Ejector-type refrigeration cycle device
A refrigeration cycle and ejector technology, applied in the field of ejector refrigeration cycle devices, can solve the problems of high COP, inability to supply refrigerant, and unavoidable COP reduction, and achieve the effect of improving COP
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
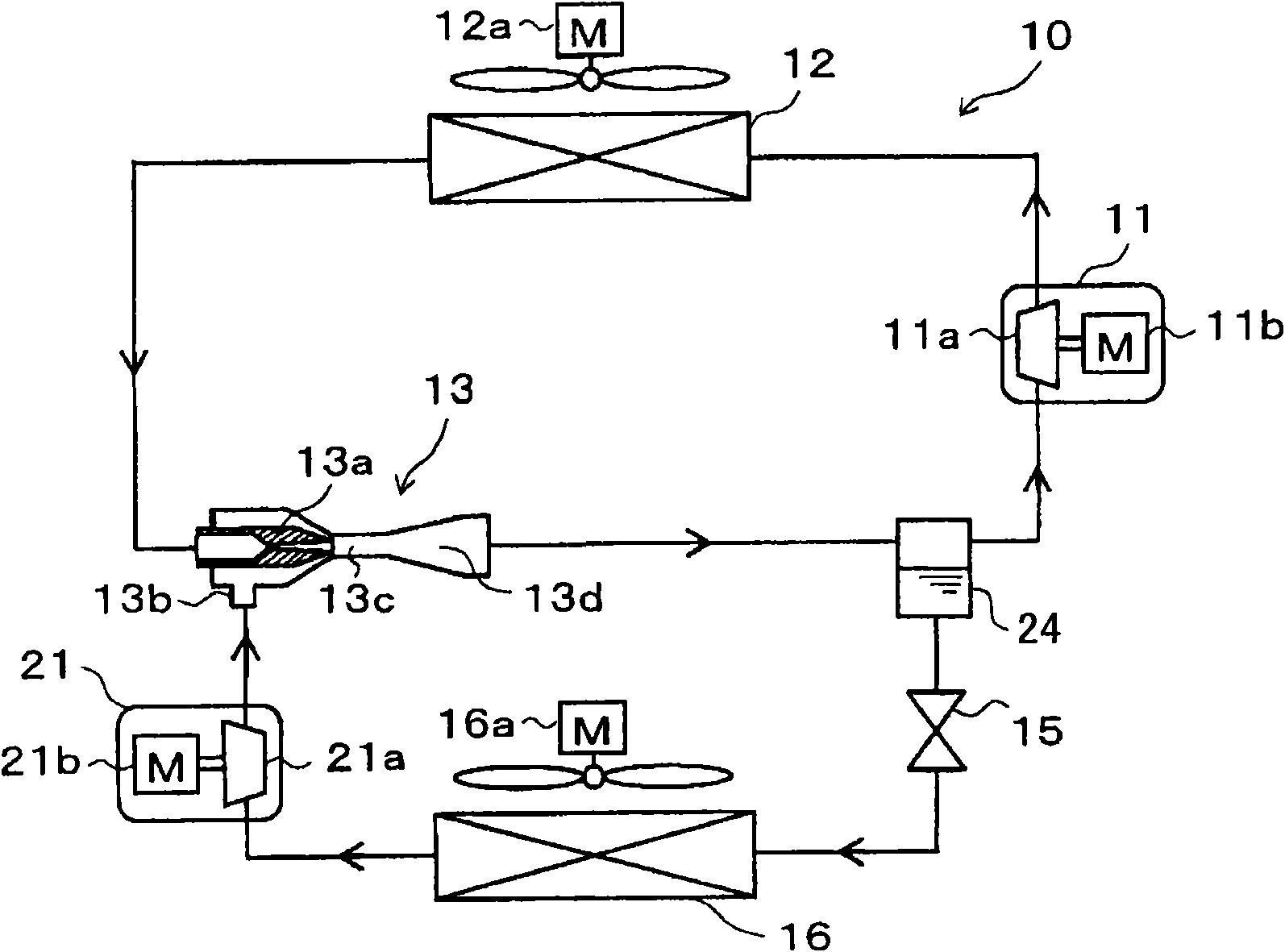
[0226] In this example, reference will be made to figure 1 and 2 The ejector type refrigeration cycle device of the present invention used in a refrigerator will be described. The refrigerator is used to cool a refrigerated inner chamber, which is a space to be cooled, to an extremely low temperature, for example, in a range between -30°C and -10°C. figure 1 It is the whole schematic diagram of the ejector type refrigeration cycle apparatus 10 of this embodiment.
