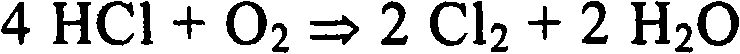Method for generating metallic ruthenium or ruthenium compounds from solids containing ruthenium
A technology of ruthenium compounds and metal ruthenium, applied in the field of volatile ruthenium compounds, can solve problems such as uneconomical recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Embodiment 1: Preparation comprises the solid of ruthenium compound
[0084] In order to be able to illustrate the present invention, first prepare the containing supported on SnO 2 or TiO 2 Shaped bodies of ruthenium compounds.
[0085] Embodiment 1a: use 9.99g ruthenium chloride n hydrate in 33.96ml H 2 solution in O to impregnate 200 g of SnO 2 Molded body (spherical, about 1.9mm in diameter, 15wt% Al 2 o 3 Adhesive, Saint-Gobain), then mixed for 1 hour. The wet solid was then dried in a muffle furnace (air) at 60°C for 4 hours and then calcined at 250°C for 16 hours.
Embodiment 1b
[0086] Embodiment 1b: with 12g ruthenium chloride n-hydrate in 40.8ml H 2 solution in O to impregnate 200 g TiO 2 Pellets (cylindrical, about 2 mm in diameter, 2-10 mm in length, Saint-Gobain) were then mixed for 1 hour. The damp shaped body thus obtained was dried overnight at 60° C. and introduced dry under nitrogen flushing into a solution of NaOH and 25% hydrazine hydrate solution in water and allowed to stand for 1 hour. Excess water was then evaporated off. The damp shaped body was dried at 60° C. for 2 hours and then washed with 4×300 g of water. The moist shaped body thus obtained was dried in a muffle furnace (air) at 120° C. for 20 minutes and then calcined at 350° C. for 3 hours.
Embodiment 2
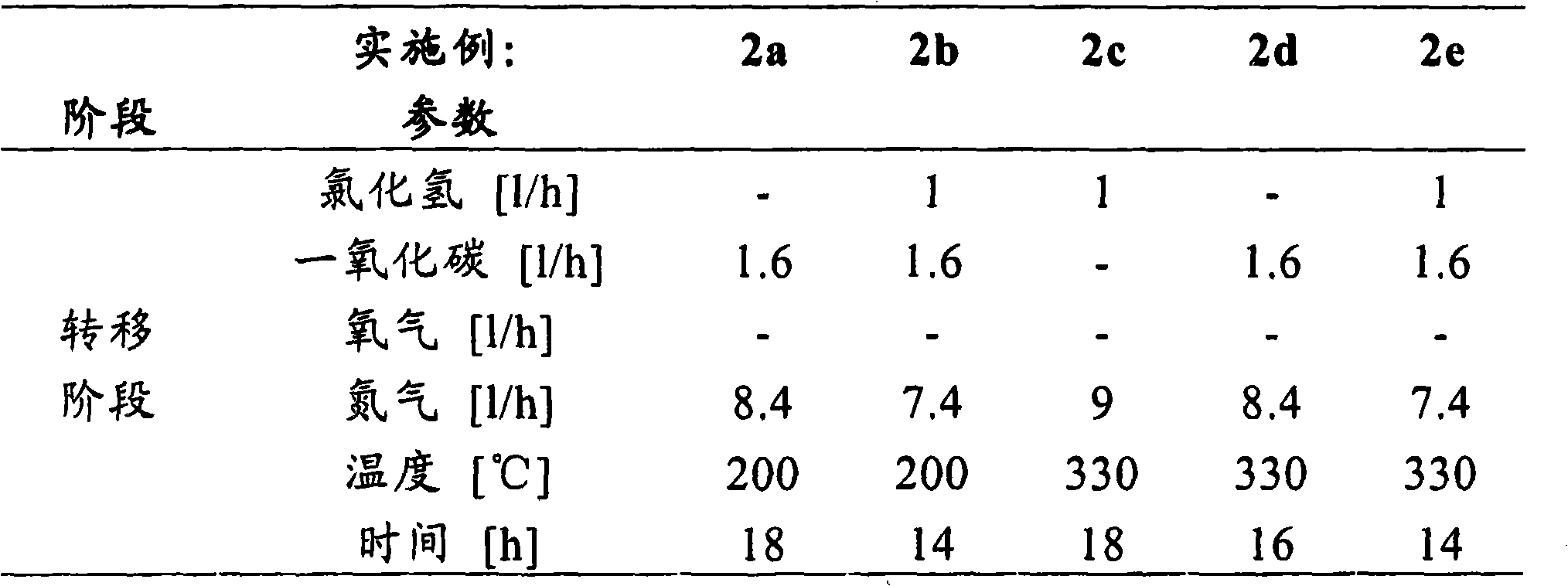
[0087] Example 2: Effects of Carbon Monoxide, Hydrogen Chloride and Oxygen on the Transfer of Ruthenium Compounds
[0088] 4 x 1 g of shaped bodies from Example 1a were placed in a fused silica reaction tube (diameter 10 mm), heated to 330° C., in each case 1 l / h hydrogen chloride, 4 l / h oxygen, 5 l / h Gas mixture 1 (10 l / h) consisting of nitrogen is passed until 16 hours (conditioning phase), then different gas mixtures are passed at 200 °C (2a-b) or 330 °C (2c-e) to form volatile ruthenium compounds (transfer phase). The parameters of the transfer phase are shown in Table 2a.
[0089] Table 2a: Parameters of the transfer phase
[0090]
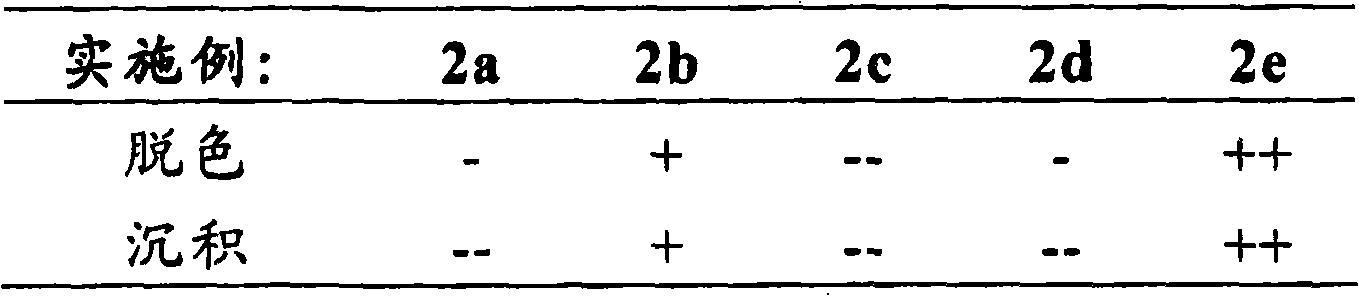
[0091] After the transfer phase, the discoloration of the shaped bodies and the formation of characteristic deposits in the cooler area downstream of the reactor were evaluated as indicators for the volatilization of the ruthenium compound (Table 2b).
[0092] Table 2b: Discoloration of shaped bodies; characteristic deposits in cooler...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap