Method for determining intensity of speckle noise in images
A technique of speckle noise, noise intensity, applied in the field of image processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Taking the speckle noise intensity of the simulated image (containing speckle noise intensity as 0.02) as an example, the method steps are as follows:
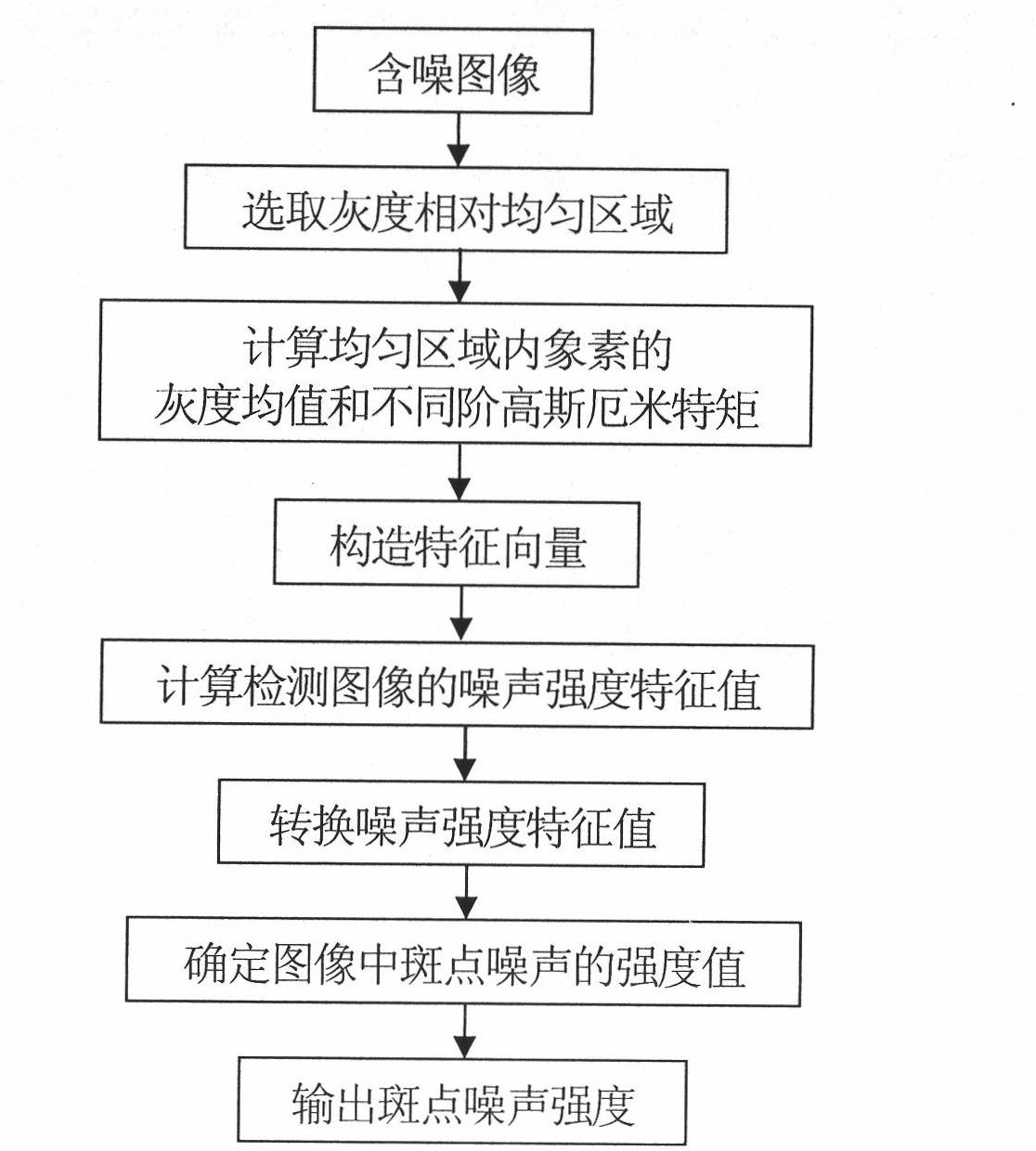
[0043] 1. Select an area with relatively uniform gray scale
[0044] Select a relatively uniform gray-scale area 1 in the simulated image with speckle noise intensity of 0.02, and the selected gray-scale area 1 is the area inside the rectangular box, see figure 2 .
[0045] 2. Calculate the gray mean value of the pixels in the selected area and the Gauss-Hermitian moments of different orders of pixels in the area
[0046] The above-mentioned average gray value is the average gray value of each pixel in the relatively uniform gray area, and the average gray value of one pixel in the gray area is 191.
[0047] The Gauss Hermitian moments of different orders of each pixel in the gray area 1 are calculated according to the following formula:
[0048] M p , ...
