Self-adaptive load balancing method for parallelization of spatial computation
A technology of adaptive load and space computing, applied in the field of high-performance computing, can solve the problems of reduced computing speed, high processor load, idle processor, etc., and achieve the effect of small communication load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
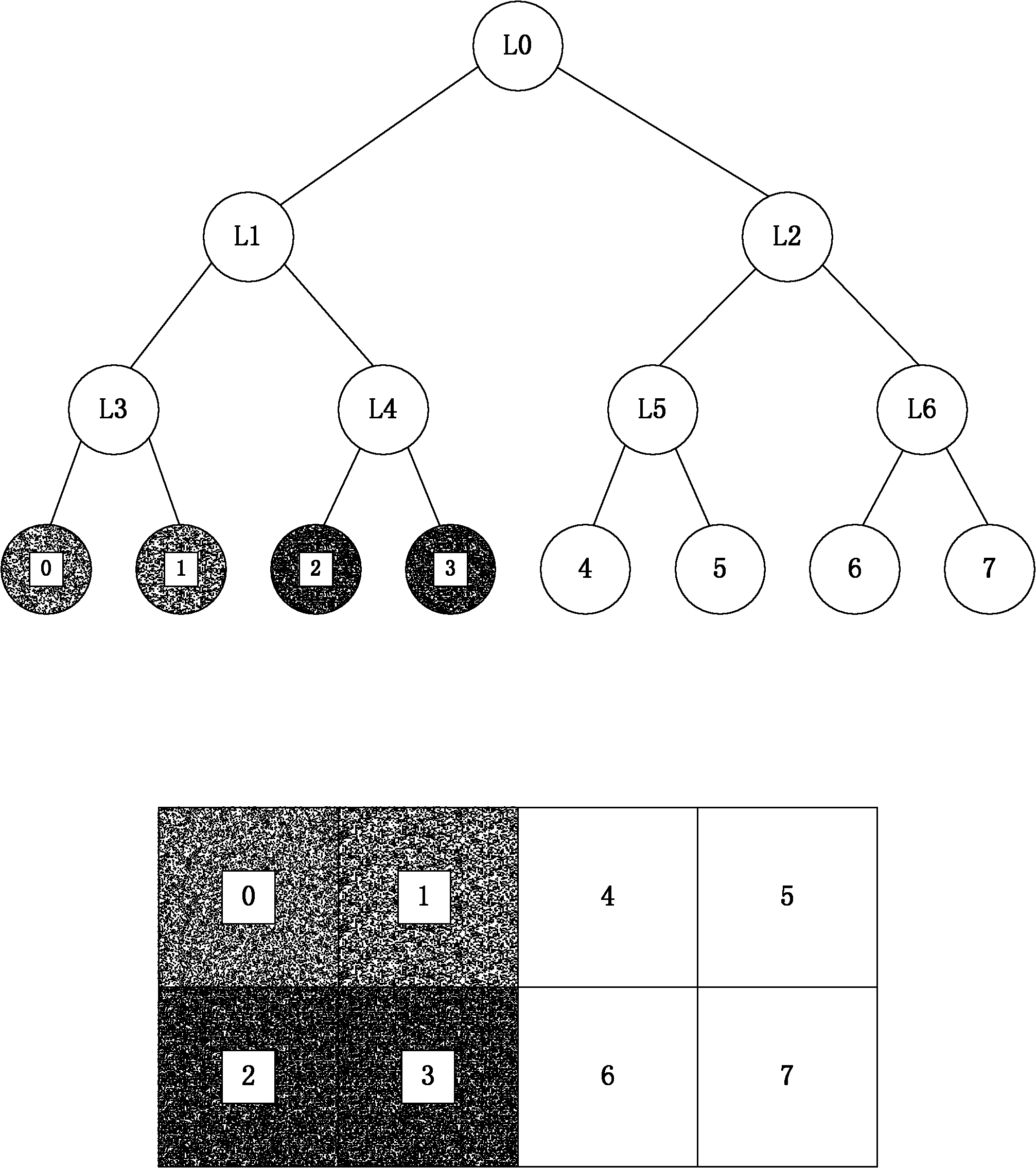
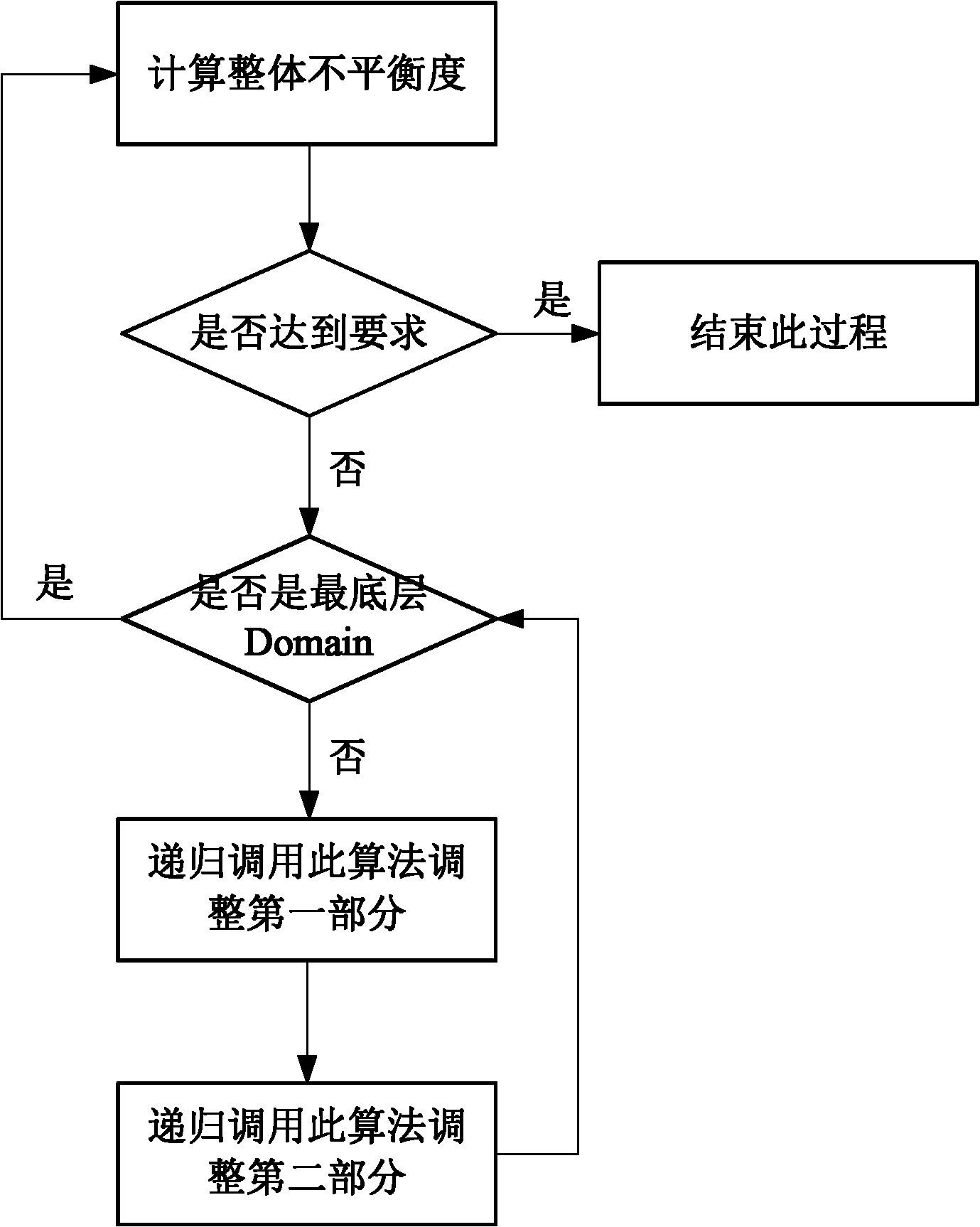
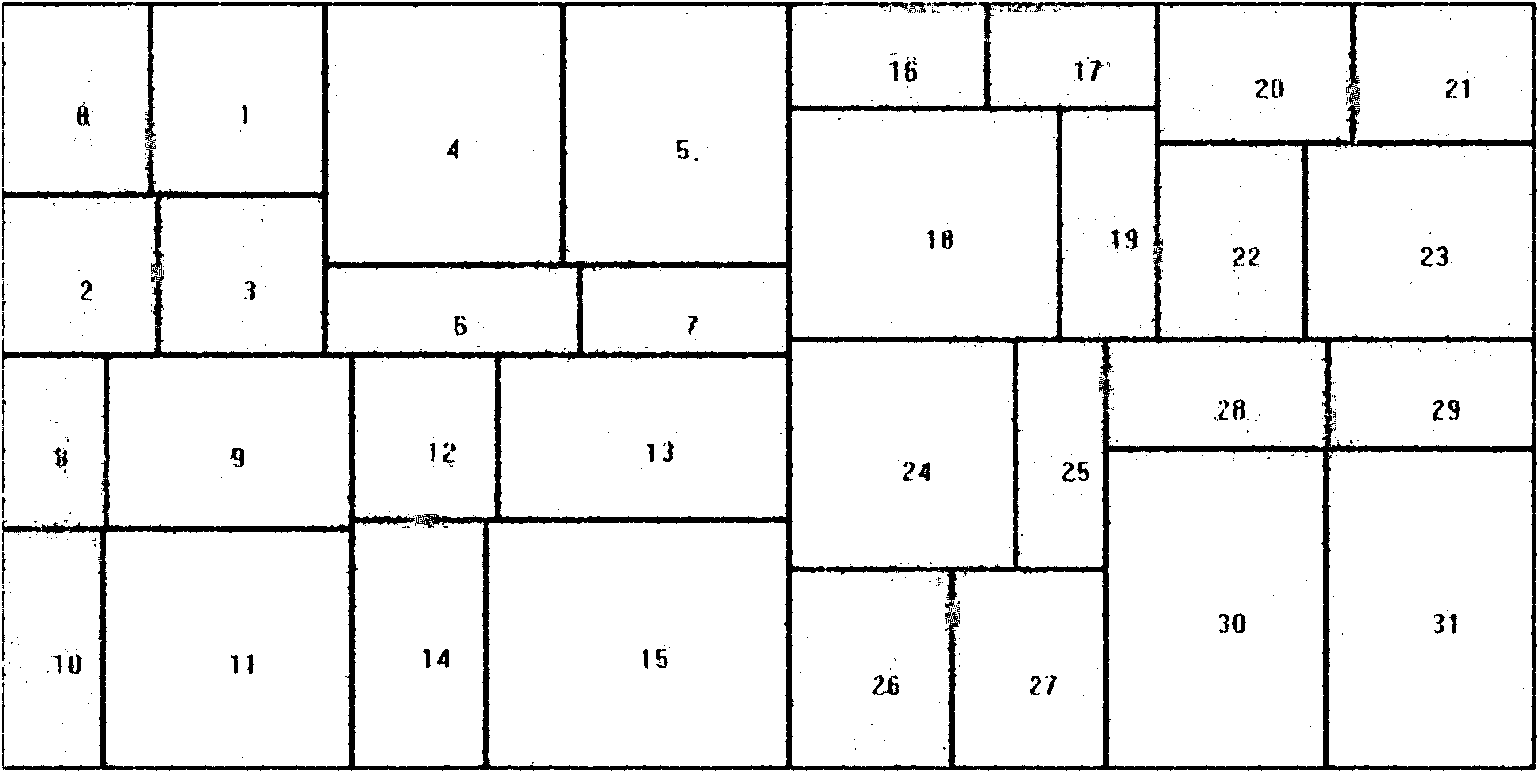
[0043] The invention discloses a space division method oriented to space calculation, and dynamically adjusts the division line according to the load variation among multiple processors during the calculation process to achieve a new balance. Its characteristic is to accelerate the re-division of space by compressing or stretching the divided word space into groups.
[0044] In parallel space computing, each processor is responsible for computing a divided subspace, and the calculation amount comes from the number and complexity of the calculation objects in the space. It is advisable to set the calculation complexity of each calculation object to be the same, then the calculation amount The size of can be represented by the number of objects. During the calculation process, when the calculation object moves in the space, it is possible to migrate from the space responsible for one processor to the space responsible for another hammer, which causes the change of the calculatio...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Molecular motion simulation is an effective tool for revealing the laws of molecular motion and recreating physical and chemical reaction processes. However, the calculation amount of molecular motion simulation is huge, and it is difficult to realize effective simulation calculation with a single computer and serial methods. With the development of network and parallel computing technology, more and more problems that are difficult to solve due to the large amount of calculation have been solved. Parallel computing is to decompose heavy computing tasks into relatively small computing tasks, and then hand them over to multiple processors for simultaneous processing, with the purpose of reducing computing time as much as possible. In parallel computing, the distribution of tasks should be balanced as much as possible, so as to avoid the overweight tasks of some computing nodes and cause low overall computing efficiency, thus losing the meaning of parallel computing. For...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com