Method and system for dynamically distributing network traffic
A technology of network traffic and dynamic allocation, applied in the Internet field, can solve problems such as bandwidth waste, achieve the effect of rational use of bandwidth and avoid bandwidth waste or congestion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
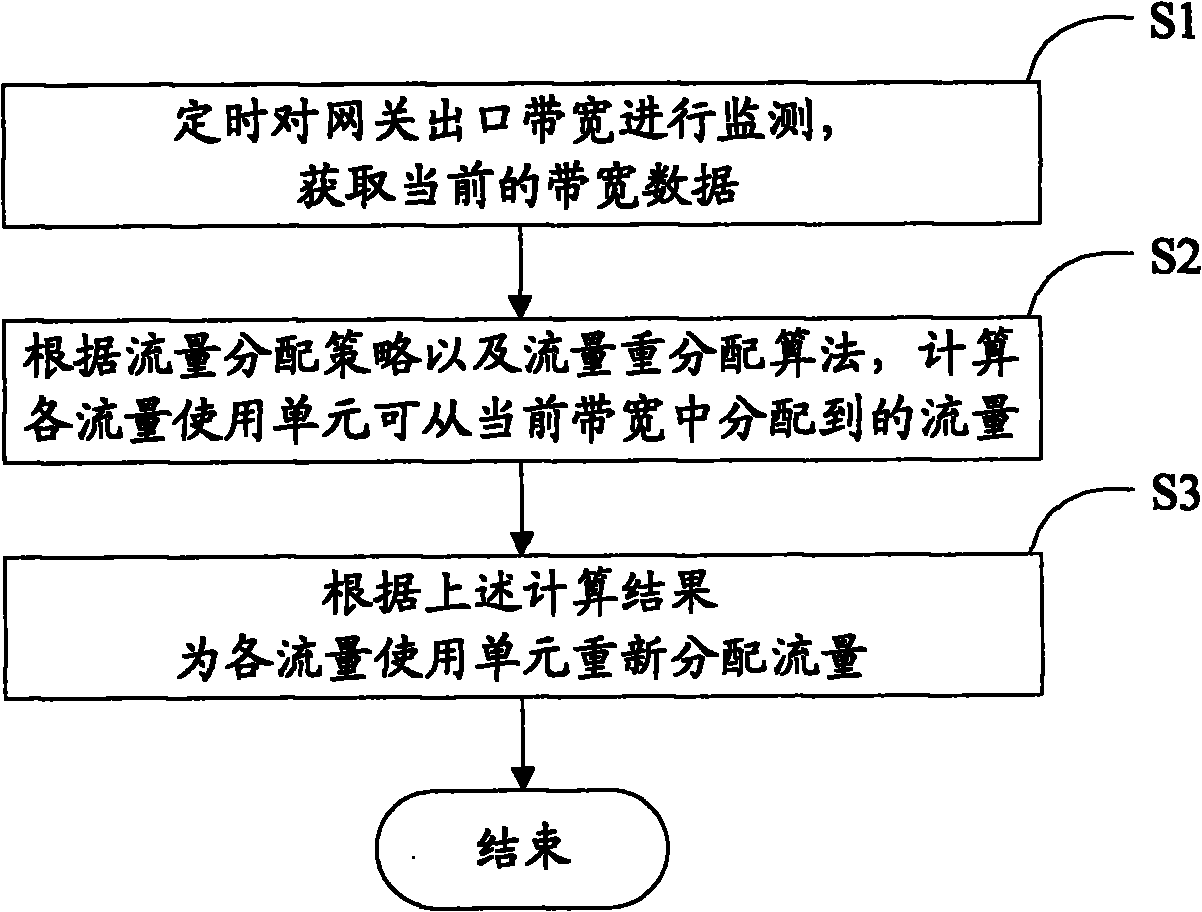
[0016] Embodiment 1, see figure 1 As shown, the method for dynamically allocating network traffic in the embodiment of the present invention includes the following main steps:
[0017] S1. Periodically monitor the egress bandwidth of the gateway to obtain current bandwidth data.
