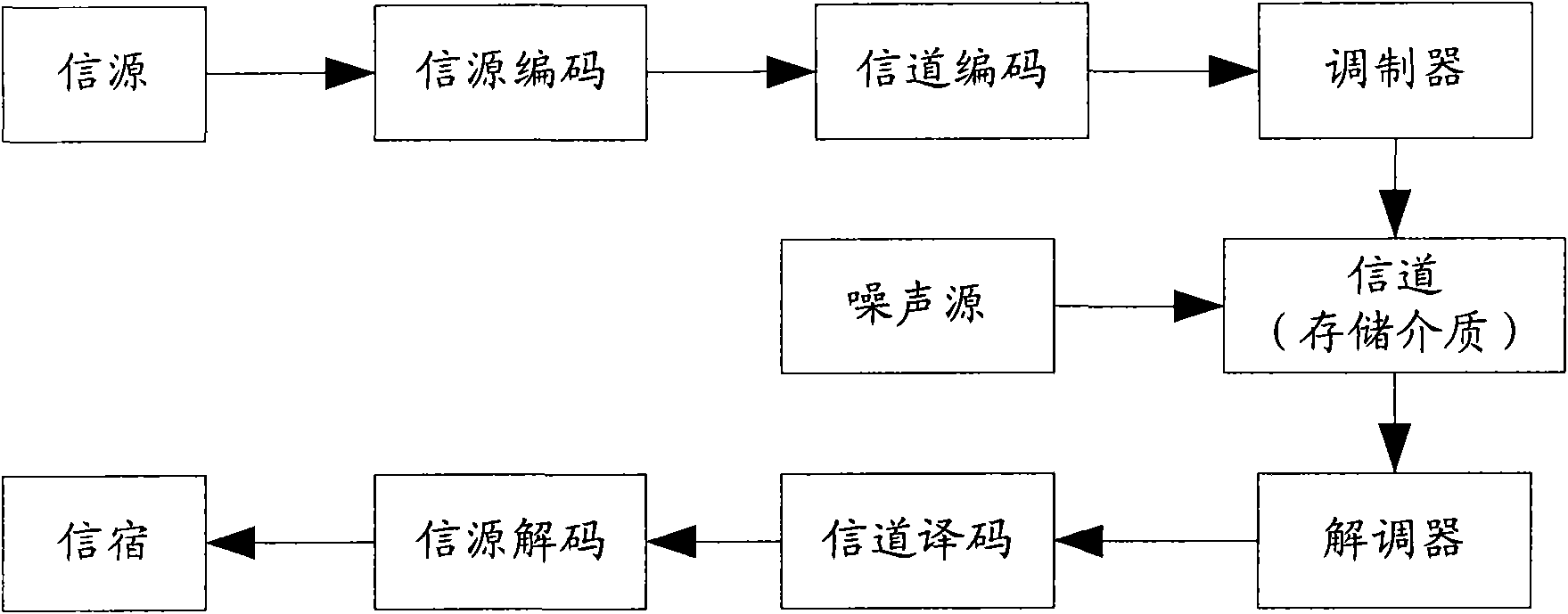
Sub-packet processing method, coding modulation method, processor and modulation coding system
A packet processing and sub-packet technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems such as the degradation of coding link performance and low reliability bits, and achieve the effect of optimizing CTC decoding performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] In this embodiment, a subpacket processing method is provided. In this method, channel coding and rate matching are performed on input bits to obtain a subpacket. The process is as described above, wherein the subpacket includes one or more bits Each bit group includes M bits, preferably, M is the number of bits in a modulation symbol, and M is an integer greater than or equal to 1; then, perform bit interleaving within the bit group for the subpacket. What needs to be explained here is that in the embodiment of the present invention, it is preferable to set the bit group to include M bits, and M is the number of bits in a modulation symbol, which can make the processing relatively simple, and the interleaving pattern is controllable, enabling Guaranteed interleaving performance. Of course, according to implementation requirements, M can also be set to other values different from the number of bits in the modulation symbol, for example, an integer multiple of the numb...