[0227] In the ejector type refrigeration cycle device 10, the first compressor 11 is configured to suck refrigerant, compress the sucked refrigerant, and discharge the compressed refrigerant. For example, the first compressor 11 is an electric compressor in which a first compression mechanism 11a having a fixed displacement is driven by a first motor 11b. For example, various compression mechanisms such as a screw-type compression mechanism, a vane-type compression mechanism, and the like can be used as the fir...
no. 2 example
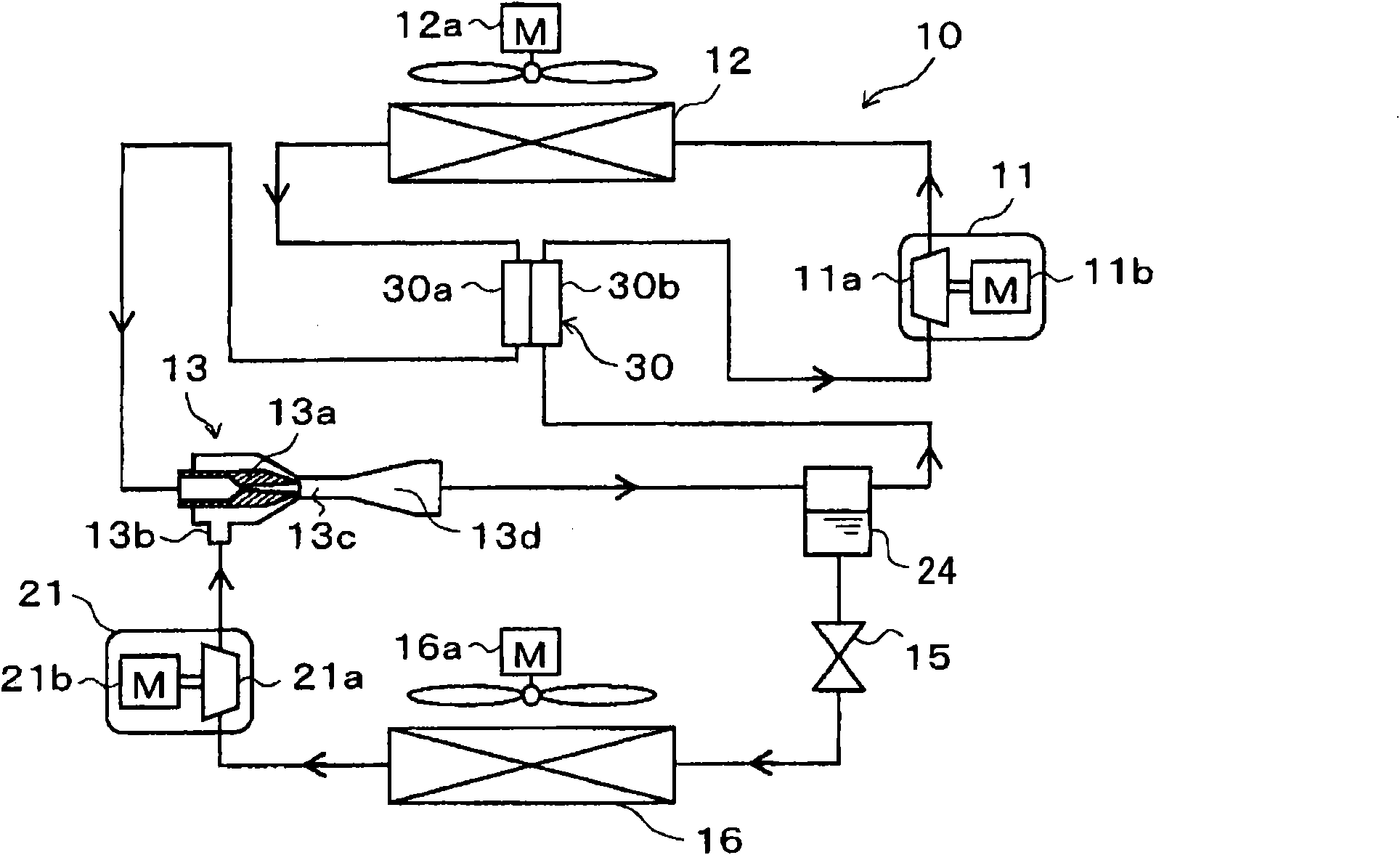
[0263] In this example, as in image 3 In the overall schematic diagram of , an internal heat exchanger 30 is added to the ejector refrigeration cycle device 10 of the first embodiment, in which, the refrigerant flowing out from the radiator 12 and the low-pressure side refrigerant in the cycle perform heat exchange . exist image 3 In , components similar to or corresponding to the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals. This is also the same in the subsequent drawings.