[0018] S2. According to the traffic allocation strategy and the traffic redistribution algorithm, calculate the traffic that each traffic usage unit can allocate from the current bandwidth.
[0019] S3. Redistributing traffic to each traffic usage unit according to the above calculation result.
[0020] The above-mentioned traffic usage unit can be in the unit of IP address, that is, to adjust and distribute the available traffic of each IP address that is legal and needs traffic control; or in the unit of the protocol packet type after DiffServ, that is, according to the field To distinguish data packets, and adjust and distribute the available flow of each type of protocol data packets.
Embodiment 2
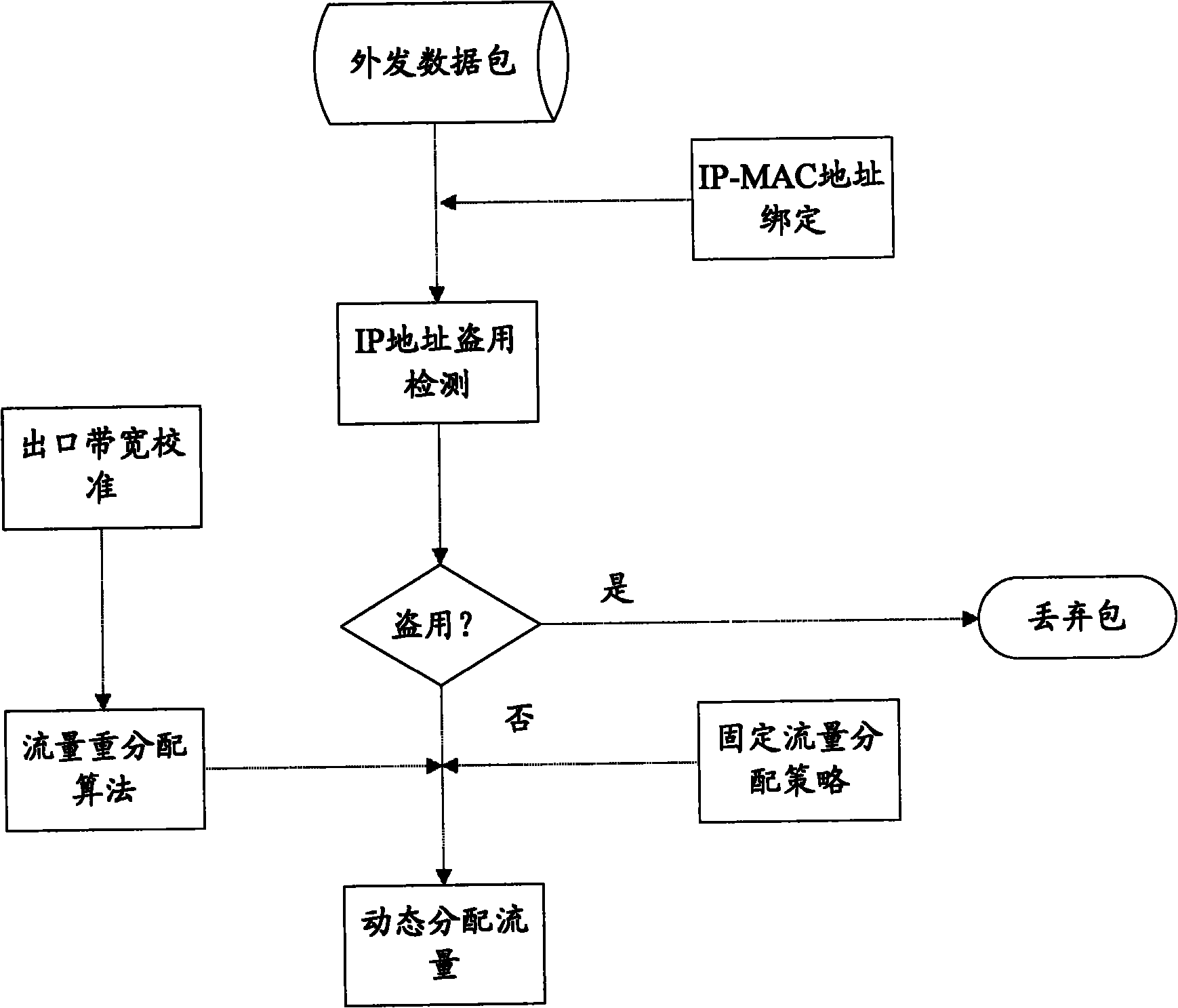
[0021] Embodiment 2, based on embodiment 1, see figure 2 As shown, the flow control for the IP address is further detailed.
