Randomness testing method of pseudorandom sequence based on packet handling
A technology of randomness detection and pseudo-random sequence, which is applied in the field of randomness detection of pseudo-random sequence, and can solve the problems that affect the detection accuracy and fail to meet the requirements of safety and effectiveness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
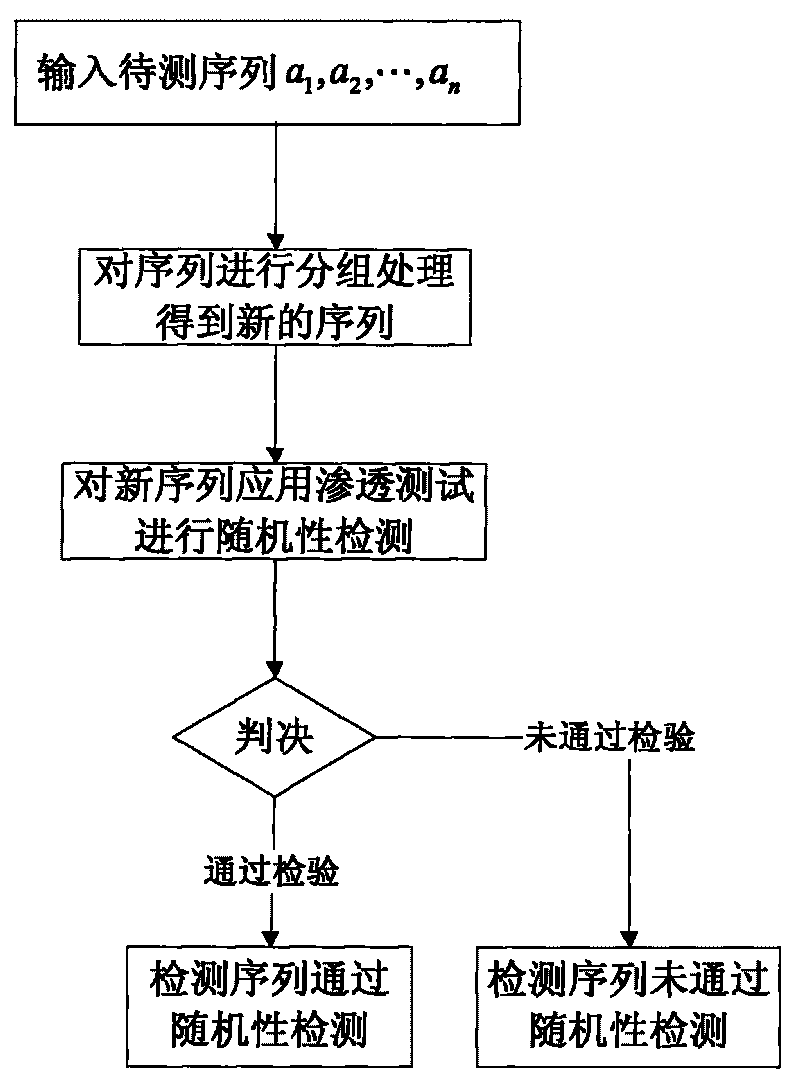
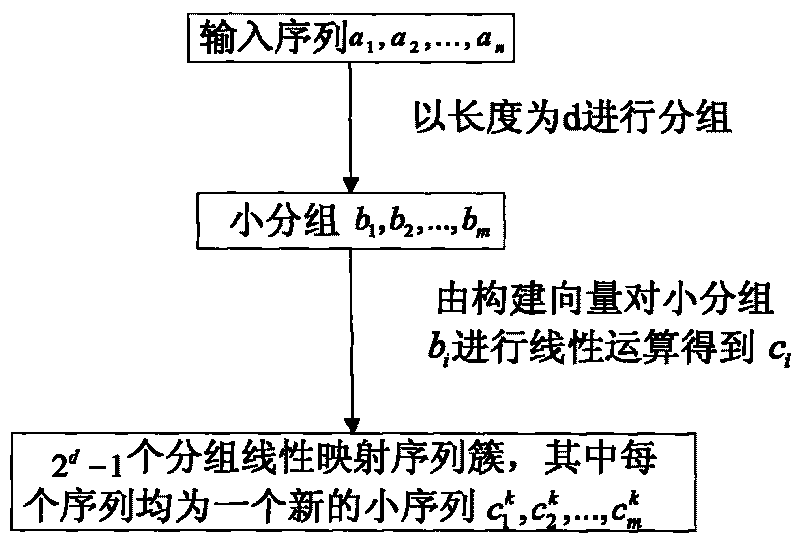
[0074] In the first embodiment, the randomness detection of the pseudo-random sequence is performed after the sequence to be tested is grouped and linearly mapped.