Embodiment 2
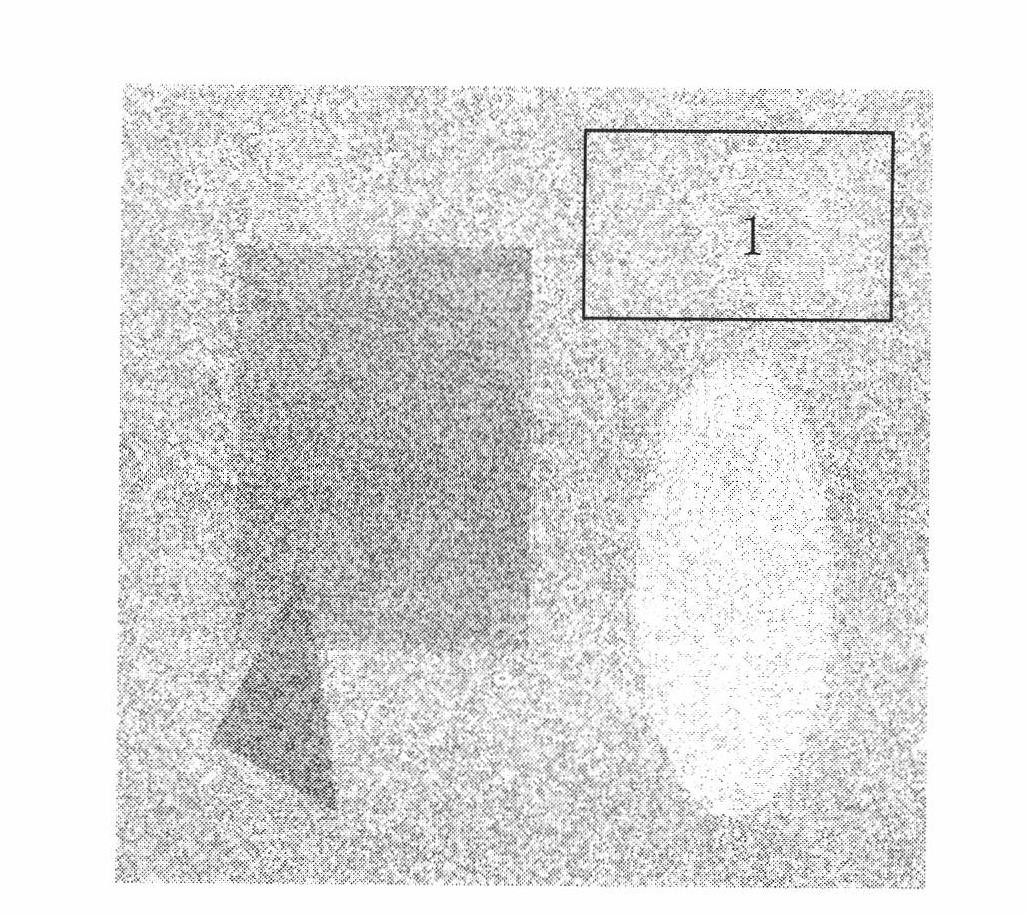
[0072] Taking the determination of the speckle noise intensity of a visible light image "coin" (with a speckle noise intensity of 0.1) as an example, the method steps are as follows:
[0073] In step 1 of selecting a relatively uniform gray scale area, select a relatively uniform gray scale area 2 in the visible light image "coin" with a speckle noise intensity of 0.1, and the selected gray scale area 2 is the area inside the rectangular box, see image 3 .
[0074] In step 2 of calculating the gray mean value of the pixels in the selected area and the different order Gauss-Hermitian moments of the pixels in the area, the gray mean value of the pixels in the gray area 2 is 226, and each pixel in the gray area 2 The calculation formulas used for different orders of Gauss-Hermitian moments are the same as in Embodiment 1, and the values of t, v, and σ in formulas (1) to (4) are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0075] Step 3 of constructing feature vectors is the same as that of...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Taking the determination of the speckle noise intensity of a synthetic aperture radar coastline image as an example, the method steps are as follows:
[0081] In the step 1 of selecting a relatively uniform gray scale area, a relatively uniform gray scale area 3 is selected in the SAR coastline image, and the selected gray scale area 3 is the area within a rectangular box, see Figure 4 .
[0082] In step 2 of calculating the gray mean value of the pixels in the selected area and the different order Gauss-Hermitian moments of the pixels in the area, the gray mean value of the 3 pixels in the gray area is 25, and the difference between the 3 pixels in the gray area The calculation formula used for the first-order Gauss-Hermitian moment is the same as that in Embodiment 1, and the values of t, v, and σ in formulas (1)-(4) are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
[0083] Step 3 of constructing feature vectors is the same as that of Embodiment 1.
[0084] In step 4 of ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com