[0264]The internal heat exchanger 30 is used between the refrigerant flowing through the high-pressure side refrigerant passage 30a from the refrigerant outlet side of the radiator 12 and the refrigerant flowing through the low-pressure side refrigerant passage 30b and sucked into the first compression mechanism 11a. heat exchange between them. Therefore, the low-pressure side refrigerant in the cycle of the present embodiment is the refrigerant to be sucked into the first compressio...
no. 3 example
[0272] In this example, as in Figure 5 In the overall schematic diagram of FIG. 2 , compared with the ejector refrigeration cycle device 10 of the first embodiment, an internal heat exchanger 31 is added. The basic structure of the internal heat exchanger 31 is similar to that of the internal heat exchanger 30 of the second embodiment.
[0273] The internal heat exchanger 31 is used between the refrigerant flowing through the high-pressure side refrigerant passage 31a from the refrigerant outlet side of the radiator 12 and the refrigerant flowing through the low-pressure side refrigerant passage 31b and sucked into the second compression mechanism 21a. heat exchange between them. Therefore, the low-pressure side refrigerant in the cycle of the present embodiment is the refrigerant to be sucked into the second compression mechanism 21a. Other configurations in this embodiment are similar to the first embodiment.
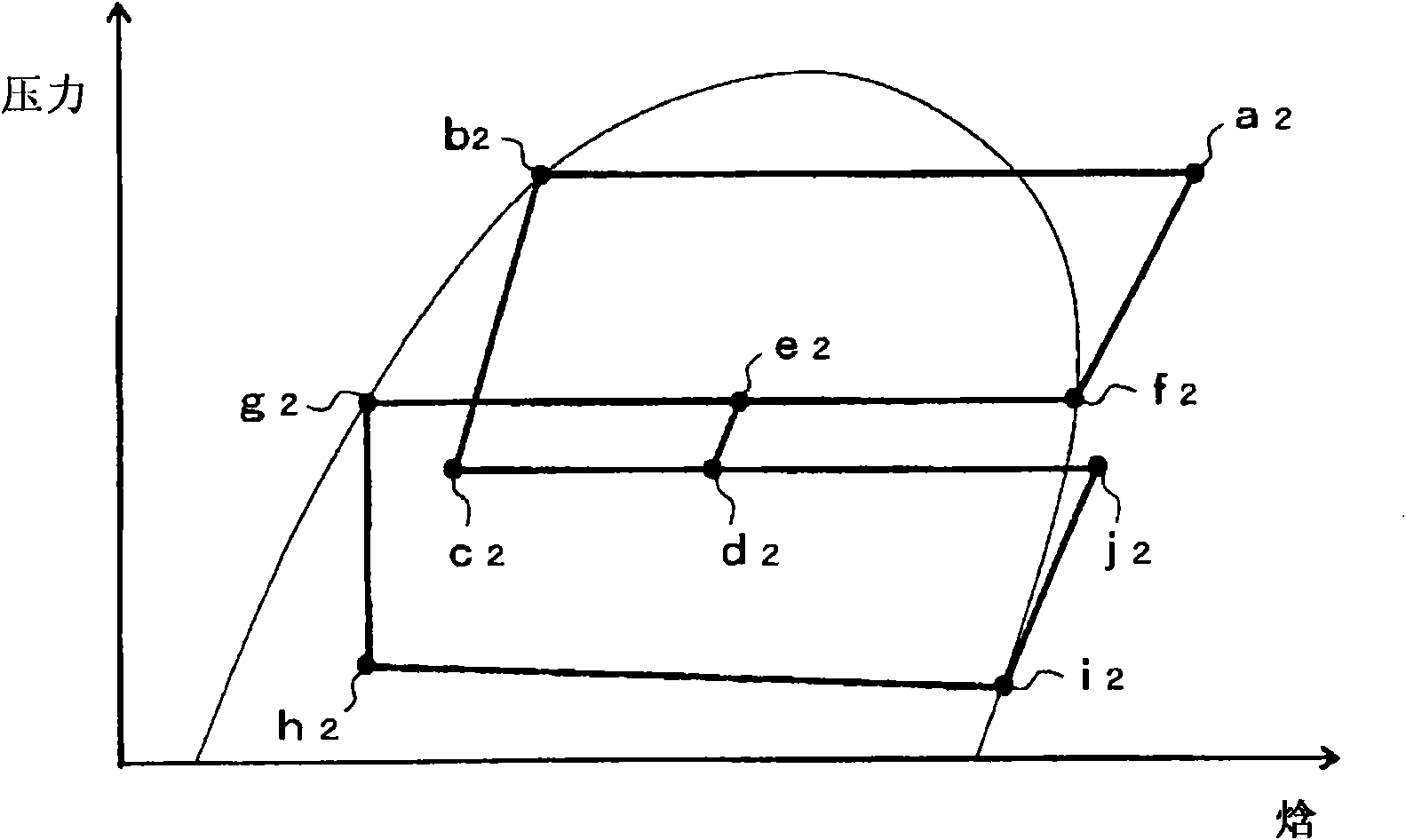
[0274] Next, refer to Image 6 The Mollier diagram describe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com