[0075] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , the implementation steps of this example are as follows:
[0076] Step 1, the input length is n=10 8 The sequence to be tested a 1 , a 2 ,...,a n .
[0077] Step 2, take the packet length d=100, set the length to 10 8 The original sequence is divided into length 10 6 100 subgroups of b 1 , b 2 ,...,b 100 ,in 1≤i≤100, record m=10 6 .
[0078] Step 3, group b i (1≤i≤100) respectively use the penetration test method for statistics:
[0079] 1) Take a standard random sequence S, and calculate the standard statistical data DEV=(H 1 , H 2 ,...,H 100 ),in 1≤j≤100, MAX layer j The maximum value of layer tree burning corresponding to the jth ignition method determined by the standard random sequence S, MEAN layer j The average value of layer tree burning cor...
Embodiment 2
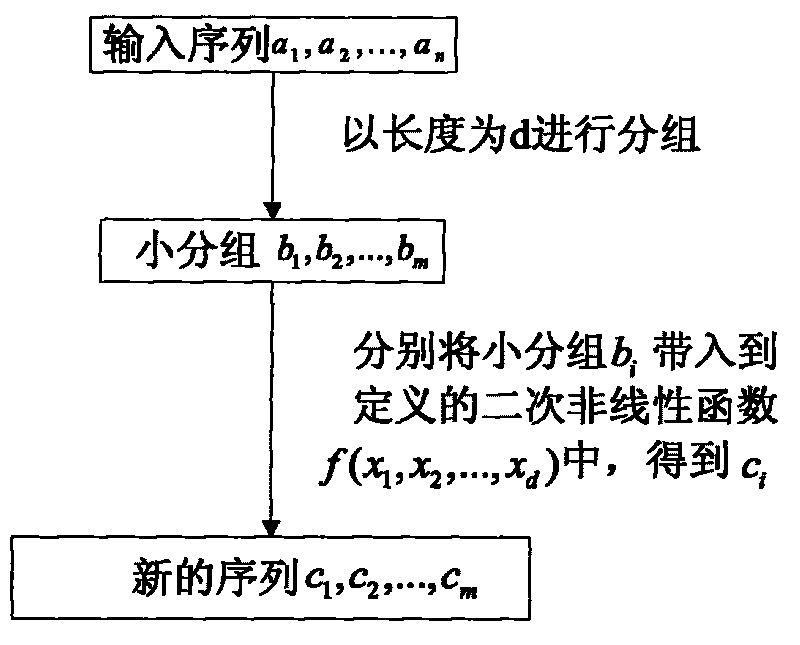
[0089] In the second embodiment, the randomness detection of the pseudo-random sequence is carried out after the secondary nonlinear transformation is performed on the sequence to be tested.
[0090] refer to figure 1 and image 3 , the implementation steps of this example are as follows:
[0091] Step 1, the input length is n=1.01×10 8 The sequence to be tested a 1 , a 2 ,...,a n .
[0092] Step 2, take the packet length d=101, and set the length to 1.01×10 8 The original sequence is divided into 10 of length 101 6 small group b 1 , b 2 ,...,b m , record m=10 6 , group each small group b i =(a 101(i-1)+1 , a 101(i-1)+2 ,...,a 101(i-1)+101 ) as a function coefficient into the quadratic nonlinear function f(x 1 , x 2 ,...,x 101 )=x 1 x 2 +x 3 x 4 +...+x 99 x 100 +x 101 , seek c i =f(a 101(i-1)+1 , a 101(i-1)+2 ,...,a 101(i-1)+101 ), i=1, 2, ..., 10 6 , get the length m=10 6 sequence c 1 , c 2 ,...,c m .
[0093] Step 3, for the sequence c afte...
Embodiment 3
[0102] In the third embodiment, the randomness detection of the pseudo-random sequence is performed after the sequence to be tested is voted by a large number.
[0103] refer to figure 1 and Figure 4 , the implementation steps of this example are as follows:
[0104] Step A, the input length is n=1.01×10 8 sequence to be tested a 1 , a 2 ,...,a n .
[0105] Step B, take the packet length d=101, and set the length to 1.01×10 8 The original sequence is divided into 10 of length 101 6 small group b 1 , b 2 ,...,b m , record m=10 6 , for each small group b i =(a 101(i-1)+1 , a 101(i-1)+2 ,...,a 101(i-1)+101 ),begging 1≤i≤m, get a sequence c of length m 1 , c 2 ,...,c m .
[0106] Step C, the sequence c after voting on the large number 1 , c 2 ,...,c m Statistics with penetration testing methods:
[0107] (C1) Take a standard random sequence S, and seek standard data DEV=(H 1 , H 2 ,...,H 100 ),
[0108] in 1≤j≤100. MAX layer j The maximum value o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com