Mechanical continuous variable valve lift mechanism
A valve lift, mechanical technology, applied in the direction of mechanical equipment, machine/engine, engine components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult control, complex mechanism, not multi-level intelligent control, etc., and achieve the effect of small work wear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0105] In order to avoid possible explanation confusion, unless otherwise specified, the following valves all refer to the valve corresponding to the variable rocker arm (301), that is, the valve (100). The reasons for the mutual occlusion or marking difficulty between components, if a certain schematic diagram cannot mark a certain component, you can refer to other schematic diagrams.
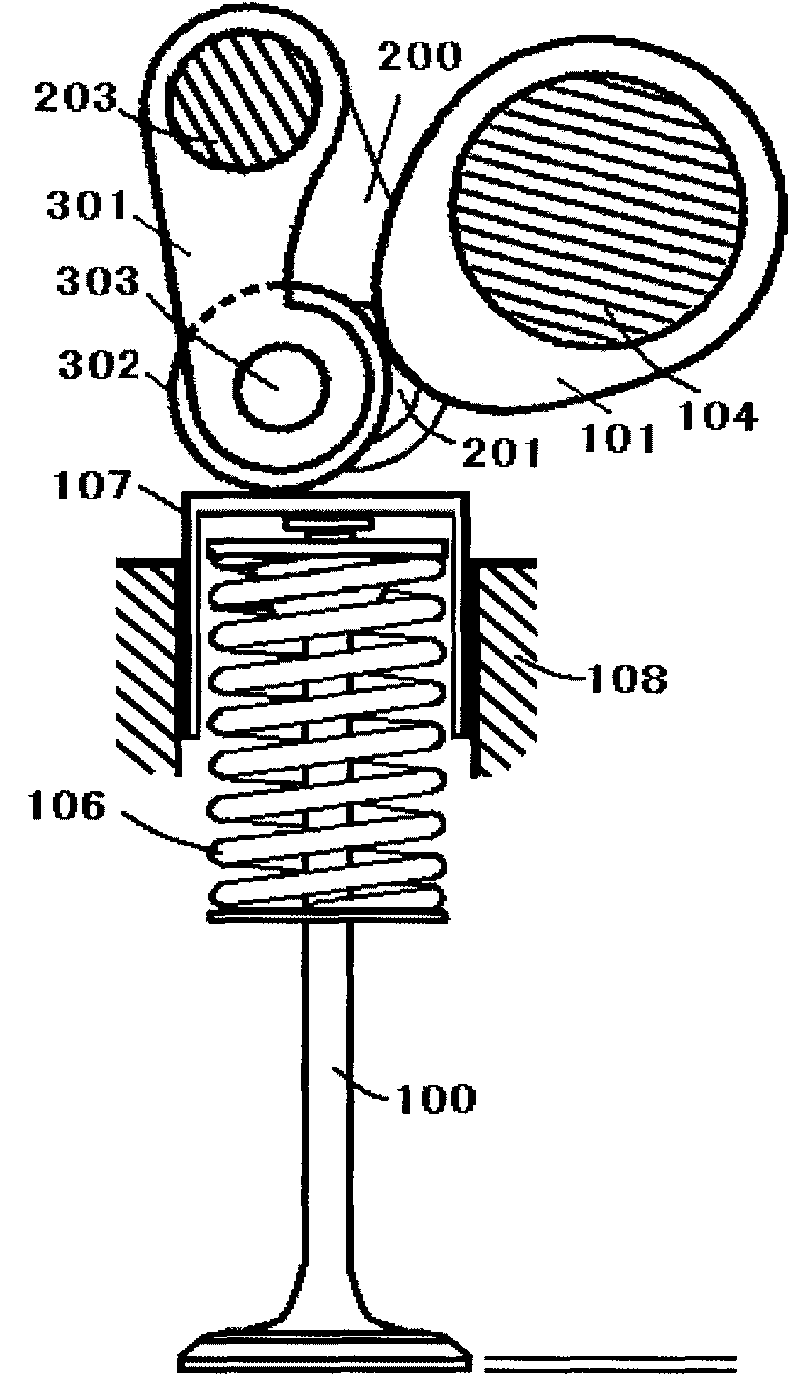
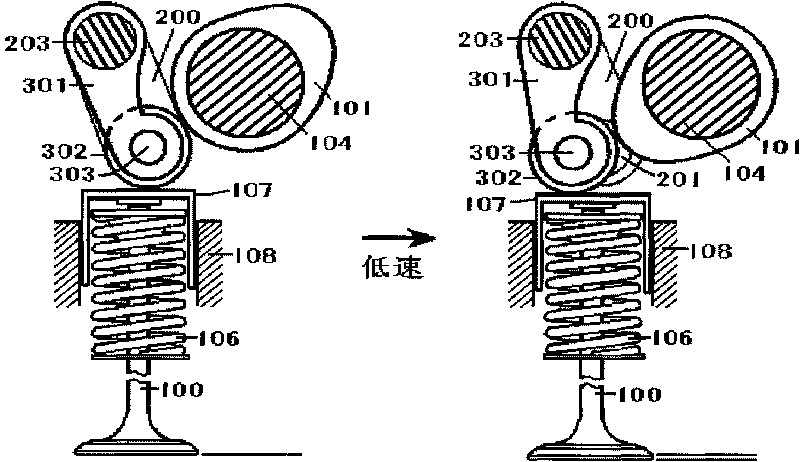
[0106] figure 1 Shown is a schematic structural diagram of a continuously variable valve lift mechanism in the case of a valve lifter (for ease of expression, the valve lifter (107) is represented by a mechanical valve lifter), mainly including the cam (101), crank arm (200), crank arm journal (201), variable rocker shaft (203), variable rocker arm (301), valve tappet (107), tappet seat (108), auxiliary return spring (403) , Valve (100). The crank arm (200) and the crank arm journal (201) are fixedly connected (also can be processed in one piece); the crank arm journal (201) is installed to ...
