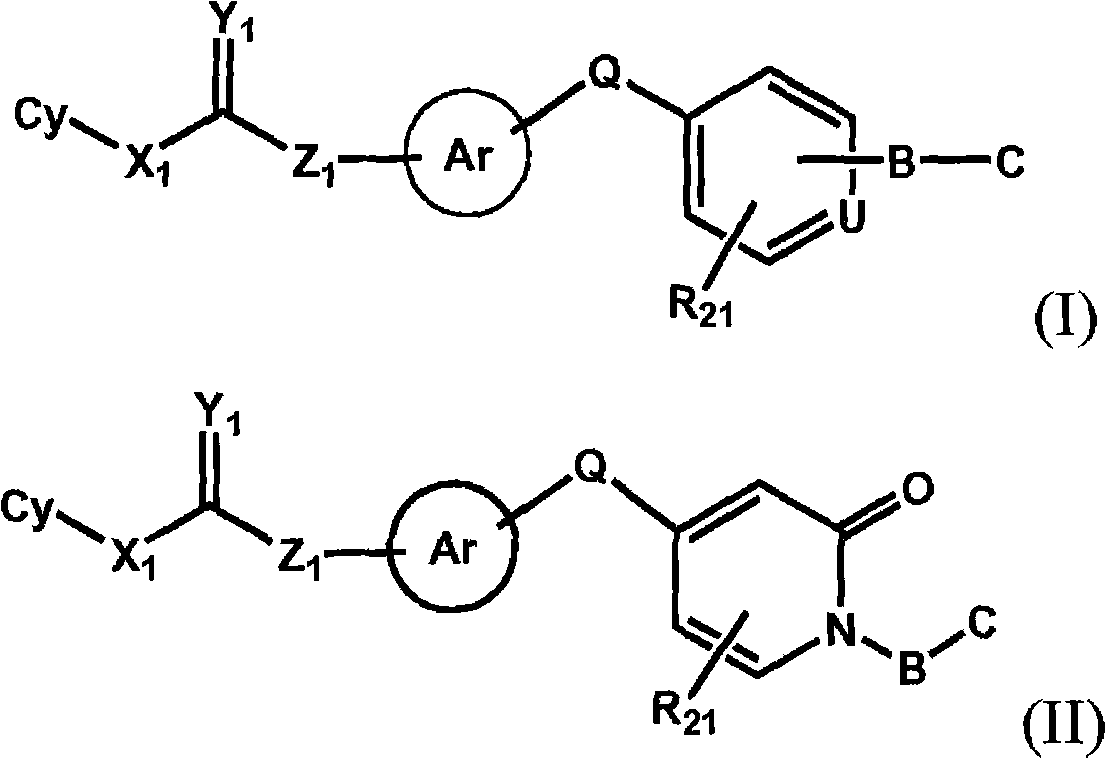
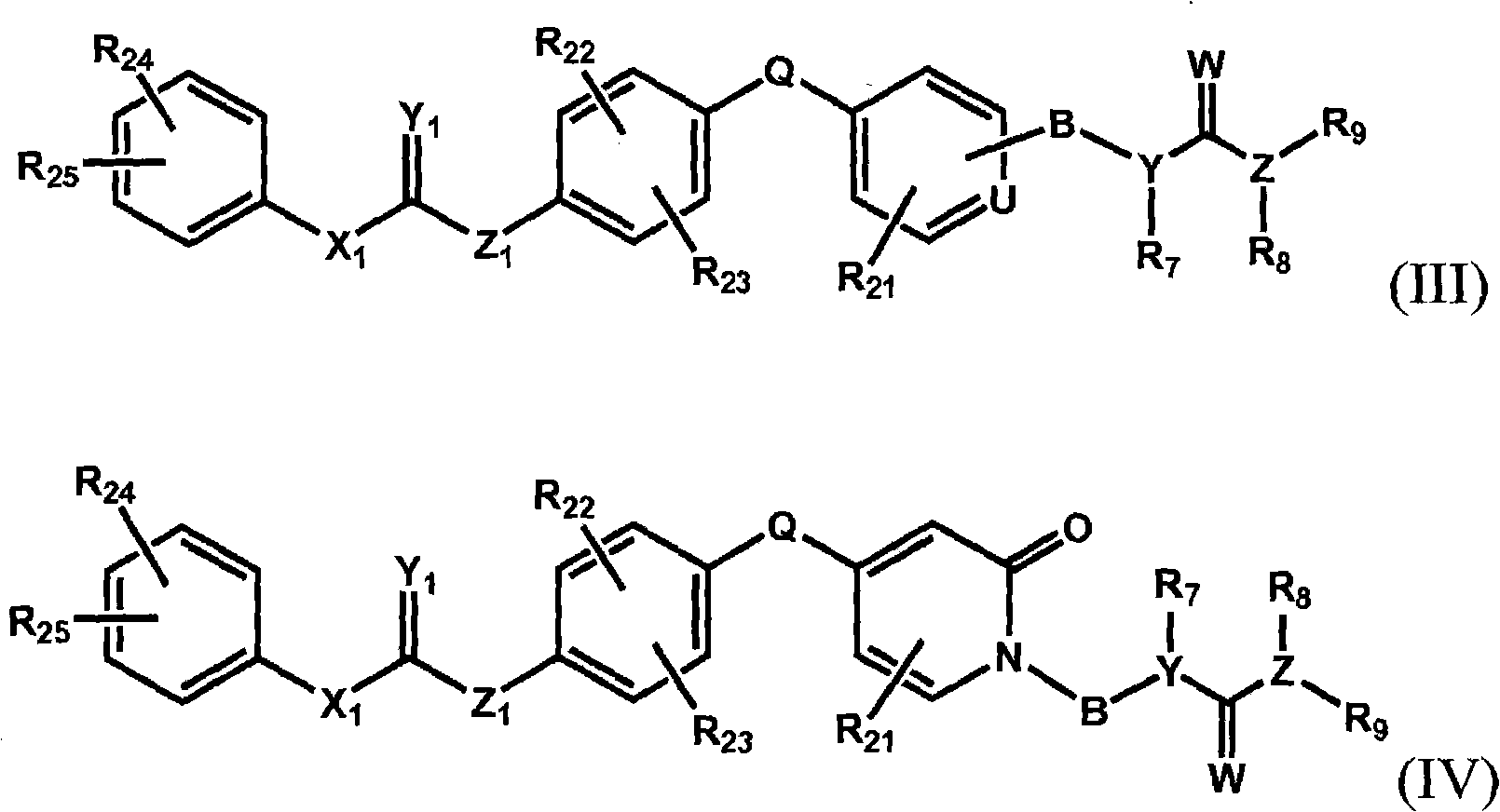
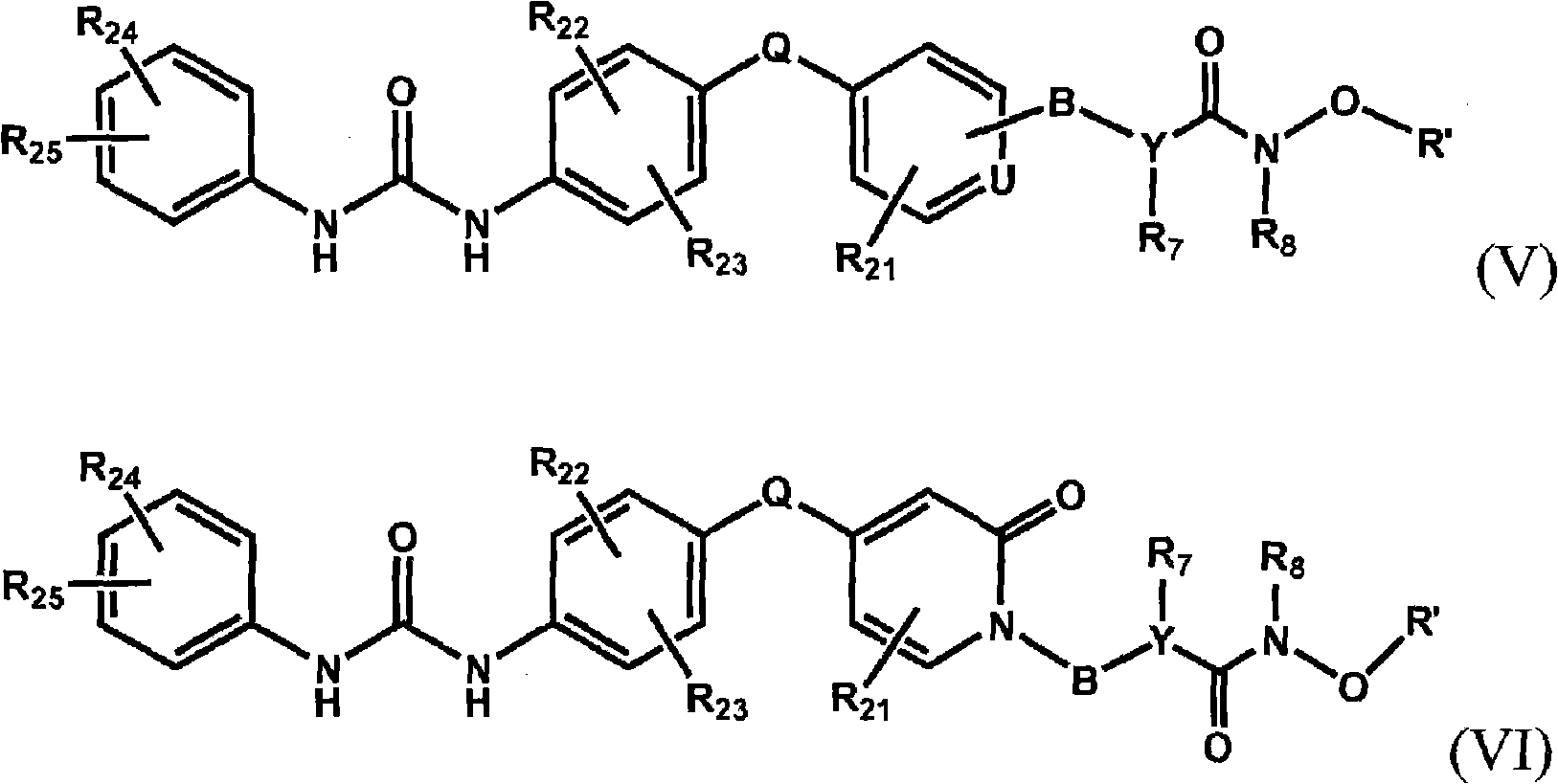
Raf kinase inhibitors containing a zinc binding moiety
A technology of compounds, formulas, applied in the field of Raf kinase inhibitors containing zinc-binding moieties, which can solve the problems of difficulty, difficulty in regulatory approval of combination therapy, high cost of health care, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0077] The preparation of pharmaceutical compositions containing active ingredients is well known in the art, for example, by mixing, granulating, or tablet-forming processes. The active therapeutic ingredient is usually mixed with excipients which are pharmaceutically acceptable and compatible with the active ingredient. For oral administration, the active agent is mixed with additives customary for the purpose, such as vehicles, stabilizers, or inert diluents, and converted by conventional methods into a suitable Forms for administration such as tablets, coated tablets, hard or soft gel capsules, aqueous, alcoholic or oily solutions and the like described in detail above.
