Process for producing lithographic printing plate
A technology for lithographic printing plates and original plates, which is used in the field of preparing lithographic printing plates, can solve the problems of deterioration of printing durability, large amount of waste liquid, and high operating costs, and achieves excellent printing durability, good printing durability, and prevention of developing floating. slag effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 to 74
[0585] Examples 1 to 74, Comparative Examples 1 to 4 and Reference Example 1
[0586] (1) Exposure, development and printing
[0587] Each of the carrier, photosensitive Image-wise exposure of the lithographic printing plate master of the layer and protective layer. Using an FM screen (TAFFETA 20, produced by FUJIFILM Corp.) at 0.05 mJ / cm 2 The surface exposure of the plate was image drawn at a resolution of 2,438 dpi and a dot of 50%.
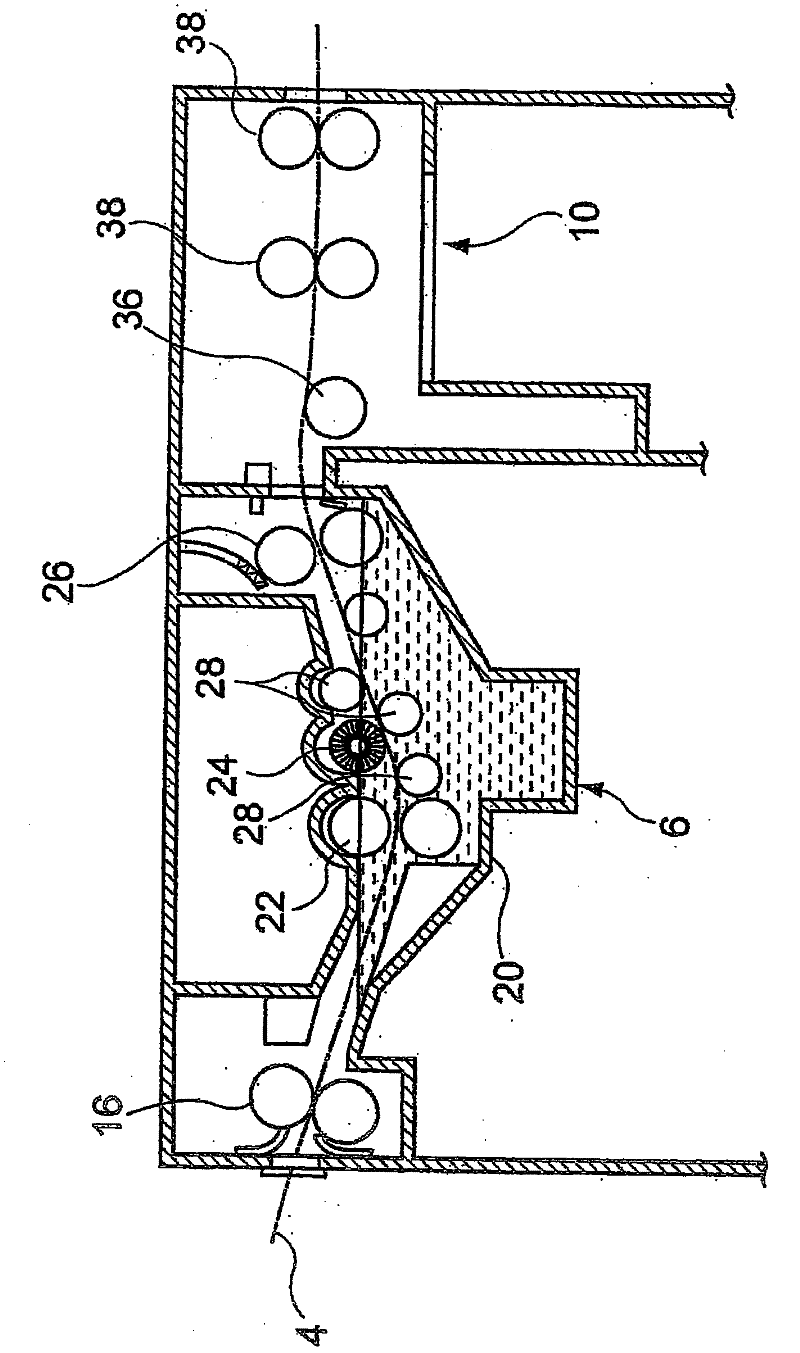
[0588] The exposed lithographic printing plate precursor was preheated at 100° C. for 30 seconds, and then as shown in Tables 9 to 11 so that the immersion time in the developer (development time) was 20 seconds, using the Each of the developers 1 to 50 of the compositions and pHs shown in to 8 were subjected to a development process in an automatic development processor having a configuration as shown in 1 .