Embodiment 2
[0112] 1. Engines above medium displacement
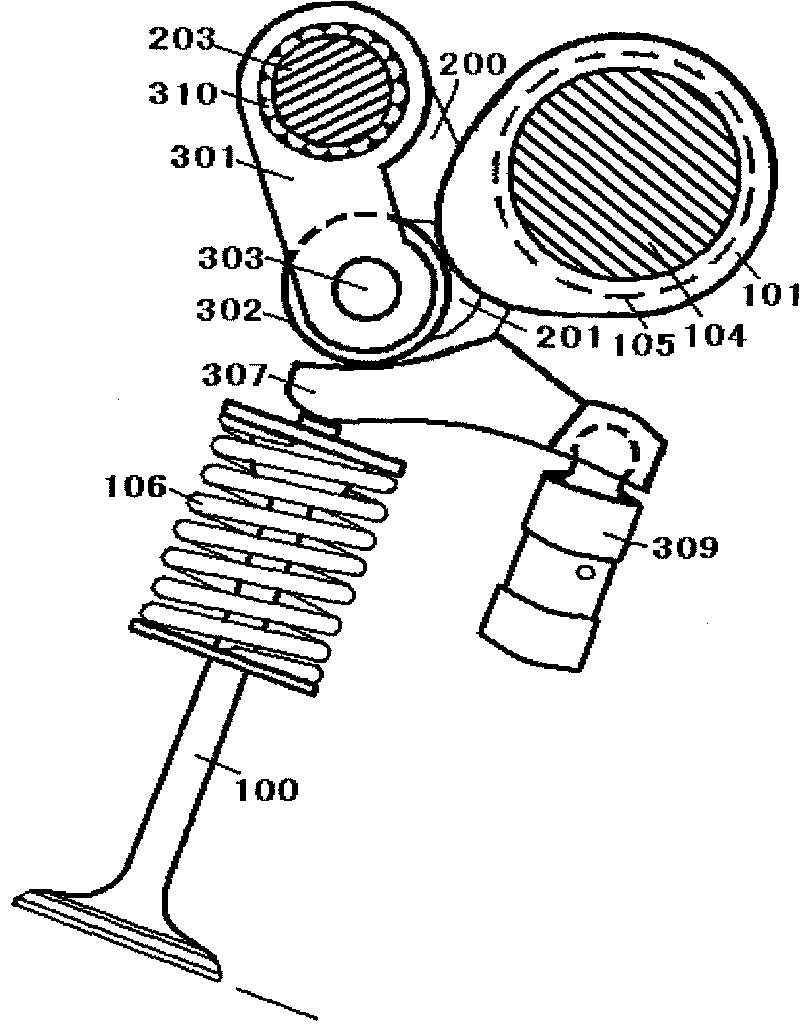
[0113] figure 2 Shown is a schematic structural diagram of a continuously variable valve lift mechanism in the case of a sliding rocker arm, which mainly includes a cam (101), a crank arm (200), a crank arm journal (201), a variable rocker shaft (203), Variable rocker arm (301), sliding surface rocker arm (307), valve clearance automatic compensator (309), auxiliary return spring (403), valve (100) and dotted lines show the camshaft journal (105); where The working state and setting of crank arm (200), crank arm journal (201), variable rocker arm (301), auxiliary return spring (403) and embodiment 1 are exactly the same. The needle roller bearing arranged in the middle on the variable rocker arm (301) is in close contact with the cam (101), and the two needle roller bearings on both sides conflict with the working end faces of the corresponding sliding surface rocker arm (307) respectively. One end of the sliding surface rocker ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com