Method for artificially raising plant bug parasitic wasps
A parasitic wasp and artificial technology, applied in animal husbandry and other directions, can solve problems such as the failure of natural enemies to fully play their role, and achieve the effects of artificial breeding methods that are simple and easy to implement, reduce damage, and take up less space.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
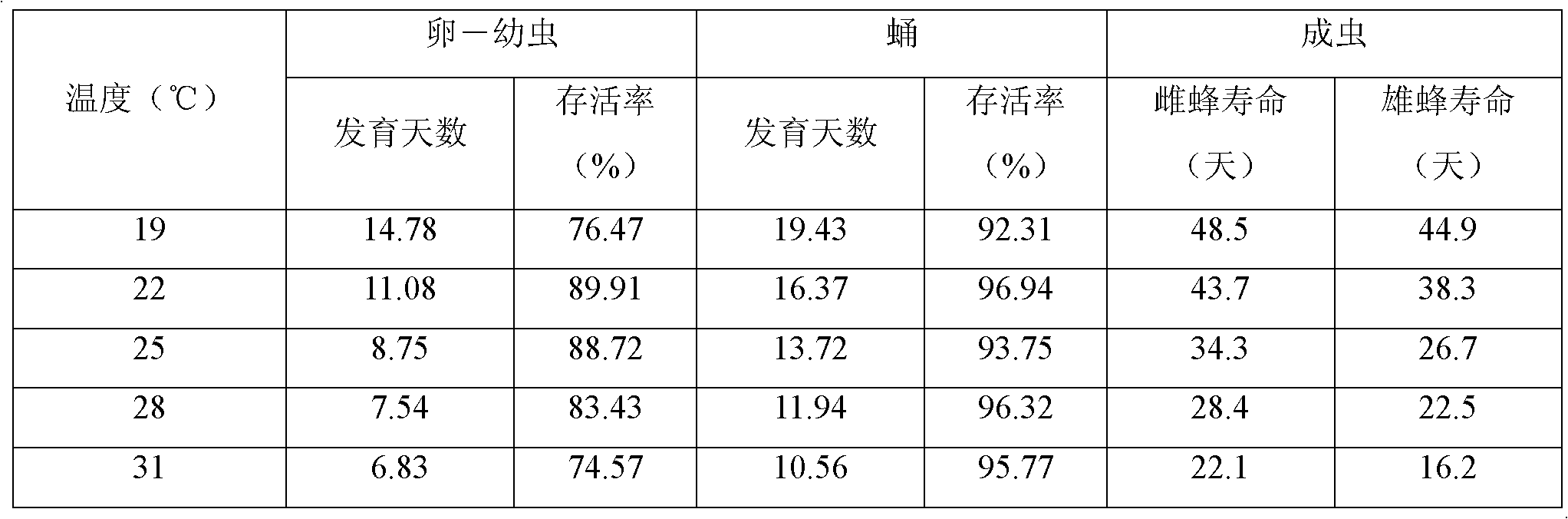
[0023] The artificial breeding method of the blind stink bug parasitoid --- the red-necked often chambered wasp is carried out according to the following steps:
[0024] (1) Put 50-200 healthy adults of Lygus lygus into the insect breeding box, sterilize the fresh green beans, cut off the pods, put them in the insect raising box, replace fresh sterilized green beans every other day, and sterilize the fresh green beans produced by the green Lygus. The pods behind the eggs are placed in a ventilated and cool place, and after the surface of the eggs is dry, they are put back into the insect-raising box, and the relative humidity of the insect-raising box is controlled to be 60%. After 7 to 10 days, the eggs of the green Lygus hatch into nymphs;
[0025] (2) Add 5 to 15 curled paper strips to the insect raising box, put the nymphs into and add freshly sterilized green beans, put 50 Lygus nymphs into each insect raising box, and keep the relative humidity at 60% , the temperature i...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The artificial breeding method of the blind stink bug parasitoid --- the red-necked often chambered wasp is carried out according to the following steps:
