Network topology identification method based on flow analysis
A network topology and traffic analysis technology, applied in the field of large-scale IP network topology detection, can solve the problems of increased node burden, limited application and long detection cycle, etc., to achieve the effect of increased node burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] A method for inferring network topology based on traffic analysis, characterized in that the steps include:
[0042] a. Deploy a measurement point on the network backbone link to capture and analyze all IP packets flowing through the link. The capture refers to: using common tools such as libpcap and general network packet capture technology, at the measurement point Receive the IP grouping that transmits in the network on the network card, described analysis refers to: observe TCP session, obtain the path characteristic of each IP host of both sides of each TCP conversation to described measuring point respectively, and described path characteristic comprises route hop count (hop_count ) and round-trip time delay (RTT), set a fixed time period T, and obtain an analysis result value of each path characteristic within a time period;
[0043] b. Through continuous capture and analysis of multiple time periods, the time series of the path characteristics of each IP host to...
Embodiment 2
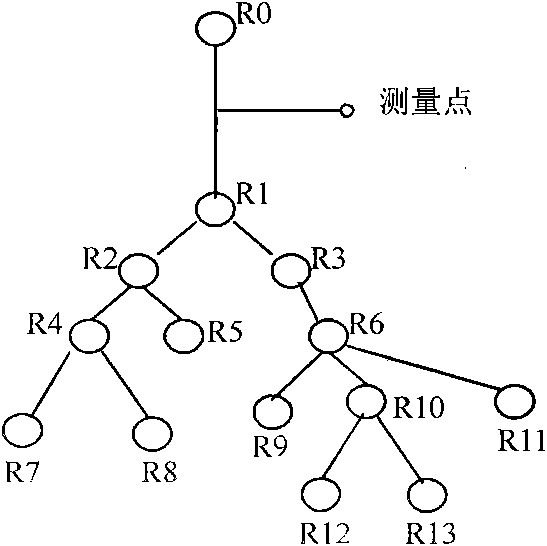
[0053] (1) Deploy measurement points on the network backbone link to capture and analyze all IP packets flowing through the link. Such as figure 1 shown.
[0054] (2) Analyze all IP packets to obtain measurement results. By observing the TCP session, the characteristics of the paths from the hosts on both sides of each TCP session to the measurement point are found. These characteristics include 2: routing hop count (hop-count), round-trip time delay (RTT).