[0022] First of all, it is necessary to perform IP-MAC binding on the entire network IP or the IP that needs flow control, and record it to prevent IP theft;
[0023] When the data packet is sent out from the IP address, the IP address is first checked. If it is an illegal IP or a stolen IP (that is, the current MAC address corresponding to the IP address does not match the recorded binding information), the packet will be discarded; if it is Normal IP data flow (the current MAC address corresponding to the IP address matches the recorded binding information), then continue;
[0024] At the same time, the gateway outlet bandwidth is regularly monitored to obtain the closest current bandwidth data (for example, 5M uploads, calibrated once every 10 seconds, and the bandwidths at time points t1 and t2 after bandwidth calibration are respectively b1=3M, b...
Embodiment 3
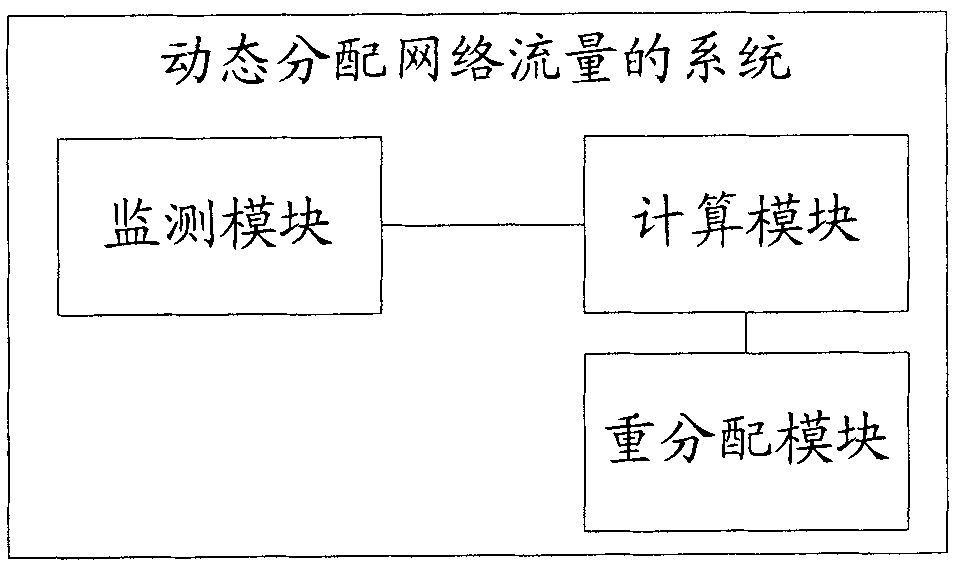
[0027] Embodiment 3, see image 3 As shown, the system for dynamically allocating network traffic in the embodiment of the present invention includes: a monitoring module, a computing module and a reallocation module.
[0028] Wherein, the monitoring module is used to regularly monitor the egress bandwidth of the gateway to obtain current bandwidth data.
[0029] The calculation module is used to calculate the traffic that each traffic usage unit can allocate from the current bandwidth according to the traffic allocation strategy and the traffic redistribution algorithm. The above-mentioned traffic usage unit can be in the unit of IP address, that is, to adjust and distribute the available traffic of each IP address that is legal and needs traffic control; or in the unit of the protocol packet type after DiffServ, that is, according to the field To distinguish data packets, and adjust and distribute the available flow of each type of protocol data packets. The traffic redist...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com