Nematode-resistant transgenic plants
A technology for transgenic plants and transformed plants, which is applied in the field of nematode-resistant transgenic plants, and can solve the problems of not releasing the control of genetically modified plants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
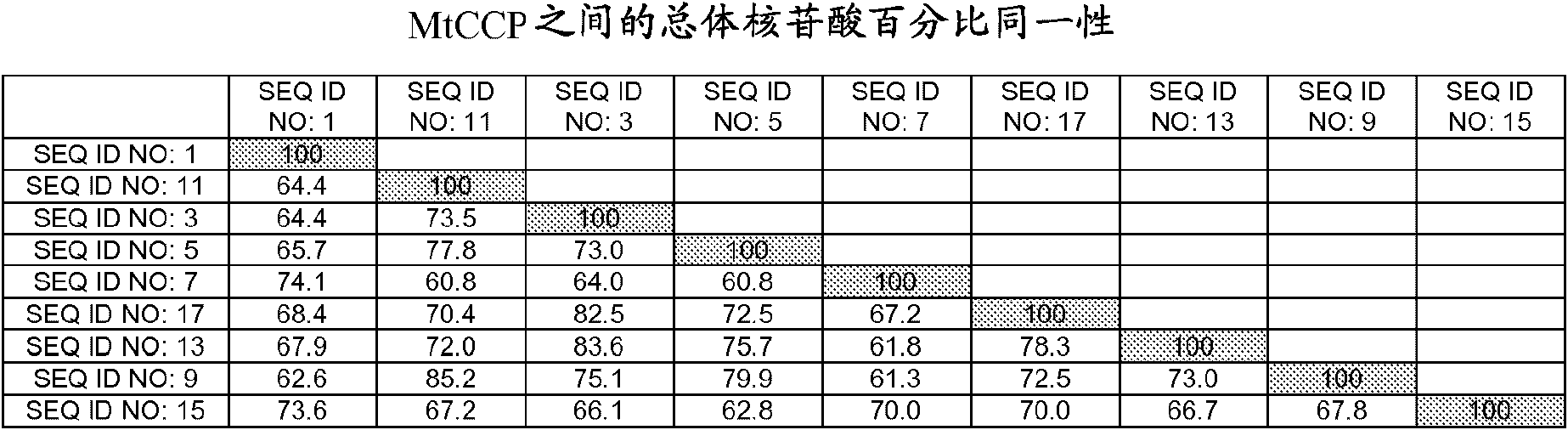
[0064] Example 1: Cloning of MtCCP gene and vector construction from Medicago truncatula
[0065]The seeds of Medicago truncatula Jemalong A17 were germinated and cultured in the greenhouse. Genomic DNA was isolated from shoots of these plants, and the MtCCP gene was PCR amplified from this genomic DNA using standard molecular biology techniques. The amplification product was ligated into TOPO entry vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA).
[0066] The cloned MtCCP gene was sequenced and subcloned into a plant expression vector containing the ubiquitin promoter from parsley (WO 03 / 102198; figure 1 in the p-PcUbi4-2 promoter (SEQ ID NO: 19)). The transformed selectable marker was a mutant form of the acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) selectable gene from Arabidopsis thaliana (Sathasivan et al., Plant Phys. 97:1044-50, 1991), conferring resistance to the herbicide ARSENAL ( Imazapyr, BASF Corporation, Mount Olive, NJ). Expression of AHAS2 was driven by the ubiquitin promoter from p...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2: Nematode Bioassays
[0071] Bioassays to assess nematode resistance conferred by the polynucleotides described herein were performed using the rooted plant assay system disclosed in co-owned co-pending USSN 12 / 001,234. Transgenic roots were generated after transformation with the binary vector described in Example 1. Multiple transgenic root lines were subcultured and inoculated with surface-cleared race 3 SCN second stage juveniles (J2) at a level of approximately 500 J2 / well. Four weeks after nematode inoculation, the number of cysts in each well was counted. For each transformation construct, the number of cysts for each line was calculated to determine the mean number and standard error of the construct. The cyst counts for each transformation construct were compared to the cyst counts for the empty vector control tested in parallel to determine whether the tested construct resulted in a reduction in cyst number. Two independent, biologically replicate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com