Quasi three-dimensional map-based mobile robot global path planning method
A global path planning, mobile robot technology, applied in directions such as road network navigators, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory real-time performance, long search time, long time consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of improving planning efficiency and improving timeliness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
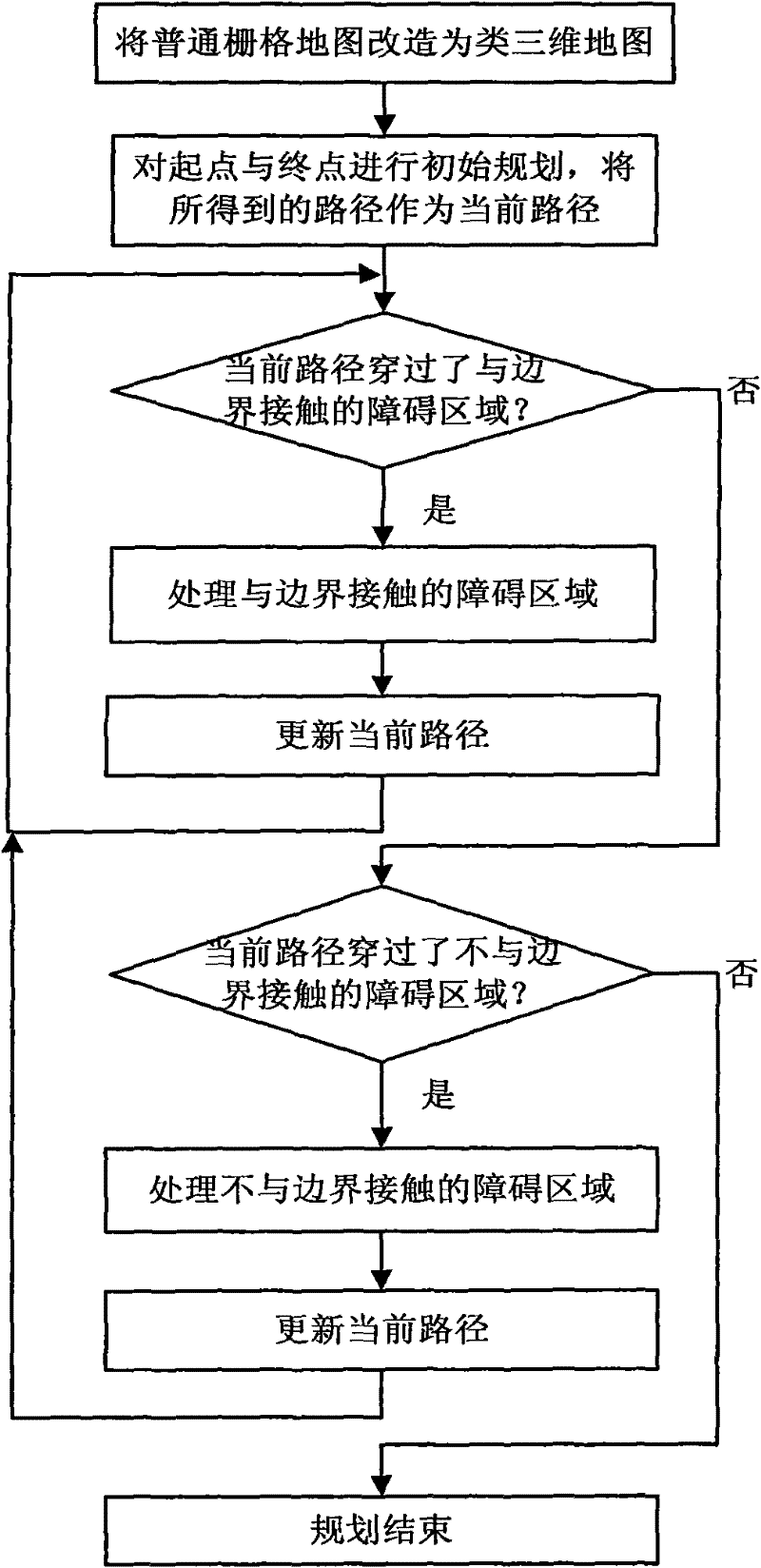
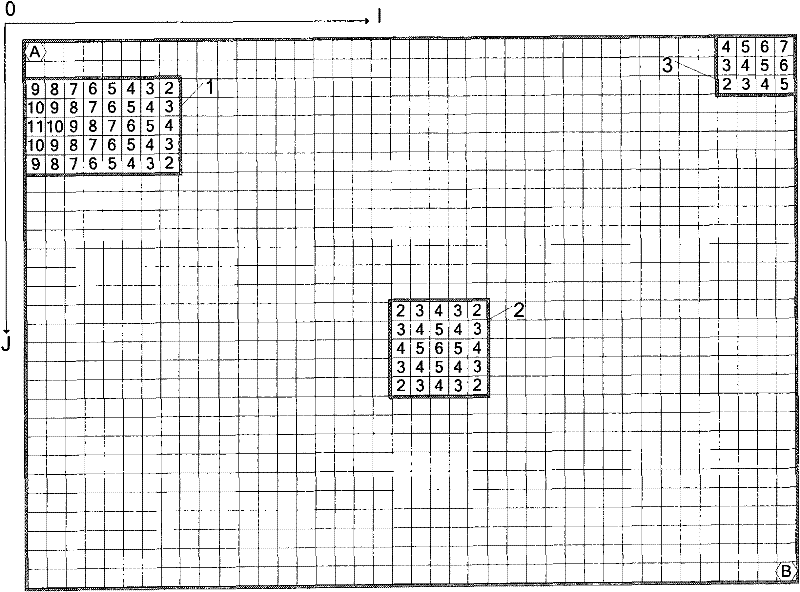
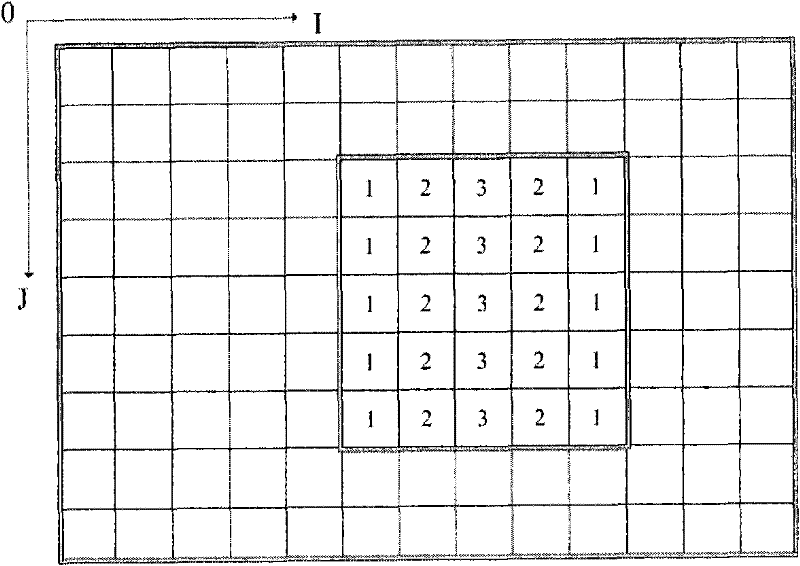
[0069] figure 1 It is the program flow chart of the main implementation process of the global path planning algorithm. The specific steps are as follows: (1) On the basis of the ordinary binary grid map, a three-dimensional map is established according to the contour line principle, and each grid point in the map is Assign a height value. Establish the I, J coordinate system for the map, and the grid in the map is represented by the array ZG[I][J]. The height value of the grid is represented by H, that is, ZG[I][J]=H, H∈{0, 1, 2, 3...}, the larger the value of H, the higher the height.
[0070] In the present invention, the map is divided into two types of areas: free area and obstacle area. The height value of the free area is H=0; the height value of the obstacle area is H>0, the height value of the grid point at the center of gravity in the obstacle area not in contact with the boundary is the largest, and the grid point in contact with the boundary in the obstacle area i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com