Embodiment 2
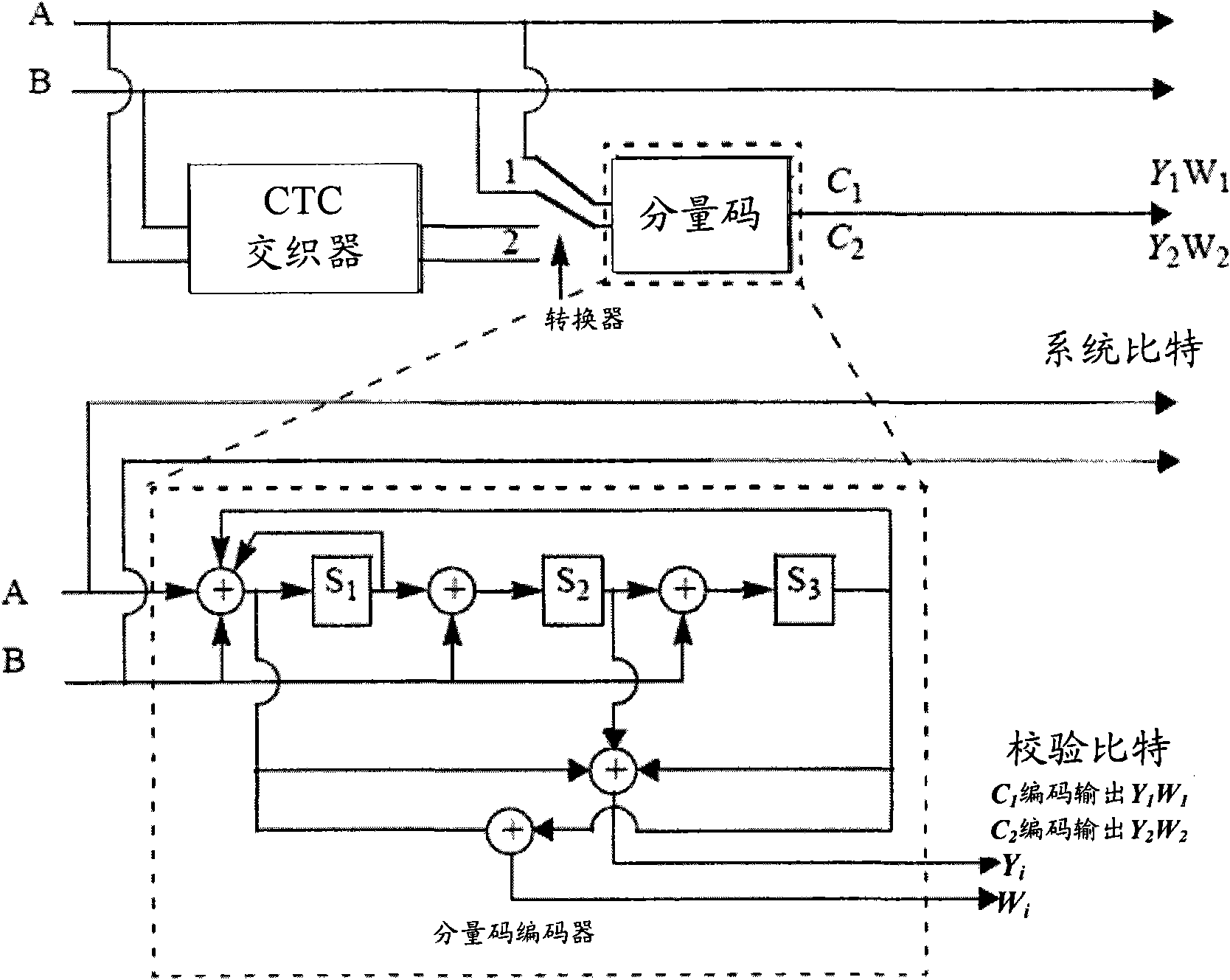
[0089] As mentioned above, in the currently used coding and modulation methods, such as in Figure 5a In the shown 16QAM modulation, the reliability of bits b3, b1 is higher than that of bits b2, b0, that is, the reliability distribution of the bit sequence caused by 16QAM modulation is "highly" interlaced, and the interleaving method of the check bits adopted, that is, Interleave Y in bits 1 and Y 2 , W 1 and W 2 way, which will lead to the use of 16QAM modulation, CTC first component code C 1 check bit sequence Y 1 , W 1 The bits in are highly reliable bits; on the contrary, the second component code C 2 check bit sequence Y 2 , W 2 The bits in are all low-reliability bits. In this way, the second component code C of CTC 2 The reliability of is much lower than that of the first component code C 1 , in this way, it does not comply with the principle of optimizing the performance of CTC decoding, which will lead to a decrease in the performance of CTC decoding.