[0055] The method of obtaining the routing hop count is relatively common. Analyze the TTL field value of each IP packet, and subtract the TTL value from 255 to get the hop-count value from the source host to the measurement point of the IP packet, namely: hop_count=255-TTL. This method is widely used and is not described in detail in the specification.
[0056] There are also many methods for obtaining RTT. Currently, commonly used analysis methods include SA method, SS method, Karn method, and Running method. These...
Embodiment 3
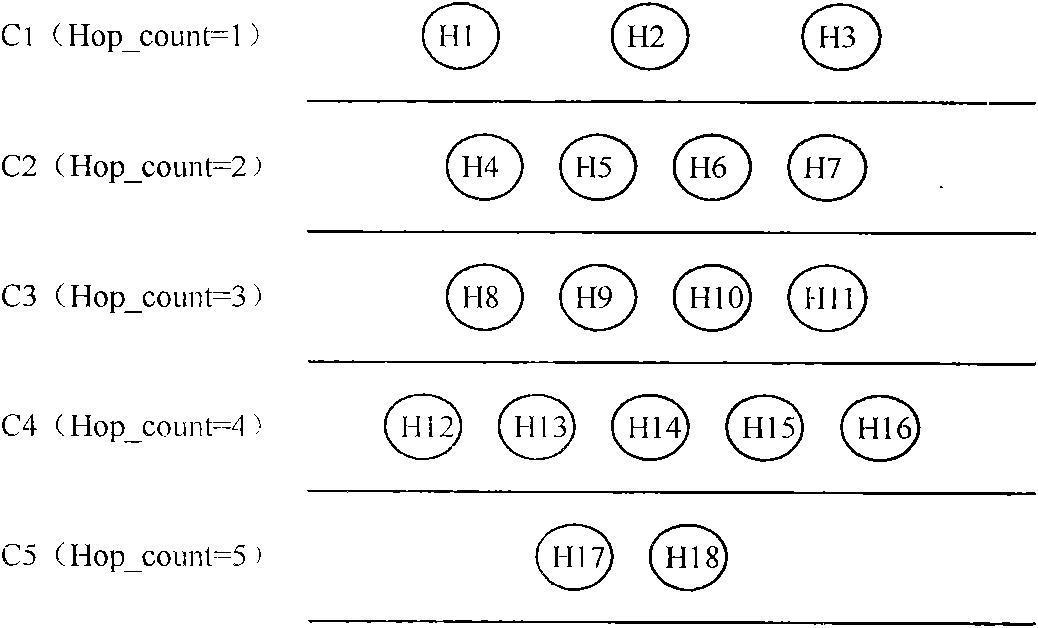
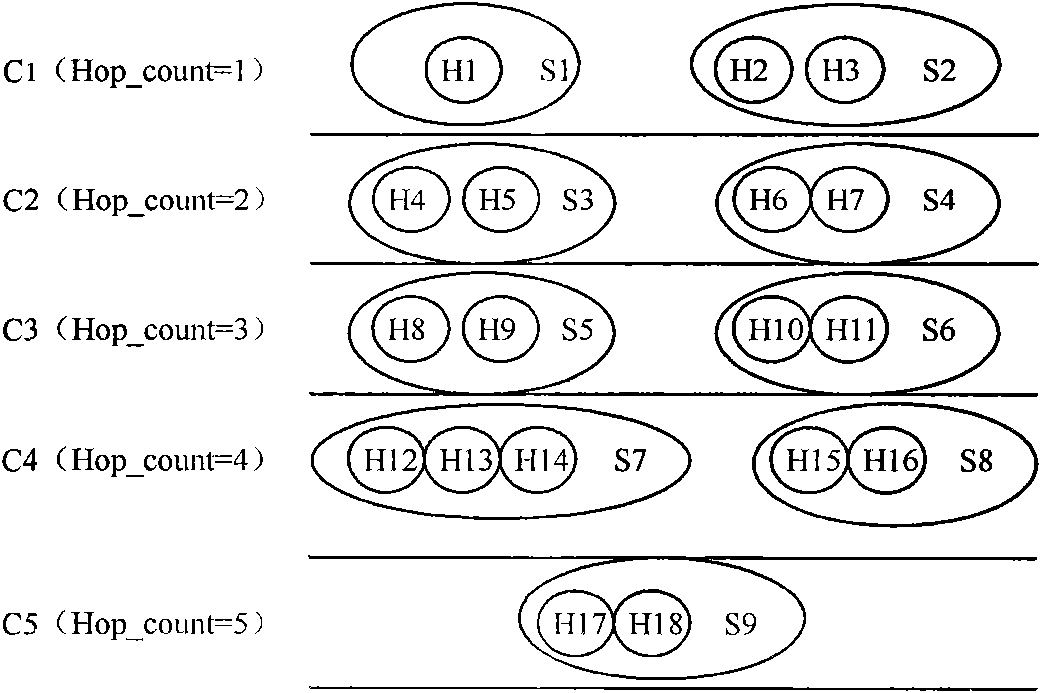
[0078] The principle of the present invention is: select a certain backbone link in the network backbone, and deploy measurement points (Measurement Points) to analyze the traffic. Suppose any two different nodes in the network (H i and H j ) to the measurement point, there are respective paths (P i and P j ), define P i and P j The correlation is R, then R largely reflects P i and P j degree of overlap. The research shows that the more shared links of nodes in the network, the more similar the characteristics of the nodes, and the greater the correlation of the change trend of their performance indicators (time series obtained through measurement). For example, when path congestion intensifies, the performance of different nodes in the path will show a similar trend of change (delay and packet loss rate increase, available bandwidth decreases). Therefore, deploying measurement points in the network backbone link, for node H i and H j Measure the performance indicato...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com