Wireless communication device, communication system, communication control method, and program
A technology of a wireless communication device and a control unit, applied in wireless communication, transmission system, error prevention/detection using a return channel, etc., capable of solving problems such as deterioration of throughput, increase of circuit scale at the receiving end, and inability to maintain the sequence of data packets, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
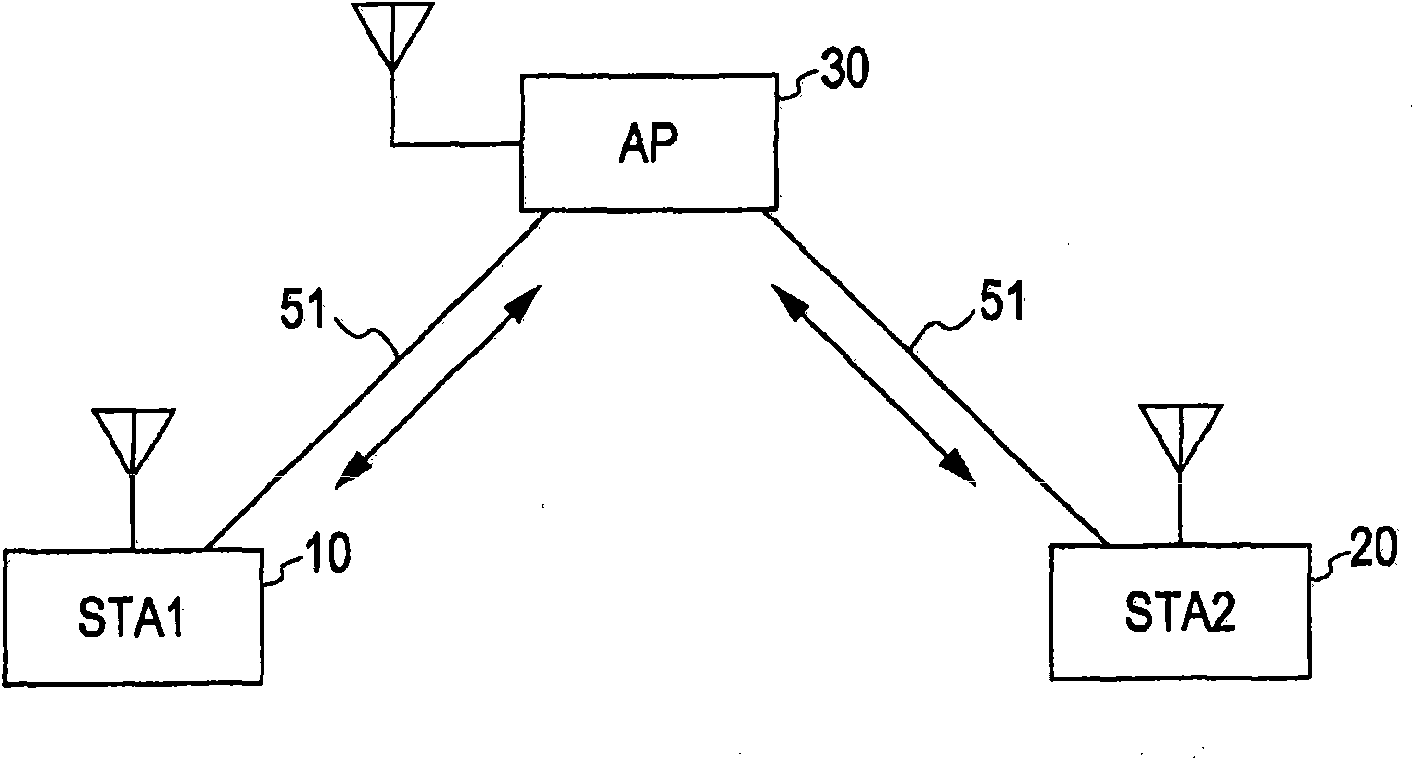
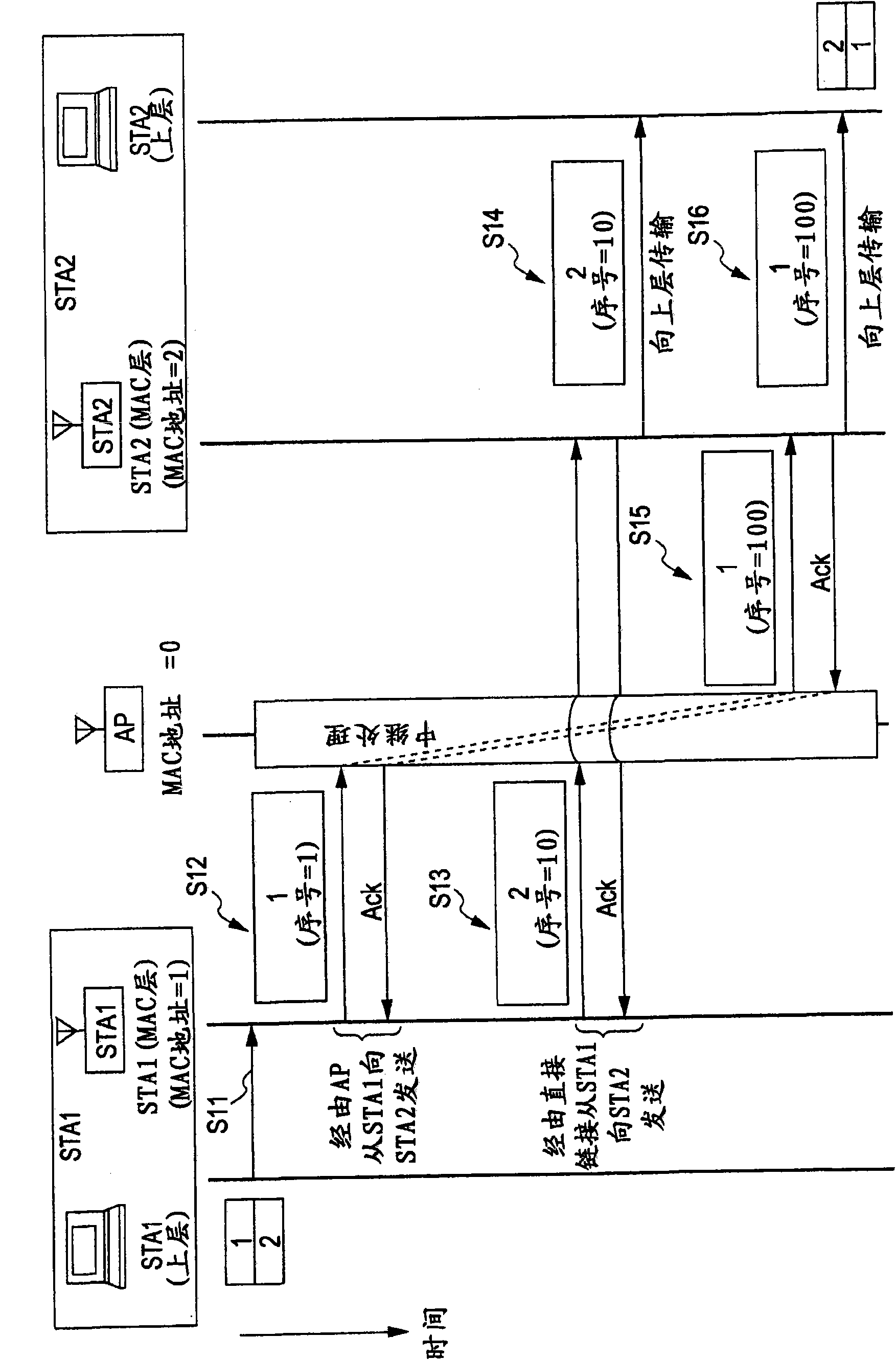
[0144] In the structure of the first embodiment described below, the access point AP does not change the sequence number set in the header for the packet relayed via the AP routing path. That is to say, with this setting, the original sequence number set by the packet source is not changed and reaches the destination. Therefore, the order of receiving packets can match the sending order of the source (sequence number set at the source) in the case of using the direct link path, and in the case of using the AP routed path, and by switching both paths, and Stored in the reordering buffer of the data receiving device in units of source addresses (SA).