[...
Embodiment 3
[0111] Embodiment 3: Interleaving method based on cyclic shift
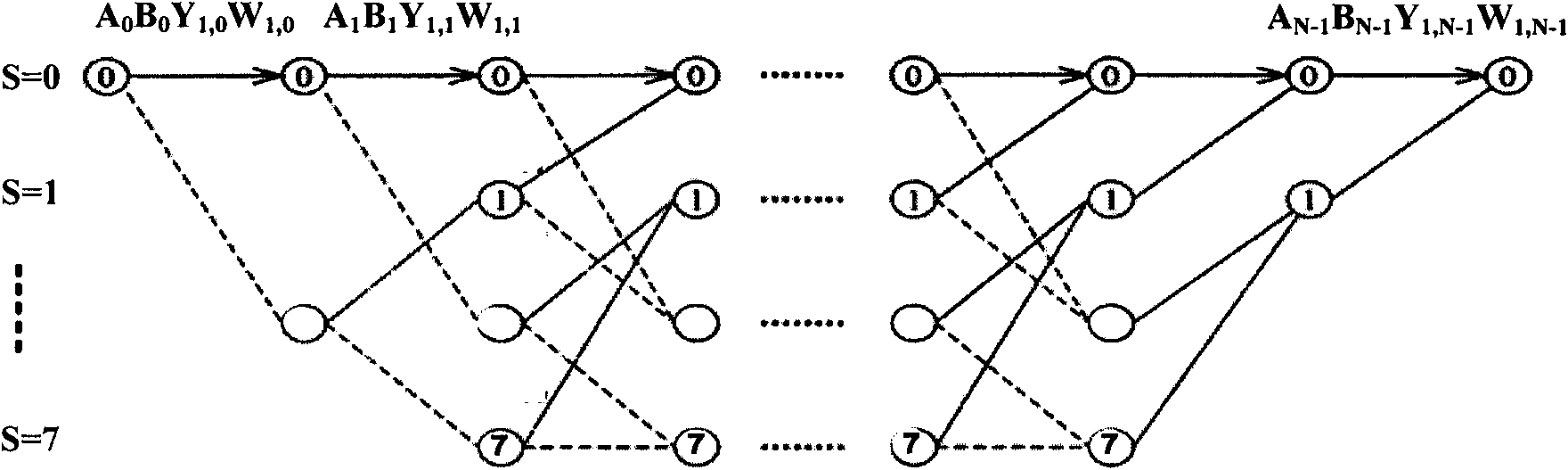
[0112] When the interleaving method based on cyclic shift is adopted, adopting the method based on cyclic shift in a block means that the bit interleaving of all bit groups in the block is based on cyclic shift. For example, Figure 7a Shows a cyclic shift method with 4 bits (M=4) in a bit group, as shown in Figure 7, the cyclic shift offset of the 0th bit group (or symbol) is 0, the 1st The cyclic shift offset of the bit group is 1, the cyclic shift offset of the second bit group is 2, and the cyclic shift offset of the third bit group is 3.
[0113] In order to solve the above-mentioned problem of continuous low-reliability bit distribution, the bit interleaving in the sub-packet needs to be designed according to certain criteria. In general, the cyclic shift formula can be expressed as: C i (j)=(j+α) mod M, j∈[0, M−1]. Among them, α is determined by several factors. In order to solve the above problem of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com