Myoelectric artificial limb control device
A control device and prosthetic technology, applied in prosthesis, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of ion gel drying, toxicity, and ion activity decline
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
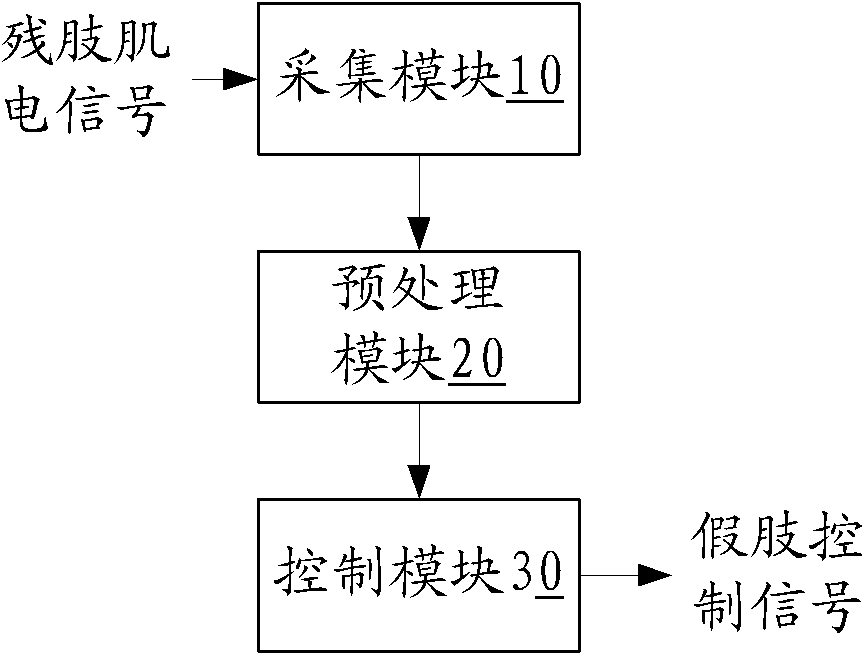
[0019] Such as figure 1 Shown is a block diagram of a myoelectric prosthesis control device. The myoelectric prosthesis control device includes an acquisition module 10 , a preprocessing module 20 and a control module 30 connected in sequence. The collection module 10 is worn on the residual limb of the human body, and is used for collecting the electromyography signal at the residual limb. The preprocessing module 20 preprocesses the electromyographic signal, so that parameters such as the strength of the electromyographic signal meet the requirements for controlling the prosthesis. The control module 30 controls the prosthesis according to the processed myoelectric signal.
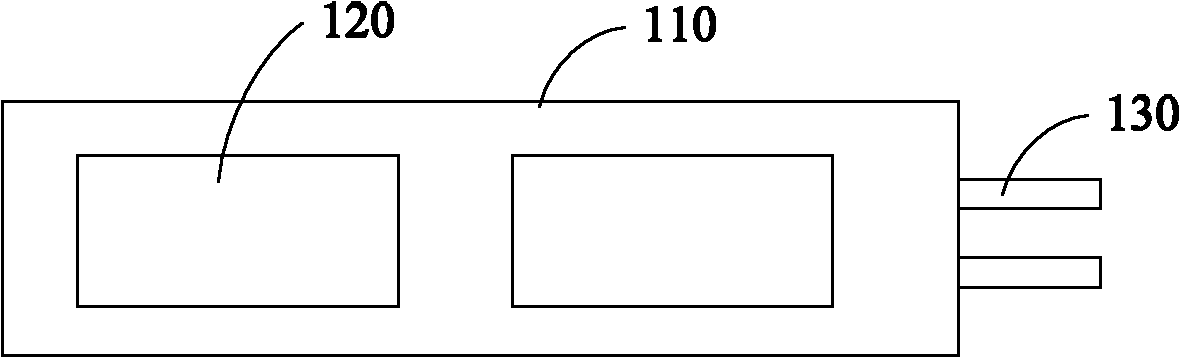
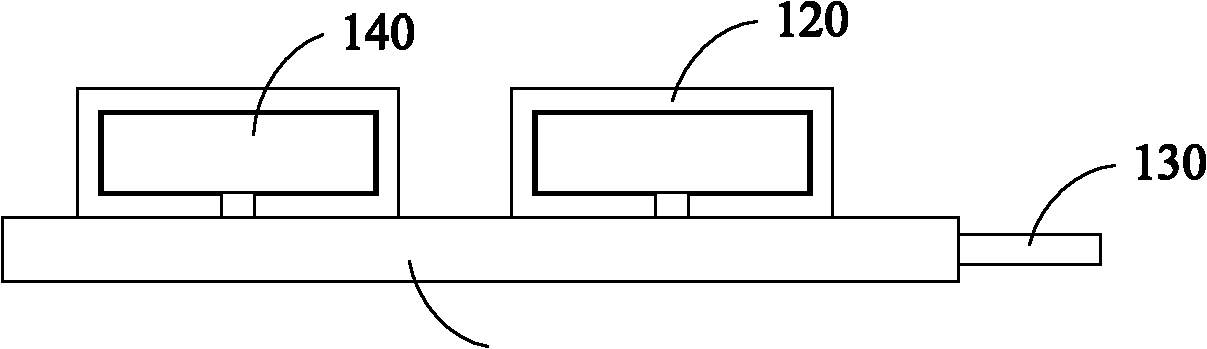
[0020] The electromyography signal is collected by contacting the electrodes with the skin. In this embodiment, the collection module 10 includes fabric electrodes. Such as figure 2 Shown is a top view of the structure of the collection device of an embodiment. Two side-by-side fabric electrodes 12...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com