[0078] The dose of the compound administered to the patient is lower than that which would induce toxicity in the patient. In certain embodiments, the dose of the compound administered to the patient is less than that which would result in the concentration of the compound in the patient's plasma at or a...
Embodiment 1
[0172] Example 1: (R)-4-(4-(3-(4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)urea Base) phenoxy) -N-(1-(hydroxylamino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl)pyridinecarboxamide (Compound 1) Preparation
[0173] Step 1a. Methyl 4-chloropicolinate (compound 102)
[0174] Anhydrous dimethylformamide (DMF) (10 mL) was slowly added to thionyl chloride (300 mL) at 40-48°C. The solution was stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes, and then compound 101 (100.0 g, 813.0 mmol) was added over a period of 30 minutes. The resulting solution was heated at 72°C (extensive sulfur dioxide evolution) for 16 hours, resulting in a yellow solid. The remaining mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with toluene (500 mL) and concentrated to 200 mL. The described toluene addition / concentration process was repeated twice. The above-obtained solution and the solid were added to 200 mL of methanol under an ice bath, keeping the internal temperature below 55°C. The contents were stirred at room temperature for 45 ...
Embodiment 2
[0192] Example 2: 4-(4-(3-(4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ureido)benzene Oxy)-N-(3-(hydroxyamino)-3-oxopropyl)pyridinecarboxamide (compound 2) preparation of
[0193] Step 2a. Methyl 3-(4-(4-(3-(4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ureido)phenoxy)pyridinecarboxamide)propanoate (compound 111-2 )
[0194] The title compound 111-2 was prepared from compound 110 (300.0 mg, 0.66 mmol) using a procedure similar to that described for the preparation of compound 111-1 (Example 1) (110 mg, 31% ): 537[M+1] + .
[0195] Step 2b. 4-(4-(3-(4-Chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ureido)phenoxy)-N-(3-(hydroxyamino)-3-oxopropane base) pyridinecarboxamide (compound 2)
[0196] The title compound 2 is a solid (50 mg, 47 %): LCMS: 468 [M+1] + ; 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ): δ2.25(t, J=6.9Hz, 2H), 3.47(m, 2H), 7.16(m, 3H), 7.38(d, J=2.4, 1H), 7.60-7.70(m, 4H), 8.15 (s, 1H), 8.50 (d, 1H), 8.78 (t, J=6.3Hz, 1H), 9.43 (s, 1H), 9.66 (s, 1H), 10.44 (s, 1H).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com