[0589]
[0590]
[0591]
[0592]
[0593]
[0594]
[0595] The pH of each developer is shown below.
[0596...
Embodiment 75
[0629] In the purple semiconductor laser plate setter Vx9600 (manufactured by FUJIFILM Electronic Imaging Ltd.), in which the InGaN semiconductor laser (emission: 405nm±10nm / output: 30mW) had been replaced by a semiconductor laser having an output power of 100mW, the Lithographic printing original plate at 0.25mJ / cm 2 Image exposure is carried out according to the exposure amount of the plate surface. Use developer 1 in a figure 1 The exposed lithographic printing plate precursor was developed without preheating in an automatic development processor of the configuration shown in . Except as described above, developability, print image forming performance, handling performance and printing durability were evaluated in the same manner as in Example 1, and the same good evaluation results as in Example 1 were obtained.
Embodiment 76
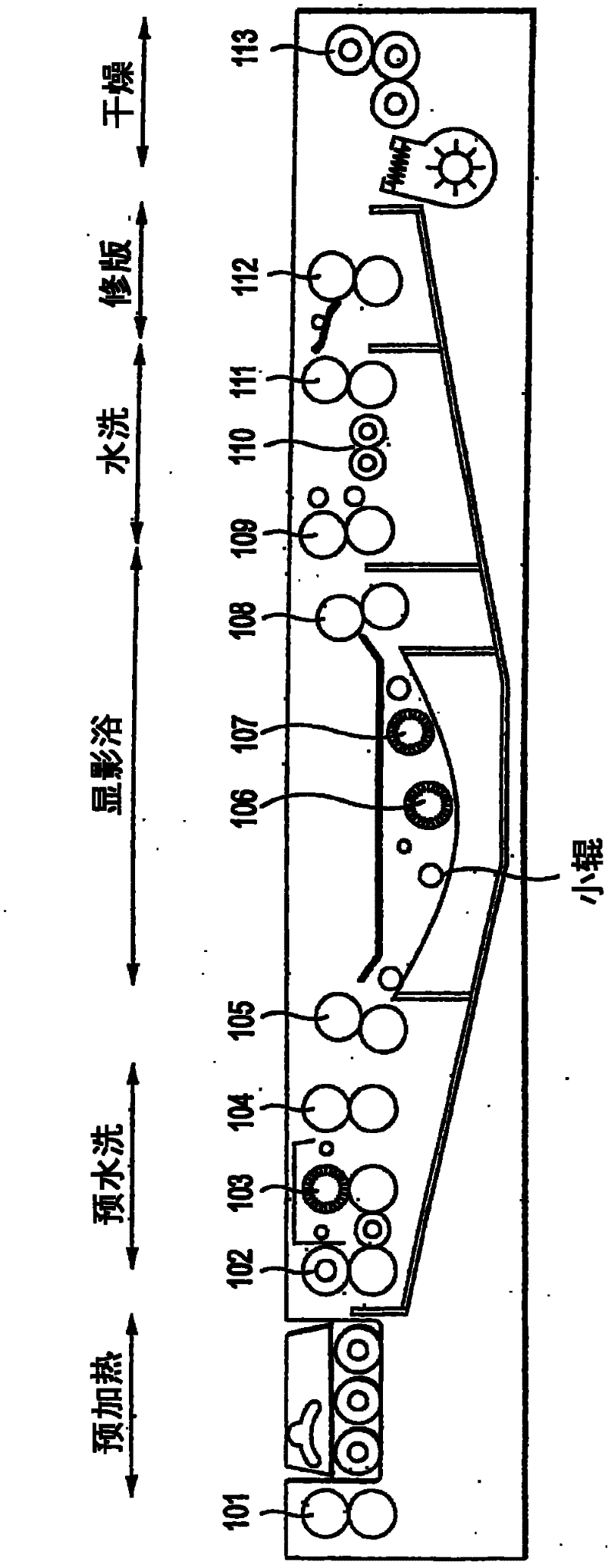
[0631] use has figure 2 An automatic development processor of the configuration shown (LP1250PLX, manufactured by FUJIFILMCorp.) image-exposed the lithographic printing plate precursor of Example 1 in the same manner as in Example 1, and subjected to development processing within 30 seconds. The automatic development processor is composed of a preheating unit, a pre-washing unit, a developing unit, a washing unit, and a finishing unit in this order. The heating condition in the preheating unit was 100° C. for 10 seconds. Into the developing bath, developer solution 1 was supplied. Do not supply any liquid to the pre-washing unit, washing unit and touch-up unit, but only use their delivery function. Except for the above-mentioned development treatment, developability, print image forming performance, handling performance and printing durability were evaluated in the same manner as in Example 1, and the same good evaluation results as in Example 1 were obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com