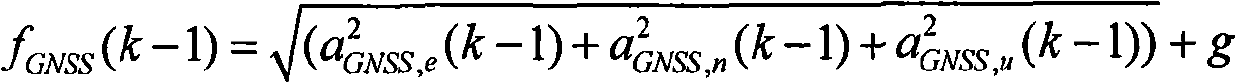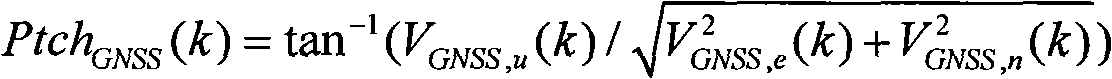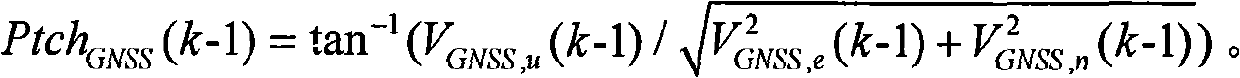Rapid online dynamic calibration method for zero offset of GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) auxiliary MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical Systems) inertial sensor
An inertial sensor and dynamic calibration technology, applied in instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable system response real-time and rapidity, inertial devices do not have zero-bias repeatability, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] Embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0041] A kind of fast online dynamic calibration method of GNSS assisted MEMS inertial sensor zero bias, described MEMS inertial sensor comprises the MEMS accelerometer and MEMS gyroscope that constitute MEMS inertial measurement unit; In GNSS / MEMS INS integrated navigation system, through online comparison by The modulus of the total specific force derived by GNSS and the modulus of the total specific force obtained by the output of the MEMS accelerometer are used to calibrate the zero bias of the accelerometer in real time; by using the velocity information measured by GNSS, the attitude information obtained online is derived and added with a constant velocity or Approximate uniform linear motion or static constraints to calibrate the zero bias of the gyroscope in real time; the MEMS refers to the micro-electromechanical system, the GNSS refer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com