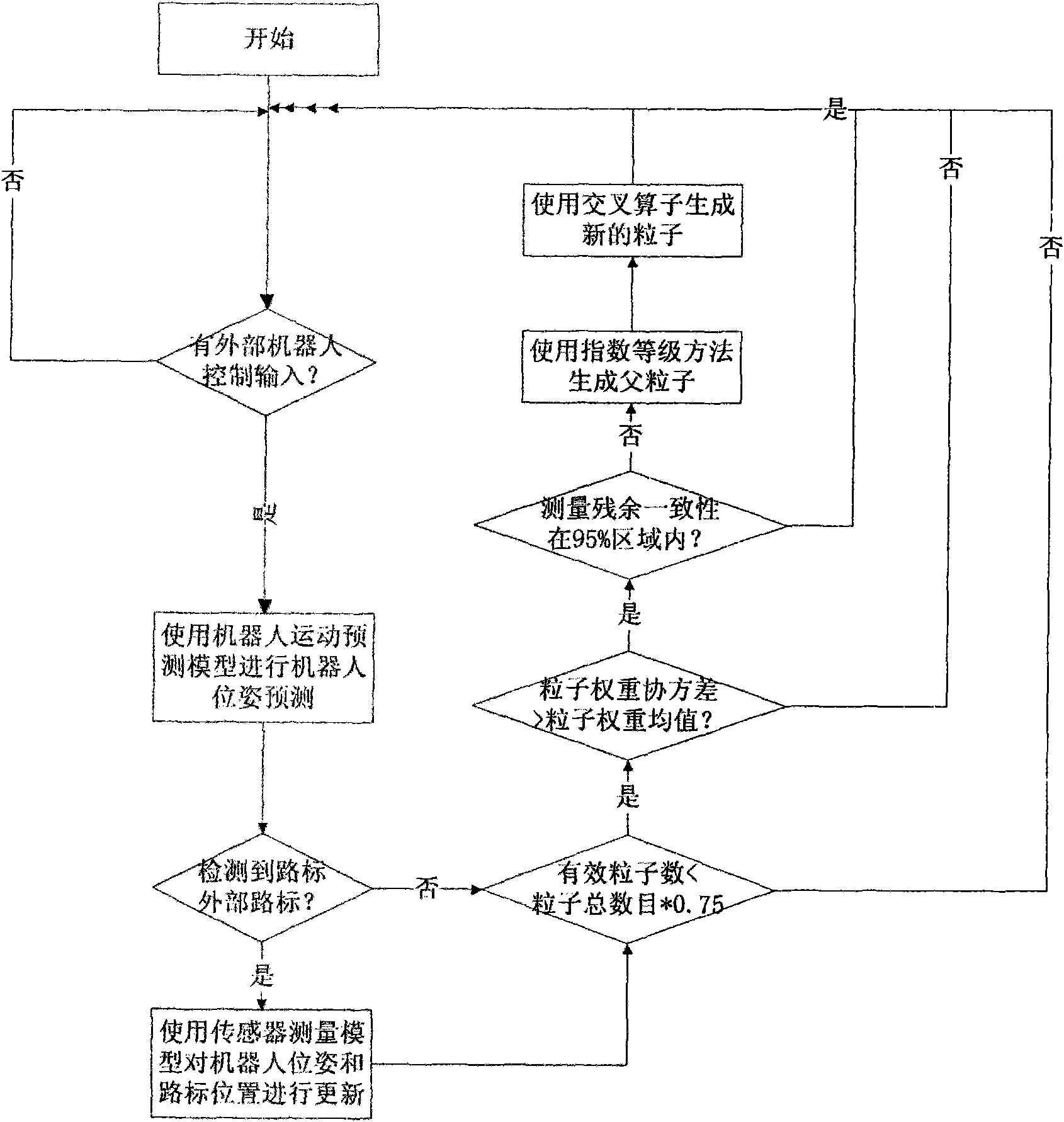
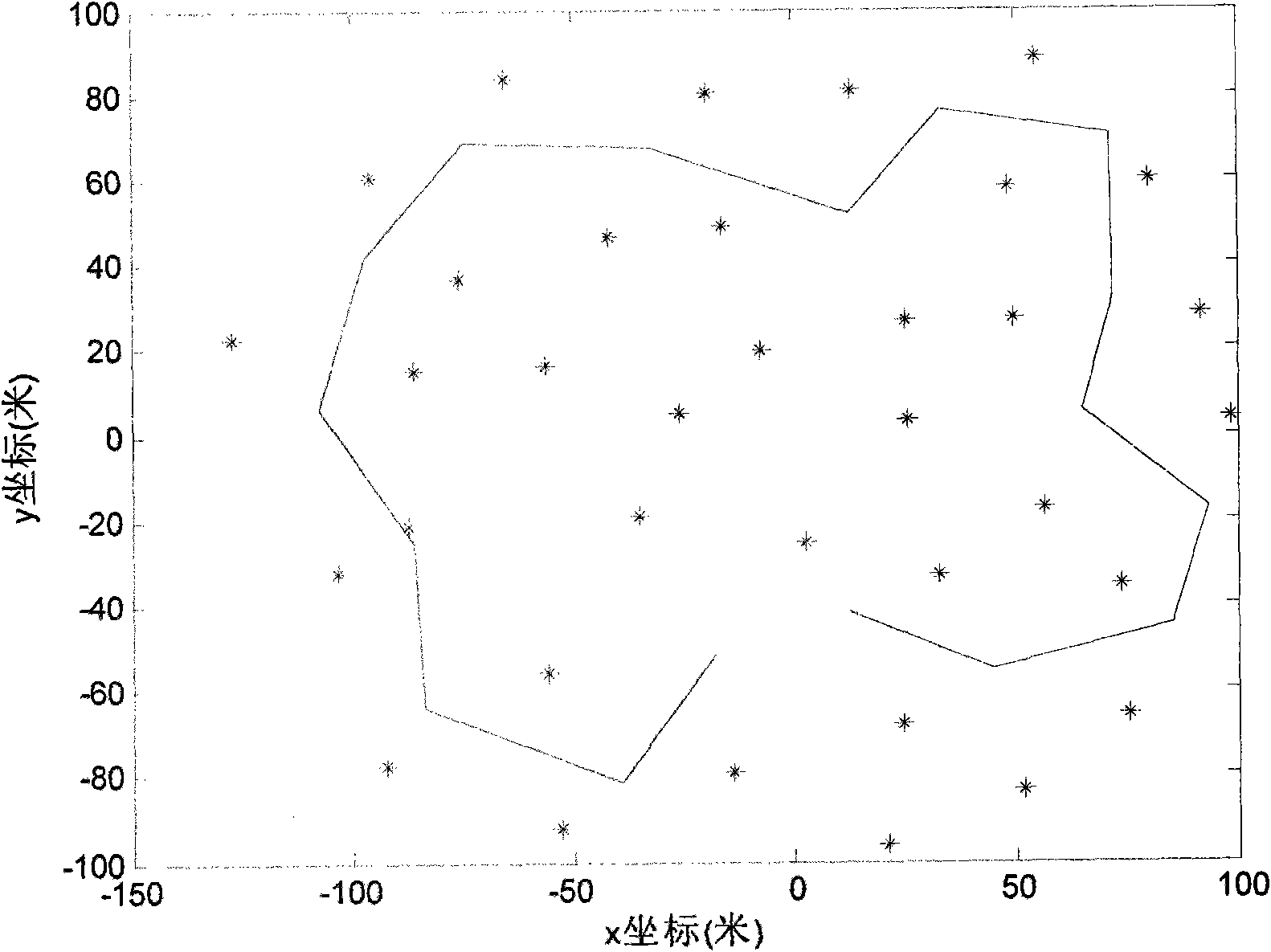
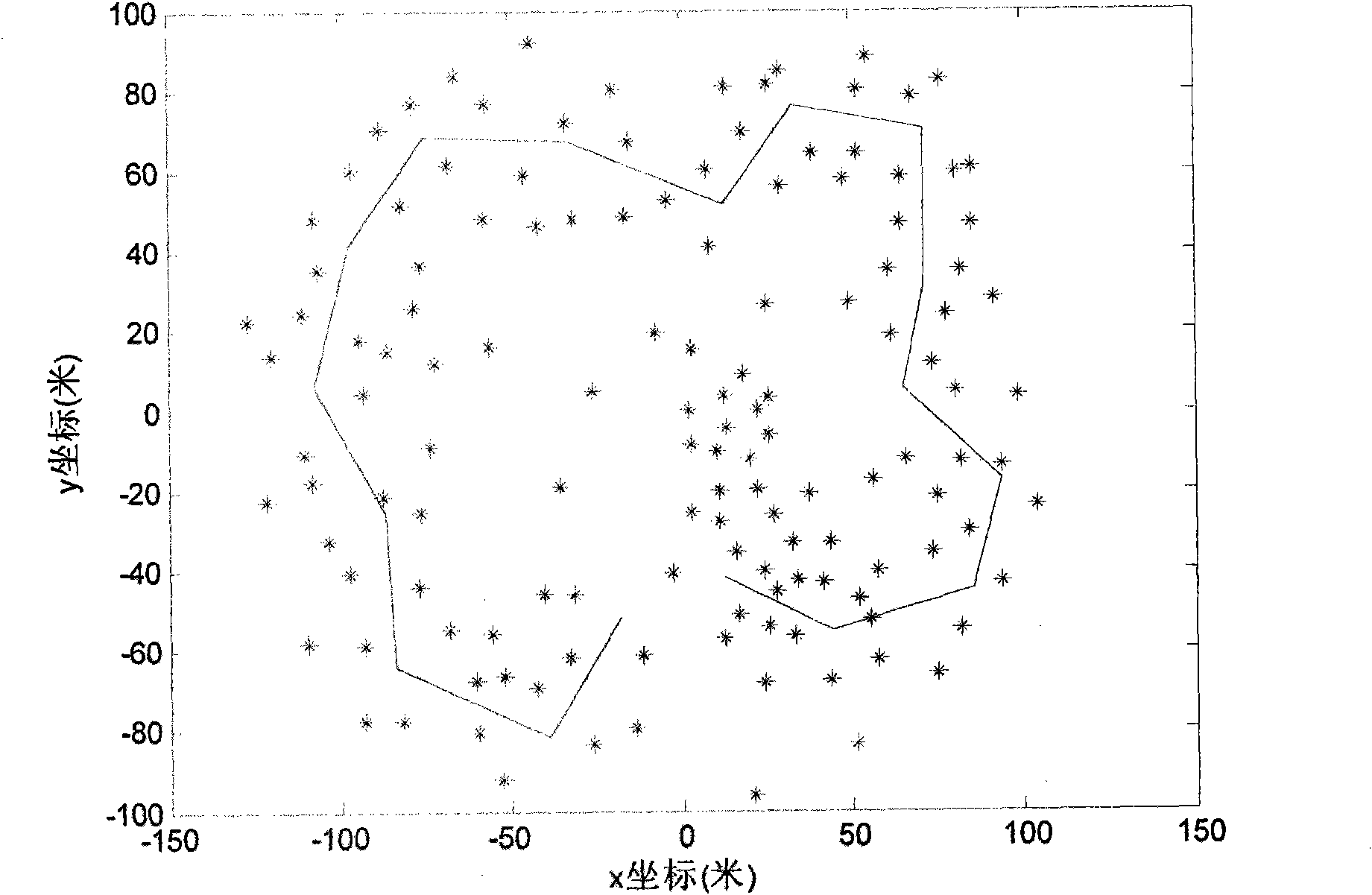
[0033] A FastSLAM algorithm based on improved resampling method and particle selection, the algorithm flow is as follows figure 1 As shown, when the robot receives external control input, the extended Kalman filter is used to predict and estimate the robot pose in each particle according to the robot motion prediction model; when receiving the detection data of the road sign from the external sensor, the same The robot pose and landmark positions in each particle are updated according to the sensor's measurement model using an extended Kalman filter. After using the motion prediction model to predict the robot pose or using the measurement model to update, start to judge whether particle resampling is required. In the judgment of particle resampling, when the number of effective particles is less than 75% of the total number of particles, the particle weight covariance is greater than the particle weight, and the particle measurement residual consistency data is not in the con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com