[0032] (1) Put 100 healthy green Lygus adults into the insect breeding box, sterilize the fresh green beans, cut off the pods, put them in the insect raising box, replace fresh disinfected green beans every other day, and put the green Lygus after laying eggs Put the pods in a ventilated and cool place, put them back into the insect box after the surface of the eggs is dry, control the relative humidity of the insect box to 65%, and after 7 to 10 days, the eggs of Lygus green bugs will hatch into nymphs;
[0033] (2) Add 5 to 15 curled paper strips to the insect raising box, put the nymphs into and add freshly sterilized green beans, put 100 Lygus nymphs into each insect raising box, and keep the relative humidity at 70% , the temperature is 22°C, and freshly sterilized green beans are replaced every other day;
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The artificial breeding method of blind stink bug parasitoid is characterized in that, according to the following steps:
[0040] (1) Put 200 healthy green Lygus adults into the insect breeding box, sterilize the fresh green beans, cut off the pods, put them in the insect raising box, replace fresh disinfected green beans every other day, and put the green Lygus after laying eggs Put the pods in a ventilated and cool place, put them back into the insect box after the surface of the eggs is dry, control the relative humidity of the insect box to 70%, and after 7 to 10 days, the eggs of the green Lygus hatch into nymphs;
[0041] (2) Add 5 to 15 curled paper strips in the insect raising box, put the nymphs into and add freshly sterilized green beans, put 250 green Lygus nymphs into each insect raising box, and keep the relative humidity at 80% , the temperature is 30°C, and freshly sterilized green beans are replaced every other day;
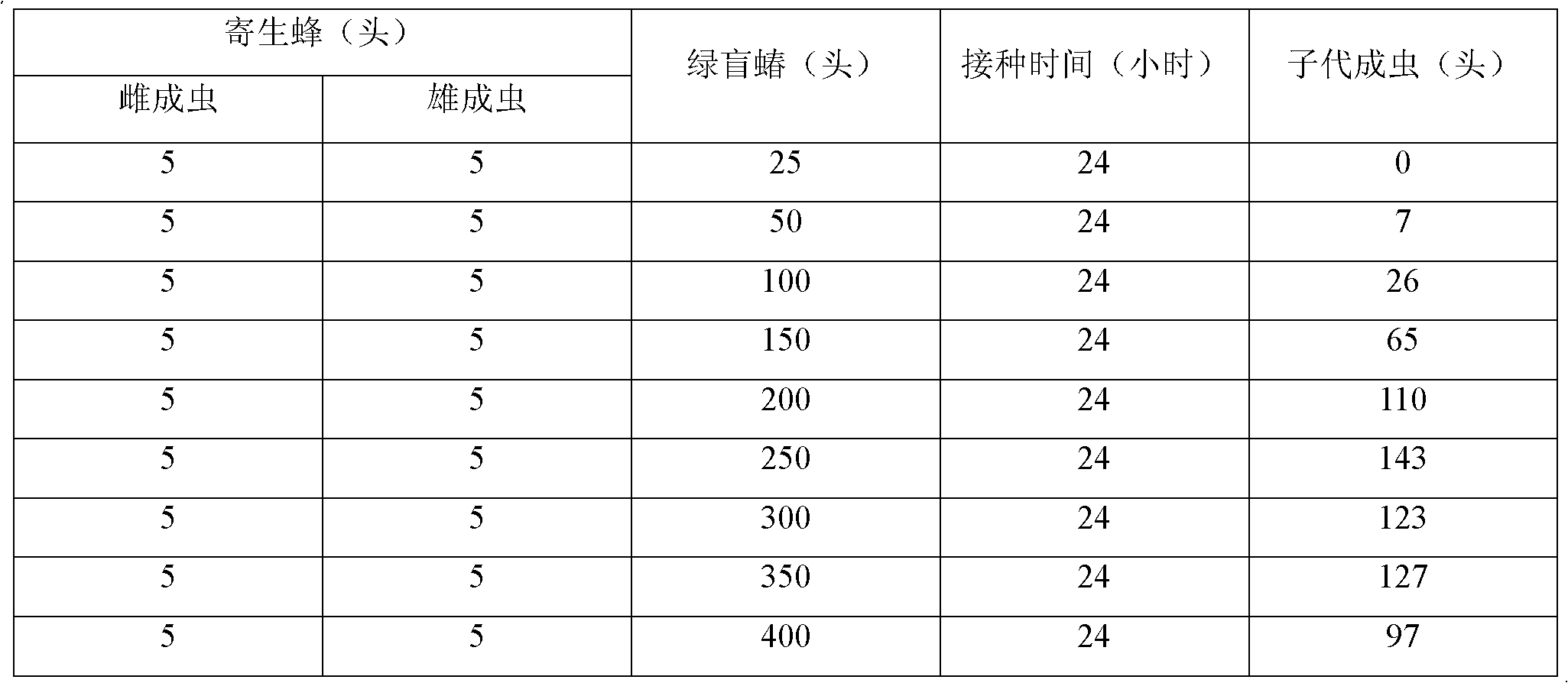
[0042] (3) Take a beekeeping cage w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com