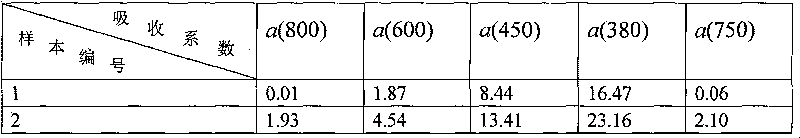Measuring method of absorption coefficients of total particulate matter and phytoplankton in the water
An absorption coefficient and phytoplankton technology, which is applied in the preparation of test samples and the measurement of color/spectral characteristics, can solve the problem of inaccurate determination of the absorption coefficient of phytoplankton in non-pigment particulate matter and the inability to extract phycobilin eukaryotic pigments well. And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0029] Specific embodiment one: this embodiment method comprises the following steps:
[0030] Step 1. Fix the glass fiber filter membrane with a pore size of 0.7 μm and a diameter of 47 mm on the filter, put the water body to be tested into the filter, and obtain the filter membrane sample after filtering through the glass fiber membrane fixed on the filter. At the same time, use glass fiber membrane to filter pure water to make two blank samples.
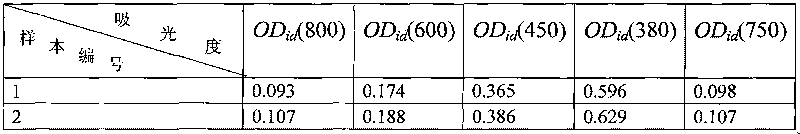
[0031] Step 2, put the filter membrane sample and filter membrane blank sample obtained in step 1 into a spectrophotometer, and measure the absorbance OD of the filter membrane sample at different wavelengths i (λ), where λ represents the wavelength,
[0032] The wavelength λ ranges from 380nm to 800nm, with an interval of 1nm,
[0033] Step 3. According to the formula a(λ)=2.303×OD s (λ)×S / V calculation to obtain the total particle absorption coefficient a(λ),
[0034] Where: S is the effective area of particles deposited o...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0055] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the embodiment is that the extraction time in step 4 is 40 minutes to 50 minutes, and other steps and parameters are the same as in the embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0056] Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and the embodiment is that the extraction time in step 4 is 45 minutes, and other steps and parameters are the same as in the embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com