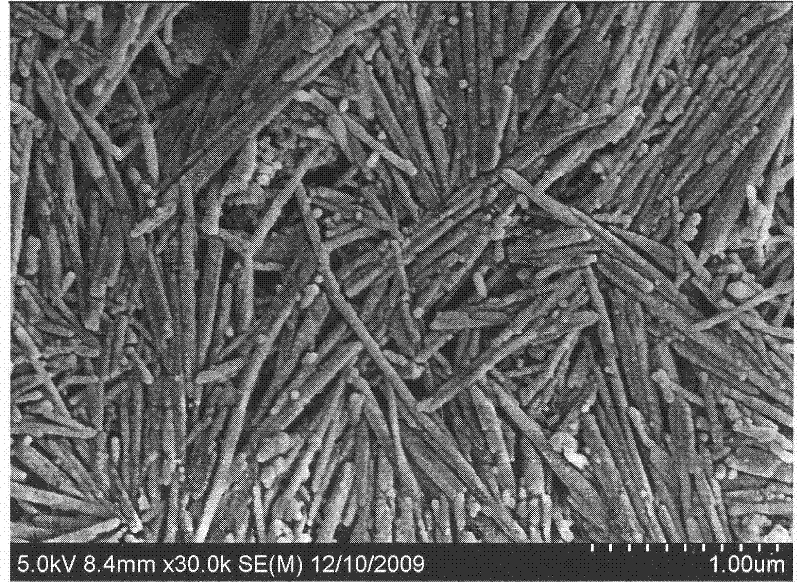
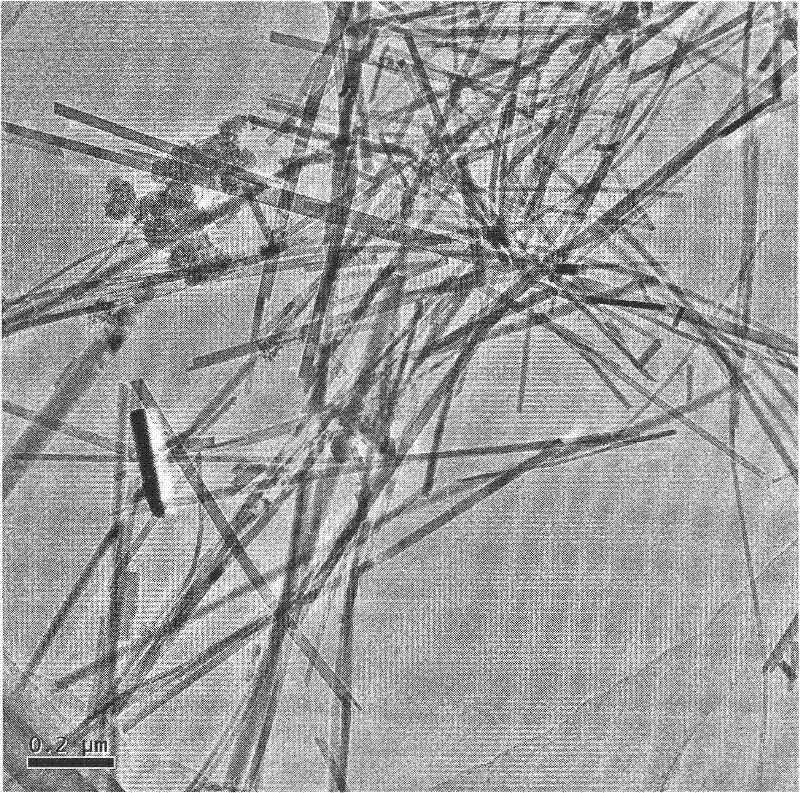
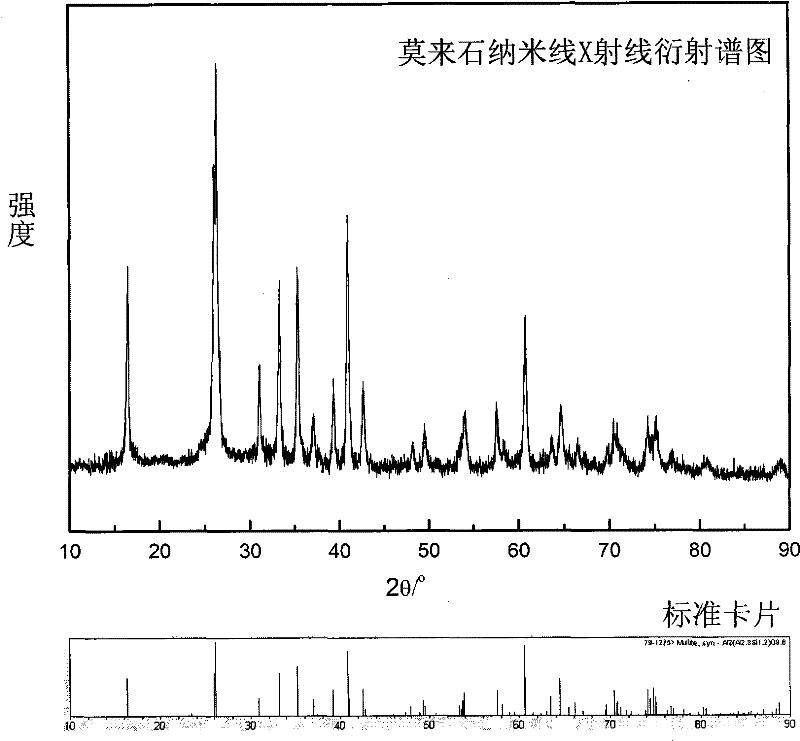
Method for preparing mullite nanowire
A technology of nanowires and mullite, applied in the field of preparing mullite nanowires, can solve the problems of restricting large-scale industrial production, difficult to control the process, difficult to meet the application, etc., and achieve straight shape, easy process control, and complete surface. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Using 3.11g of anhydrous aluminum sulfate, 0.55g of amorphous silicon dioxide, 0.11g of diboron trioxide, and 6.23g of anhydrous sodium sulfate, mechanically milled with high-purity zirconia balls for 4 hours to obtain uniformly mixed powder. The obtained powder was passed through a 200-mesh sieve, kept at 1050°C for 6 hours, and the sintered powder was cooled to room temperature with the furnace. The obtained product was repeatedly rinsed with water and filtered to remove sodium sulfate in the product until no precipitation occurred after titration with barium nitrate solution. The obtained product was acid-washed with hydrofluoric acid and then dried at 100°C.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Using 3.2 g of anhydrous aluminum sulfate, 0.37 g of amorphous silicon dioxide, 0.02 g of diboron trioxide, and 6.41 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate, mechanically milled with high-purity zirconia balls for 5 hours to obtain uniformly mixed powder. The obtained powder was passed through a 400-mesh sieve, kept at 900°C for 3 hours, and the fused powder was cooled to room temperature with the furnace. The obtained product was repeatedly rinsed with water and filtered to remove sodium sulfate in the product until no precipitation occurred after titration with barium nitrate solution. The obtained product was acid-washed with hydrofluoric acid and then dried at 100°C.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Using 3.15 g of anhydrous aluminum sulfate, 0.42 g of amorphous silicon dioxide, 0.08 g of diboron trioxide, and 6.35 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate, mechanically milled with high-purity zirconia balls for 4 hours to obtain uniformly mixed powder. The obtained powder was passed through a 500-mesh sieve, kept at 950° C. for 4 hours, and the sintered powder was cooled to room temperature with the furnace. The obtained product was repeatedly rinsed with water and filtered to remove sodium sulfate in the product until no precipitation occurred after titration with barium nitrate solution. The obtained product was acid-washed with hydrofluoric acid and then dried at 100°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aspect ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com