[0145] The sequence number set at the data source is recorded in the MAC header of the packet. The access point AP as a relay point does not rewrite the sequence number, but simply copies and transmits it. The wireless communication device according to the present embodiment stores received packets in the reordering buffer so as...
no. 2 example
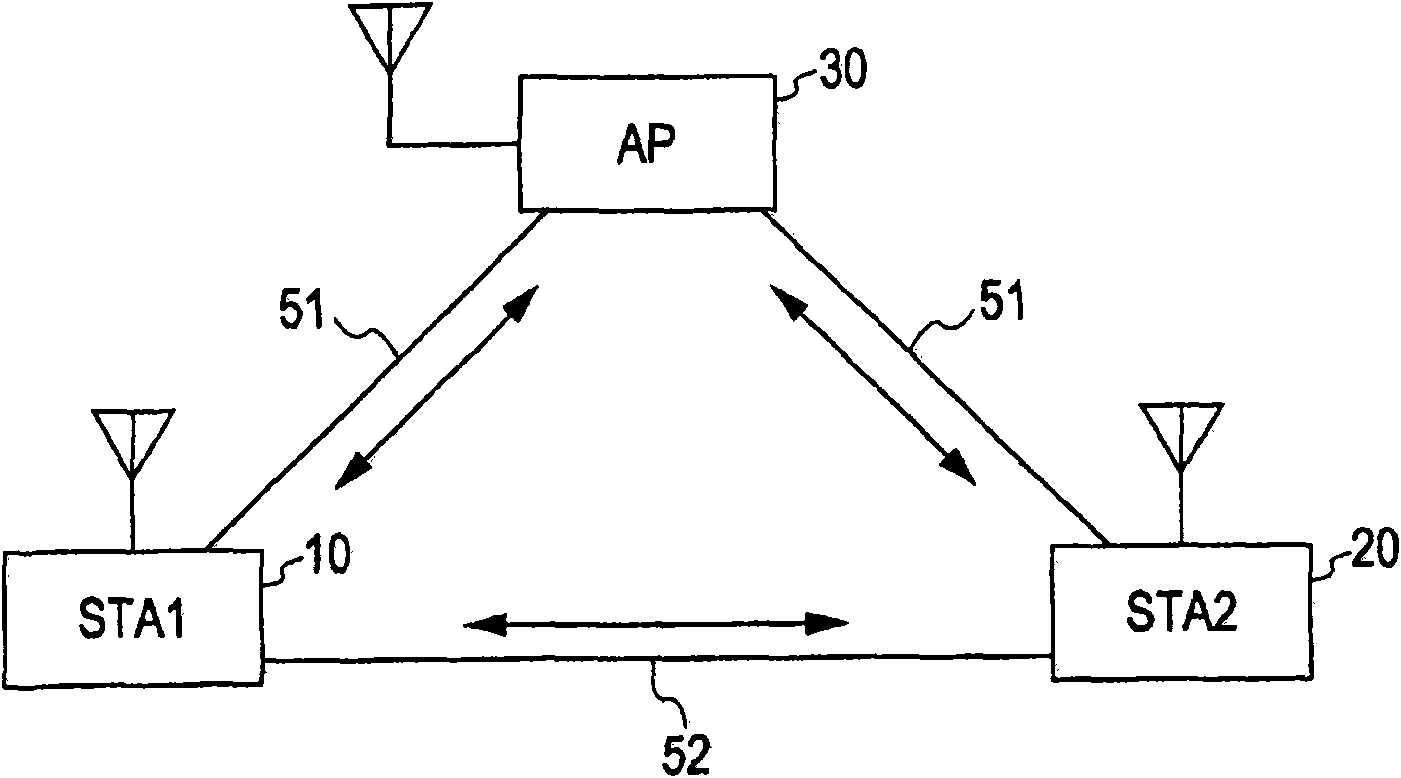
[0191] A second embodiment of the present invention will be described later. With the second embodiment, the access point AP rewrites the sequence number set in the packet header, which is the same as the system according to the prior art. This is the same Peer-to-Peer management process, i.e. the same as already existing 802.11.
[0192] When transmitting a data packet, STA1 as a source device manages a sequence number to be set in a packet header in units of a receiver address (RA) indicating a direct data receiver of the packet. This is also the same as the Peer-to-Peer management process, i.e. the same as already existing 802.11.
[0193] In the second embodiment, when performing path change, STA1 as a data transmitter sends a path change request to STA2 as a data receiver. STA2 receives the path change request from STA1, and in case of accepting the path change, transmits a path change response to STA1. The path change response sent by STA2 to STA1 stores the following...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com